Introduction
This chapter introduces OpenFrame/Base (hereafter Base) and describes its components.
1. Overview
OpenFrame is a rehosting solution that allows mainframe applications to run in an open system environment. The applications that are migrated from the mainframe to the open system environment generally fall into two main categories: online applications or batch applications. OpenFrame provides the OSC module for online applications, and the Batch module for batch applications.
The Base system is a package solution that combines the common modules and services of OpenFrame Online and Batch systems. The Base system must be installed regardless of whether the system is mainly used to process online or batch applications. In a different perspective, the Base system can be seen as a virtual layer in Unix that emulates the OS-level resources and services of mainframe.
The following diagram illustrates the position and role of the Base system in the OpenFrame solution.
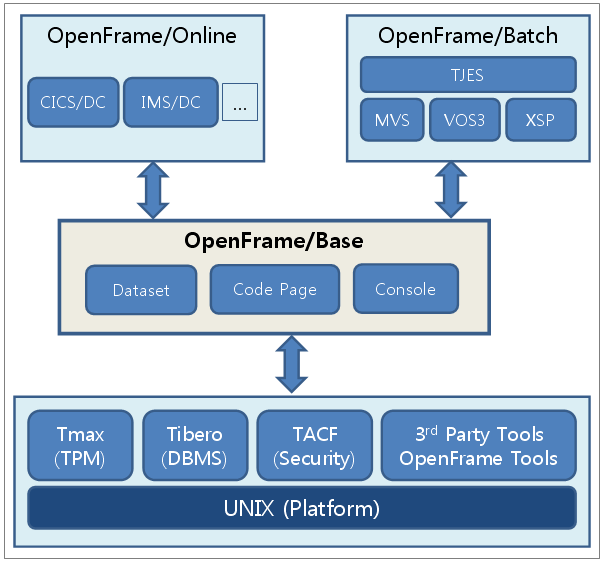
2. Key Components
The Base module is composed of the Tmax engine and the data set, code page, and console components.
-
Tmax engine
The Tmax TP monitor guarantees transactions among heterogeneous computing systems, balances loads, and handles errors in a distributed system. Tmax provides process management, transaction management, load balancing, and failover features.
OpenFrame is based on the Tmax engine and inherits many of its features, including multi-node clustering, load balancing, and failover. These features guarantee high-usability and reliability – the same features that make mainframes attractive.
-
Data sets
While mainframes use a variety of data sets that support record-level read/write transactions, Unix file systems support only block based read/write functions. The data set component supplies Base with relational database functions. This allows the open system environment to support the data set functions used by the mainframe.
-
Code page
Another inconsistency between mainframes and open system environments is the format in which data is stored. On a mainframe, for example, user data is stored in EBCDIC (or EBCDIK) format. However, OpenFrame stores data in ASCII format, the open system environment standard. Therefore, when data is migrated from a mainframe to OpenFrame or vice versa, a code page must be created as a mapping table for format conversions.
-
Console
The console refers to the screen where messages from the system kernel to system administrator are displayed and the keyboard through which the system administrator can enter system commands.
On some mainframes, the console is used not only to manage the system but also to enter data directly into some applications during runtime. OpenFrame provides a virtual system console interface to support this type of console function.