예제
본 장에서는 간단한 애플리케이션 예제를 통해서 API의 기본적인 사용법과 전체적인 흐름을 설명한다.
1. 메시지 전송 프로그램
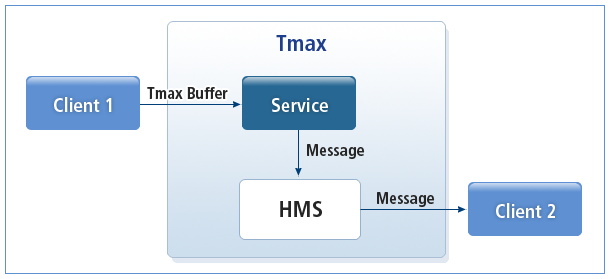
다음은 클라이언트와 서버에서 HMS API를 사용하여 메시지를 주고받는 간단한 프로그램 흐름이다.
-
클라이언트(Client1)는 string 타입의 버퍼에 입력된 문자열을 복사해서 서비스를 호출한다.
-
서버의 서비스 루틴에서는 이 문자열을 받아서 소문자를 대문자로 변경한 뒤 HMS로 메시지를 전송한다.
-
클라이언트(Client2)는 일정 시간이 지난 뒤 HMS로부터 메시지를 수신받는다.
1.1. HMS 환경설정
다음은 HMS 환경설정 파일 예제이다.
*DOMAIN
hms SHMKEY = 74347,
TPORTNO = 8808
*NODE
Locke2 TMAXDIR ="/home/tmax5/tmax",
APPDIR ="/home/tmax5/tmax/appbin/",
MAXSESSION = 100
*SVRGROUP
hms01 NODENAME = "Locke2", CPC = 1, SVGTYPE = "HMS", RESTART = Y,
OPENINFO = "ORACLE_XA+Acc=P/scott/tiger+SesTm=60",
HMSINDEX = 2, HMSMSGLIVE = 1, HMSMAXTHR = 2, HMSMAXDBTHR = 5,
HMSNAME = hms_ora
svg1 NODENAME = "Locke2"
*HMS
queue01 SVGNAME = hms01, BOOT = "WARM", TYPE = "QUEUE"
topic01 SVGNAME = hms01, BOOT = "WARM", TYPE = "TOPIC"
*SERVER
svr SVGNAME = svg1
*SERVICE
SVC SVRNAME = svr
1.2. 클라이언트 프로그램
다음은 클라이언트 프로그램 예제이다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <usrinc/atmi.h>
#include <usrinc/hmsapi.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char *sndbuf, *rcvbuf;
long rcvlen, sndlen;
HMS_SHND *sess;
HMS_CHND *cons;
hms_msg_t *msg;
if (argc != 2) {
printf("Usage : %s <message>\n\n", argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
if (tmaxreadenv("tmax.env", "TMAX") == -1) {
printf("error: tmaxreadenv() failed - %d\n", tperrno);
exit(1);
}
if (tpstart((TPSTART_T *) NULL) == -1) {
printf("error: tpstart() fail - %d\n", tperrno);
exit(1);
}
if ((sndbuf = (char *)tpalloc("STRING", NULL, 0)) == NULL) {
printf("error: sendbuf alloc failed !\n");
tpend();
exit(1);
}
if ((rcvbuf = (char *)tpalloc("STRING", NULL, 0)) == NULL) {
printf("error: recvbuf alloc failed !\n");
tpfree((char *)sndbuf);
tpend();
exit(1);
}
strcpy(sndbuf, argv[1]);
if(tpcall("SVC", sndbuf, 0, &rcvbuf, &rcvlen, 0)==-1){
printf("error: Can't send request to service SVC\n");
tpfree((char *)sndbuf);
tpfree((char *)rcvbuf);
tpend();
exit(1);
}
sleep(5);
/* RECV MESSAGE FROM HMS */
if ((sess = hms_create_session("hms01", 0, HMS_AUTO_ACK, 0)) == NULL) {
printf("error: hms_create_session() failed tperrno = %d\n", tperrno);
tpend();
exit(1);
}
if ((cons = hms_create_receiver(sess, "queue01", "cons01", NULL, NULL, 0))
== NULL) {
printf("error: hms_create_receiver() failed tperrno = %d\n", tperrno);
tpend();
exit(1);
}
/* ALLOCATION */
if ((msg = hms_alloc(sess, 1024)) == NULL) {
printf("error: hms_alloc() failed tperrno = %d\n", tperrno);
tpend();
exit(1);
}
/* RECV MESSAGE */
if (hms_recvex(cons, &msg, 5, 0) == -1) {
printf("error: hms_recvex() failed tperrno = %d\n", tperrno);
hms_free(msg);
tpend();
exit(1);
}
/* GET BODY */
rcvlen = 1024;
if (hms_get_body(msg, rcvbuf, &rcvlen) == -1) {
printf("error: hms_get_body() failed tperrno = %d\n", tperrno);
hms_free(msg);
tpend();
exit(1);
}
printf("HMS MESSAGE : %s\n", rcvbuf);
/* CLOSE RECEIVER */
if (hms_close_receiver(cons, 0) == -1) {
printf("error: hms_close_receiver() failed tperrno = %d\n", tperrno);
hms_free(msg);
tpend();
exit(1);
}
/* CLOSE SESSION */
if (hms_close_session(sess, 0) == -1) {
printf("error: hms_close_session() failed tperrno = %d\n", tperrno);
hms_free(msg);
tpend();
exit(1);
}
hms_free(msg);
tpend();
return 0;
}
1.3. 서버 프로그램
다음은 서버 프로그램의 예제이다.
<svr.c>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <usrinc/atmi.h>
#include <usrinc/hmsapi.h>
HMS_SHND *sess = NULL;
HMS_CHND *prod = NULL;
int tpsvrinit(int argc, char **argv)
{
while(1) {
sess = hms_create_session("hms01", 0, HMS_AUTO_ACK, 0);
if (sess != NULL) {
break;
}
if (tperrno != TPENOREADY) {
printf("hms_create_session(hms01) : FAIL tperrno = %d\n", tperrno);
return -1;
}
}
prod = hms_create_sender(sess, "queue01", "prod_svc", 0);
if (prod == NULL) {
printf("hms_create_sender() : FAIL tperrno = %d\n", tperrno);
return -1;
}
return 1;
}
int tpsvrdone()
{
hms_close_sender(prod, 0);
hms_close_session(sess, 0);
return 1;
}
SVC(TPSVCINFO *msg)
{
int n, i;
hms_msg_t *hmsmsg = NULL;
char *data = msg->data;
int len = msg->len, asize;
printf("SVC STARTED!\n");
/* TOUPPER */
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
data[i] = toupper(data[i]);
/* ALLOCATION */
asize = len +1024;
hmsmsg = hms_alloc(sess, asize);
if (hmsmsg == NULL) {
printf("hms_alloc : fail tperrno = %d\n", tperrno);
tpreturn(TPFAIL, 0, NULL, 0, 0);
}
/* SET BODY */
n = hms_set_body(hmsmsg, data, len);
if (n < 0) {
hms_free(hmsmsg);
printf("hms_set_body : fail tperrno = %d\n", tperrno);
tpreturn(TPFAIL, 0, NULL, 0, 0);
}
/* SEND : hms01, persistent */
n = hms_sendex(prod, hmsmsg, HMS_DLV_PERSISTENT, 0, 0, 0);
if (n < 0) {
hms_free(hmsmsg);
printf("hms_sendex(prod) : fail tperrno = %d\n", tperrno);
tpreturn(TPFAIL, 0, NULL, 0, 0);
}
/* FREE */
hms_free(hmsmsg);
printf("SVC SUCCESS!\n");
tpreturn(TPSUCCESS, 0, NULL, 0, 0);
}
1.4. 프로그램 컴파일
클라이언트/서버 프로그램은 Tmax 애플리케이션을 컴파일하는 과정과 동일하게 컴파일한다.
|
프로그램 컴파일에 대한 자세한 내용은 Tmax Application Development Guide를 참고한다. |
2. 메시지 저장 프로그램
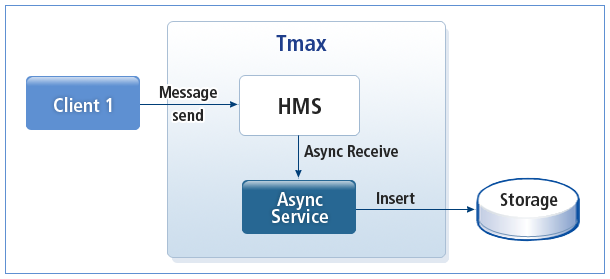
다음은 서버/클라이언트 프로그램에서 HMS 전달받은 메시지를 데이터베이스에 저장하는 프로그램의 흐름이다.
-
클라이언트는 사용자의 입력을 받아서 HMS로 Queue 타입의 메시지를 전송한다.
-
서버측에서는 비동기 세션을 통해 소비자(Consumer)를 생성하고 메시지가 전송될 경우 ASYNC 서비스가 이 메시지를 수신한다.
-
ASYNC 서비스는 수신받은 메시지를 데이터베이스에 Insert한다.
2.1. HMS 환경설정
다음은 HMS 환경설정에 대한 예제이다.
*DOMAIN
hms SHMKEY = 74347,
TPORTNO = 8808
*NODE
Locke2 TMAXDIR ="/home/tmax5/tmax",
APPDIR ="/home/tmax5/tmax/appbin/",
MAXSESSION = 100
*SVRGROUP
hms01 NODENAME = "Locke2", CPC = 1, SVGTYPE = "HMS", RESTART = Y,
OPENINFO = "ORACLE_XA+Acc=P/scott/tiger+SesTm=60",
HMSINDEX = 2, HMSMSGLIVE = 1, HMSMAXTHR = 2, HMSMAXDBTHR = 5,
HMSNAME = hms_ora
svg1 NODENAME = "Locke2", RESTART = N,
OPENINFO = "ORACLE_XA+Acc=P/scott/tiger+SesTm=60",
DBNAME = "ORACLE", TMSNAME = tms_ora, MINTMS = 1
*HMS
queue01 SVGNAME = hms01, BOOT = "WARM", TYPE = "QUEUE"
topic01 SVGNAME = hms01, BOOT = "WARM", TYPE = "TOPIC"
*SERVER
async SVGNAME = svg1, CLOPT = "-- -i"
*SERVICE
ASYNCSVC SVRNAME = async
2.2. 클라이언트 프로그램
다음은 클라이언트 프로그램 예제이다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <usrinc/atmi.h>
#include <usrinc/hmsapi.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
long len;
HMS_SHND *sess;
HMS_PHND *prod;
hms_msg_t *msg;
char *data;
int no;
if (argc != 3) {
printf("Usage : %s <no> <message>\n\n", argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
if (tmaxreadenv("tmax.env", "TMAX") == -1) {
printf("error: tmaxreadenv() failed - %d\n", tperrno);
exit(1);
}
if (tpstart((TPSTART_T *) NULL) == -1) {
printf("error: tpstart() fail - %d\n", tperrno);
exit(1);
}
len = strlen(argv[2]);
data = argv[2];
no = atoi(argv[1]);
/* SEND MESSAGE TO HMS */
if ((sess = hms_create_session("hms01", 0, HMS_AUTO_ACK, 0)) == NULL) {
printf("error: hms_create_session() failed tperrno = %d\n", tperrno);
tpend();
exit(1);
}
if ((prod = hms_create_sender(sess, "queue01", "prod01", 0)) == NULL) {
printf("error: hms_create_sender() failed tperrno = %d\n", tperrno);
tpend();
exit(1);
}
/* ALLOCATION */
if ((msg = hms_alloc(sess, len + 1024)) == NULL) {
printf("error: hms_alloc() failed tperrno = %d\n", tperrno);
tpend();
exit(1);
}
/* SET BODY */
if (hms_set_body(msg, data, len) == -1) {
printf("error: hms_set_body() failed tperrno = %d\n", tperrno);
hms_free(msg);
tpend();
exit(1);
}
/* SET PROPERTY */
if (hms_set_property(msg, "NO", HMS_INT, (char *)&no, sizeof(int)) == -1) {
printf("error: hms_set_property() failed tperrno = %d\n", tperrno);
hms_free(msg);
tpend();
exit(1);
}
/* SEND MESSAGE */
if (hms_sendex(prod, msg, HMS_DLV_PERSISTENT, 0, 0, 0) == -1) {
printf("error: hms_sendex() failed tperrno = %d\n", tperrno);
hms_free(msg);
tpend();
exit(1);
}
if (hms_close_sender(prod, 0) == -1) {
printf("error: hms_close_sender() failed tperrno = %d\n", tperrno);
hms_free(msg);
tpend();
exit(1);
}
if (hms_close_session(sess, 0) == -1) {
printf("error: hms_close_session() failed tperrno = %d\n", tperrno);
hms_free(msg);
tpend();
exit(1);
}
hms_free(msg);
tpend();
return 0;
}
2.3. 서버 프로그램
다음은 서버 프로그램 예제이다.
<async.pc>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <usrinc/atmi.h>
#include <usrinc/hmsapi.h>
HMS_SHND *sess;
HMS_CHND *cons;
int svrinit_start = 0;
void abend_callback(HMS_SHND *session)
{
printf("START ABEND_CALLBACK FUNCTION\n");
hms_close_session(session, 0);
printf("hms_close_session success\n");
while (1) {
sess = (HMS_SHND *) hms_create_async_session("hms01", abend_callback, 0);
if (sess == NULL) {
if (tperrno == TPENOREADY) {
usleep(500000);
continue;
}
printf("hms_create_session() : FAIL [%d]\n\n", tperrno);
return;
}
break;
}
cons = (HMS_CHND *) hms_create_receiver(sess, "queue01", "consasync", NULL,
"ASYNCSVC", 0);
if (cons == NULL) {
printf("hms_create_receiver() : FAIL tperrno = %d\n\n", tperrno);
return;
}
printf("END ABEND_CALLBACK FUNCTION\n");
}
int tpsvrinit(int argc, char **argv)
{
int c;
while ((c = getopt(argc, argv, "i")) != EOF) {
switch (c) {
case 'i':
svrinit_start = 1;
break;
}
}
if (svrinit_start == 1) {
printf("ASYNC SERVICE svrinit()\n");
while(1) {
sess = (HMS_SHND *) hms_create_async_session("hms01", abend_callback,
0);
if (sess == NULL) {
if (tperrno == TPENOREADY) {
usleep(500000);
continue;
}
printf("ASYNC SERVICE hms_create_async_session() failed,
tperrno[%d]\n", tperrno);
return;
}
break;
}
cons = (HMS_CHND *) hms_create_consumer(sess, "queue01", HMS_QUEUE,
"consasync", "", "ASYNCSVC", 0);
if (cons == NULL)
printf("ASYNC SERVICE hms_create_consumer() failed, tperrno[%d]\n",
tperrno);
return -1;
}
printf("ASYNC SERVICE svrinit() success\n");
}
return 1;
}
int tpsvrdone()
{
if (svrinit_start == 1) {
printf("ASYNC SERVICE svrdone()\n");
hms_close_consumer(cons, 0);
hms_close_session(sess, 0);
}
return 1;
}
/* DB INSERT */
EXEC SQL include sqlca.h;
EXEC SQL begin declare section;
int no;
char message[128];
EXEC SQL end declare section;
int DBInsert( int n, char *data )
{
printf("UPDATE START!!!\n");
memset( message, 0x00, sizeof(message) );
no = n;
strcpy(message, data);
EXEC SQL insert into hmstest(no, message) values(:no, :message);
if ( sqlca.sqlcode != 0 ){
printf( "insert failed sqlcode = %d\n",sqlca.sqlcode );
return -1;
}
return 1;
}
ASYNCSVC(TPSVCINFO *svc)
{
hms_msg_t *msg;
char *data;
long llen = 4096;
int prop = 0;
int type;
printf("ASYNC SERVICE CALLED\n");
msg = (hms_msg_t *)svc->data;
if ((data = (char *)tpalloc("CARRAY", NULL, 4096)) == NULL) {
printf("ASYNC SERVICE tpalloc return failed. tperrno[%d]\n",
tperrno);
tpreturn(TPFAIL, TPFAIL_ACK, svc->data, svc->len, 0);
}
if (hms_get_body(msg, data, &llen) < 0) {
printf("ASYNC SERVICE hms_get_body() return failed. tperrno[%d]\n",
tperrno);
tpreturn(TPFAIL, TPFAIL_ACK, svc->data, svc->len, 0);
}
data[llen] = '\0';
llen = sizeof(int);
if (hms_get_property(msg, "NO", &type, (char *)&prop, &llen) < 0) {
printf("ASYNC SERVICE hms_get_property() return failed. tperrno[%d]\n",
tperrno);
}
printf("ASYNC SERVICE RECV MESSAGE, BODY[%s], PROPERTY[NO:%d]\n", data, prop);
if (DBInsert(prop, data) == -1)
tpreturn(TPFAIL, TPFAIL_ACK, svc->data, svc->len, 0);
tpreturn(TPSUCCESS, 0, svc->data, svc->len, 0);
}
2.4. 데이터베이스 스크립트
테이블 작성 스크립트
다음은 Oracle 테이블 작성 스크립트이다.
sqlplus scott/tiger << EOF
create table hmstest (
no number(7),
message char(128)
);
EOF
테이블 및 데이터 출력 스크립트
다음은 Oracle 테이블 및 데이터 출력 스크립트이다.
sqlplus scott/tiger << EOF desc hmstest; select * from hmstest; select count(*) from hmstest; EOF
2.5. 프로그램 컴파일
서버/클라이언트 프로그램은 Tmax 애플리케이션을 컴파일하는 과정과 동일하게 컴파일한다.
|
프로그램 컴파일에 대한 자세한 내용은 Tmax Application Development Guide를 참고한다. |