Introduction to ProSort
This chapter describes the basic concepts, features, and major functions of ProSort.
1. Overview
ProSort is a tool for sorting, merging, transforming, and operating large amounts of data. It improves application performance by reducing system resource usage and workload.
The following shows how ProSort works.
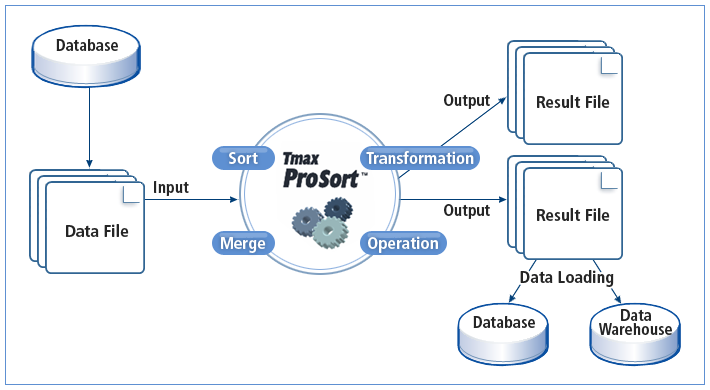
ProSort can execute a DFSORT script used in the mainframe and offers APIs that are available in C programs. It provides high system efficiency and manageability by integrating with Tmax OpenFrame® (hereafter OpenFrame), which is TmaxSoft’s rehosting solution. It also guarantees high system performance by using asynchronous I/O and a sorting method that maximizes CPU cache usage. In addition, it can control resource usage according to file size to process and automatically use disks in order to perform multi-way and multi-pass sorting. Therefore, it performs reliable sorting with limited memory.
|
Multi-way sorting sorts and merges multiple divided input data (Runs) in parallel. Multi-pass sorting sorts and merges data that have been already sorted and merged in order to get the final result. |
2. Features
ProSort has the following features.
-
High I/O performance by using kernel threads
-
Reliable sorting with limited memory
-
Compatibility with a mainframe sorting tool
-
Optimized resource usage
-
Optimized sorting
High I/O Performance by Using Kernel Threads
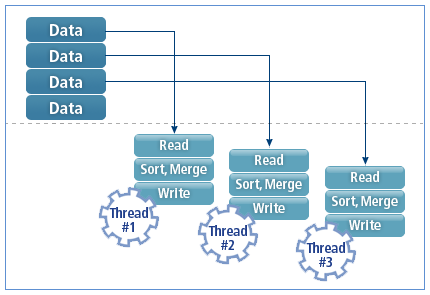
Typical sorting tools perform sorting after file I/O is completed. This causes bottleneck and decreases system performance.
The following shows how typical sorting tools perform sorting.
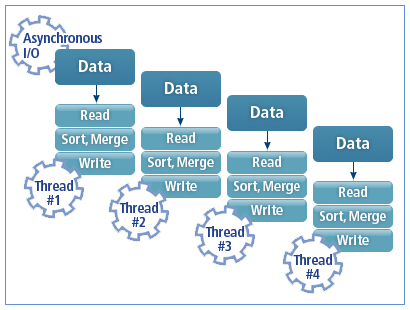
ProSort is designed like a pipeline by supporting asynchronous I/O and using multiple threads that process file I/O and sorting in parallel. Therefore, it improves file I/O performance through asynchronous I/O and kernel threads. In addition, it supports direct I/O depending on the system environment.
The following shows how ProSort performs sorting.
Reliable Sorting with Limited Memory
ProSort performs multi-way and multi-pass sorting with limited memory by automatically using disks. It can sort files of any size as long as 32 MB of memory is available.
The following shows the optimized multi-way and multi-pass sorting algorithm.
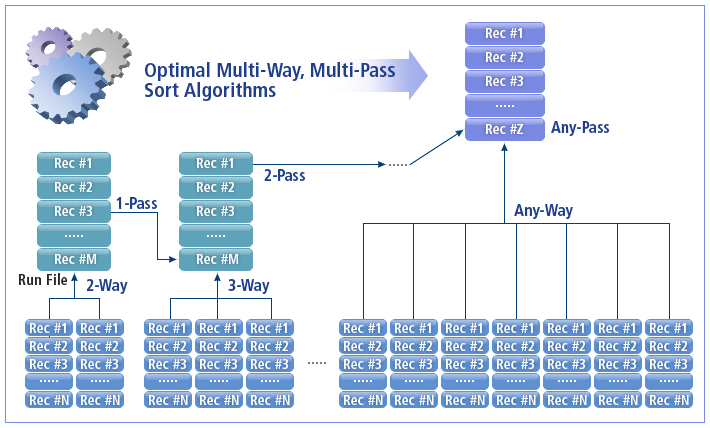
This algorithm finds an appropriate disk run file merge method that can minimize disk usage according to memory size and maximize system performance. Therefore, ProSort can perform reliable sorting with an optimized sorting method.
Compatibility with a Mainframe Sorting Tool
ProSort is compatible with DFSORT, a mainframe sorting tool, so that mainframe users can use ProSort easily.

Optimized Resource Usage
Since typical sorting tools use simple algorithms, they create large Run files in a disk and waste file I/O time.
The following shows how typical sorting tools use memory.
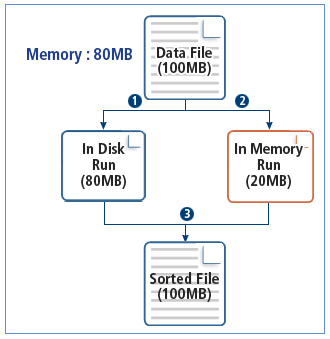
ProSort uses an algorithm that processes as much data as the memory can, depending on the input file size. That is, large Run files are processed in memory and file I/O time decreases. Since it searches for and uses an optimized algorithm automatically, it improves system performance.
If an input file size is big, the file is divided into two or more data and then stored in memory or saved as separate files. The divided data is called a Run.
The following shows how ProSort uses memory.
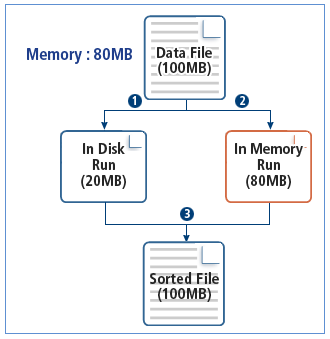
Optimized Sorting
Typical sorting tools only consider the number of sorting threads when partitioning data. This makes it difficult to perform sorting with high performance.
The following shows how typical sorting tools sort data.
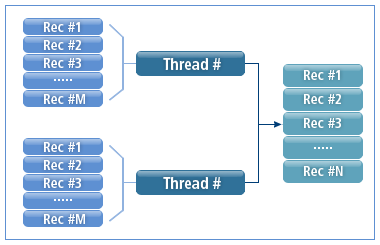
ProSort has been developed to use an optimized sorting method. When partitioning data, it uses a sorting algorithm that maximizes CPU cache usage based on threads used for sorting.
The following shows how ProSort sorts data.
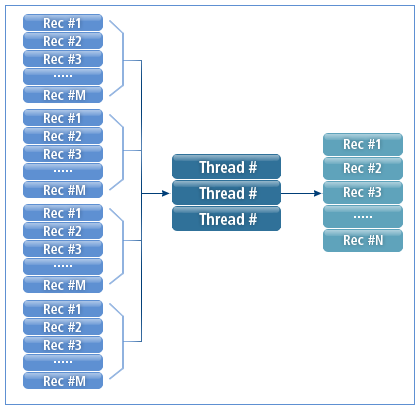
3. Major Functions
ProSort contains the following functions.
-
SORT, MERGE, COPY
The following describes each operation.
Operation Description SORT
Sorts an input file based on a specified field.
MERGE
Merges multiple sorted files.
COPY
Does not sort and only copies data.
Used along with an input record field conversion function.
-
INCLUDE, OMIT
Includes or omits records in or from output by specifying conditions or expressions.
-
Record Reformatting
Reformats input records before or after sorting. The INREC, OUTFIL, and OUTREC control statements are available.
-
Record Aggregation
Sums number fields. The SUM control statement is available.
-
User Exit Function
ProSort supports User Exit Function to insert, convert, and delete records. User Exit Function can be implemented through the INCLUDE, OMIT, INREC, OUTFIL, OUTREC, and SUM control statements. It is recommended to use User Exit Function only for complex operations.
User Exit Function can be used only by using ProSort APIs. For more information about ProSort APIs, refer to ProSort API Functions.
-
MEMORY
Specifies memory to be used.
-
WORKSPACE
Specifies the area (temporary) and location of a disk to be used.
-
OPTION
OUTFIL supports the FNAMES, SAVE, STARTREC, and ENDREC options. The following options can also be used to reduce the number of input records.
Option Description SKIPREC
Specifies the number of records to skip before performing a sort or copy operation.
STOPAFT
Specifies the maximum number of records to sort or copy.