ProSort Control Statements
This chapter describes control statements available in ProSort scripts.
1. Overview
ProSort supports the following control statements.
-
Sorting
Statement Description Performs a sort or copy operation.
Performs a merge operation.
Overrides and sets some parameter values.
-
Record Filtering
Statement Description Includes specific records.
Omits specific records.
Creates new records by applying a condition to records resulting from an operation.
-
Record Reformatting
Statement Description Reformats input records into new records with a specified format before an operation.
Reformats input records into new records with a specified format after an operation.
Reformats records resulting from an operation.
-
Others
Statement Description Changes the sorting order of particular characters by using an ALTSEQ conversion table.
-
SORT, MERGE, INCLUDE, OMIT: AQ format is used.
-
INREC, OUTREC, OUTFIL OUTREC: TRAN=ALTSEQ is used.
Allows users to change a sorting order.
Sets an expected input data size.
Sets a record format.
Ends a ProSort script, and ignores statements written after the END statement.
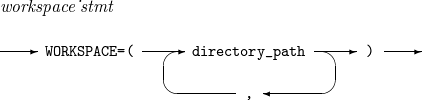
Sets an input file’s path and expected size.
Inserts a specified file into a script.
Sets the memory size used when performing operations.
Registers a function as User Exit Function by using a ProSort script.
Outputs one of sorted or merged records that have the same key field.
Specifies directories to save temporary files used for external sorting.
-
2. ALTSEQ
Changes the sorting order of particular characters by using an ALTSEQ conversion table. This is used only to adjust a sorting order for sort and merge operations, and has no influence on actual output characters.
The ALTSEQ conversion table can be used as follows:
-
For SORT, MERGE, INCLUDE, and OMIT
The AQ format is used. Existing data is converted through ALTSEQ and then applied to an operation. Key orders can be changed, and different filtering conditions can be used.
-
For INREC, OUTREC, and OUTFIL OUTREC
Characters are converted with TRAN=ALTSEQ. Existing data is converted through ALTSEQ, and the converted data is applied to the next process.
The details of ALTSEQ are as follows:
-
Syntax
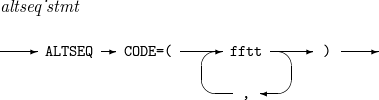 ALTSEQ
ALTSEQ -
Component
Component Description ff
Hexadecimal character to change.
tt
New hexadecimal character.
-
Example
The following performs a SORT operation after changing the character X'5B' to X’EA'.
SORT FILEDS=(1,8,AQ,A) ALTSEQ CODE=(5BEA)
The following performs a MERGE operation after changing the character X'5B' to X’EA'.
MERGE FIELDS=(1,8,AQ,A) ALTSEQ=(5BEA)
The following performs a COPY operation and outputs bytes 1 through 80 of each record. The character X'00' is changed to X'40'.
SORT FIELDS=(COPY) ALTSEQ CODE=(0040) OUTREC FIELDS=(1,80,TRAN=ALTSEQ)
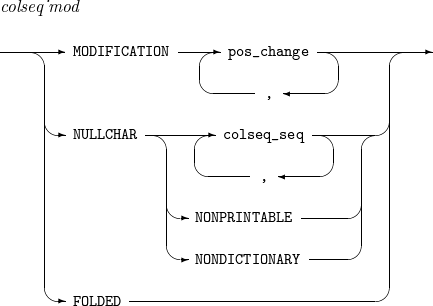
3. COLSEQ
Allows users to change a sorting order. Character strings are compared to each other while a SORT or MERGE operation is performed.
Unlike comparing integers (for example, 1 < 2), comparing character strings is not easy and requires a sorting order rule such as ASCII and EBCDIC. For example, '9' < 'A' in ASCII code, but 'A' < '9' in EBCDIC code. Users can define such a sorting order rule by using COLSEQ.
The details of COLSEQ are as follows:
-
Syntax
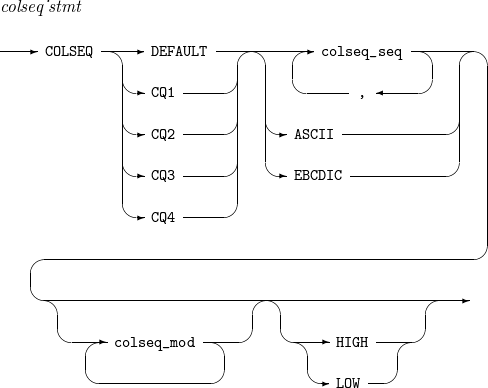
 COLSEQ
COLSEQ -
Component
Component Description DEFAULT
Default sorting order for CH fields.
CQ1
Sorting order for CQ1 fields.
CQ2
Sorting order for CQ2 fields.
CQ3
Sorting order for CQ3 fields.
CQ4
Sorting order for CQ4 fields.
ASCII
Uses ASCII code for sorting.
EBCDIC
Uses EBCDIC code for sorting.
HIGH
Characters in which a sorting order is not specified have greater collation values than characters in which a sorting order is specified, which means that the former characters have lower priority.
LOW
Characters in which a sorting order is not specified have less collation values than characters in which a sorting order is specified, which means that the former characters have higher priority.
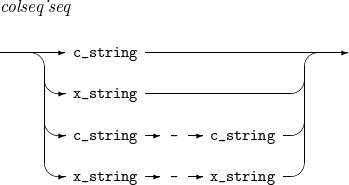
c_string
Either C’x1' or C’x1x2', where x1 and x2 are arbitrary characters (except for some special characters such as a single quotation mark).
x_string
Either X’x1x2' or X’x1x2x3x4', where x1, …, and x4 are hexadecimal characters.
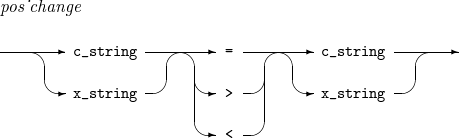
MODIFICATION
Specifies that the collation value of a left-side character is equal to, less than, or greater than that of a right-side character.
NULLCHAR
Characters to be ignored during a sort operation. A sorting key is created without the specified characters.
NONPRINTABLE
Non-displayed control characters.
NONDICTIONARY
All characters except for alphabets, digits, blank spaces, and tabs.
FOLDED
All lowercase alphabetic characters have the same collation value as corresponding uppercase alphabetic characters.
-
Example
-
Order specification
Users can list characters, or specify a character range with the same type and length.
The followings are available.
C'a'-C'z' C'AA'-C'AB' X'010f'-X'010f' X'10'-X'20'
The followings are unavailable.
C'a'-X'0f' C'A'-C'각'
-
MODIFICATION
In the following example, the character 'a' has the same collation value with the character 'z'.
COLSEQ CQ1 ASCII MODIFICATION C'a' = C'z'
In the following example, the collation value of 'a' is greater than that of 'd' but less than that of 'e'.
COLSEQ CQ1 ASCII MODIFICATION C'a' > C'd'
For example, a, b, c, d, e, and f in a record are sorted to b, c, d, a, e, and f in ascending order.
The following example has the same result as the previous example. The collation value of 'a' is less than that of 'e' but greater than that of 'd'.
COLSEQ CQ1 ASCII MODIFICATION C'a' < C'e'
-
NULLCHAR
In the following example, the character 'a' is excluded from sorting.
COLSEQ CQ1 ASCII NULLCHAR C'a'
For example, aE, Da, aCa, aaBa, and aaAaa in a record are sorted to aaAaa, aaBa, aCa, Da, and aE in ascending order.
If nothing of NULLCHAR, HIGH, and LOW is specified in COLSEQ, all characters that are not specified in COLSEQ will be automatically specified as NULLCHAR.
-
FOLDED
The following sorts data in the order of a - z and 0 - 9. Characters in which a sorting order is not specified have greater collation values than characters in which a sorting order is specified (lowercase alphanumeric characters).
SORT FILEDS=(1,8,CQ1,A) COLSEQ CQ1 C'a'-C'z', C'0'-C'9' HIGH
The following sorts data in the order of X'010F' - X'01FF' (double-byte characters). Lowercase alphabetic characters are ignored. Characters in which a sorting order is not specified have less collation values than characters in which a sorting order is specified (X'010F' - X'01FF' and lowercase alphabetic characters).
SORT FILEDS=(1,4,CQ2,A) COLSEQ CQ2 X'010F'-X'01FF' NULLCHAR C'a'-C'z' LOW
-
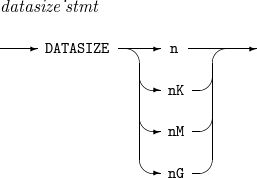
4. DATASIZE
Sets an expected input data size. The size is specified only when calling a script by using ProSort API.
The details of DATASIZE are as follows:
-
Syntax
 DATASIZE
DATASIZE -
Component
Component Description n
Expected input data size in n bytes.
nK
Expected input data size in n KB.
nM
Expected input data size in n MB.
nG
Expected input data size in n GB.
-
Example
The following sets the expected input data size to 100 MB.
DATASIZE 100M
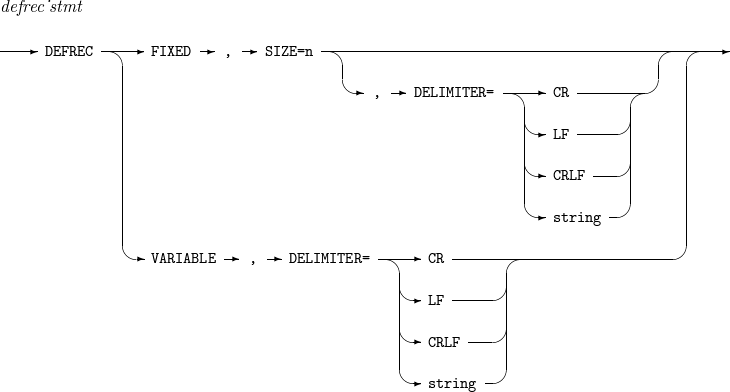
5. DEFREC
Sets a record format.
The details of DEFREC are as follows:
-
Syntax
 DEFREC
DEFREC -
Component
Component Description SIZE
Input record length.
DELIMITER
Record delimiter. Only CR (carriage return) is supported currently.
-
Example
The following sets a fixed-length record with a size of 10.
DEFREC FIXED, SIZE = 10
The following sets a variable-length record, and CR is used as a delimiter.
DEFREC VARIABLE, DELIMITER = CR
6. END
Ends a ProSort script execution.
The details of END are as follows:
-
Syntax
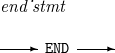 END
END -
Component
Component Description END
Ends a ProSort script execution. Statements written after the END statement in the script are not executed.
7. INCLUDE, OMIT
Includes or omits specific records.
The details of INCLUDE and OMIT are as follows:
-
Syntax
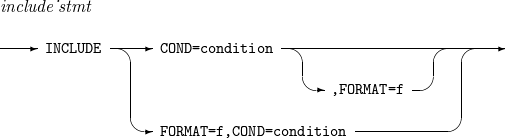 INCLUDE
INCLUDE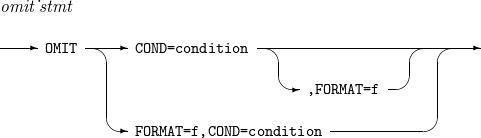 OMIT
OMIT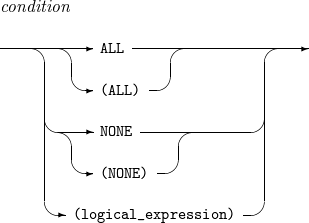
 INCLUDE, OMIT - condition
INCLUDE, OMIT - condition -
Component
Component Description condition
Condition used to include records in the INCLUDE statement or used to exclude records in the OMIT statement.
f
Default format used when f1 or f2 is omitted.
ALL
Includes all records in the INCLUDE statement and omits all records in the OMIT statement.
NONE
Includes no records in the INCLUDE statement and omits no records in the OMIT statement.
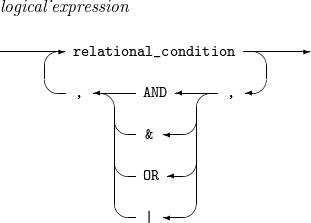
logical_expression
Logical expression that specifies a condition used to include or omit records.
A logical expression consists of one or more relational expressions combined with AND (or &), OR (or |), and parentheses.
The priorities of the operators are as follows: parentheses > AND (or &) > OR (or |). The leftmost relational expression is evaluated first. In a logical expression with relational expressions combined with AND (or &), the result is true when all the relational expressions are true. In a logical expression with relational expressions combined with OR (or |), the result is true when one or more relational expressions are true.
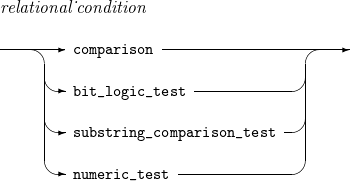
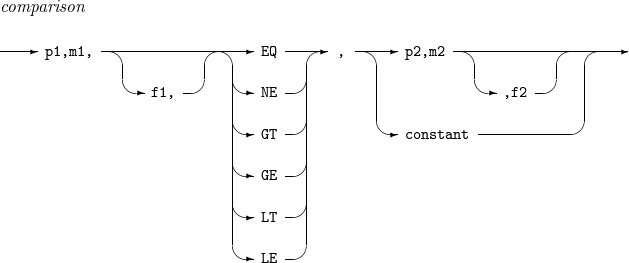
comparison
Relational expression that compares two fields (field 1 and field 2).
-
Field 1 is the input record’s p1th to (p1 + m1 - 1)th bytes in the f1 format. If f1 is not specified, f is used.
-
Field 2 is the input record’s p2th to (p2 + m2 - 1)th bytes in the f2 format or a constant. If f2 is not specified, f is used.
The following operators are available.
-
EQ: true if field 1 is equal to field 2.
-
NE: true if field 1 is not equal to field 2.
-
GT: true if field 1 is greater than field 2.
-
GE: true if field 1 is greater than or equal to field 2.
-
LT: true if field 1 is less than field 2.
-
LE: true if field 1 is less than or equal to field 2.
-
constant
Constant used for comparison. For more information, refer to Constants.
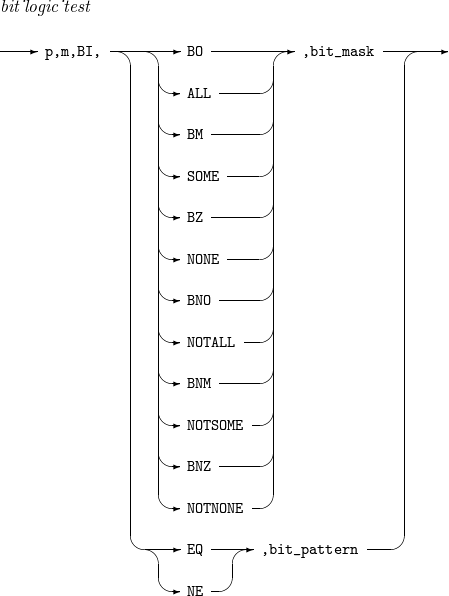
bit_logic_test
Relational expression for bit logical evaluation with input record’s p-th to (p + m - 1)th bytes in the BI format.
The evaluation is performed as follows:
-
Uses a bit mask (bit_mask) or bit pattern (bit_pattern).
-
The bit mask is a hexadecimal (X’x1…xn') or binary (B’x1…xn') string. Each bit that is on (1) in the bit mask is compared with each bit in a corresponding position in an input field.
The following operators are available.
-
BO or ALL: true if all target bits are on.
-
BM or SOME: true if some (not all) target bits are on.
-
BZ or NONE: true if no target bits are on.
-
BNO or NOTALL: true if some or no target bits are on.
-
BNM or NOTSOME: true if all or no target bits are on.
-
BNZ or NOTNONE: true if all or some target bits are on.
-
-
The bit pattern is a string in the format of B’x1…xn', where x1, …, and xn is 1, 0, or a period (.). Each bit that is on (1) and off (0) in a bit pattern is compared with each bit in a corresponding position in an input field.
The following operators are available.
-
EQ: true if each bit state (on or off) in the bit pattern is the same as that in an input field.
-
NE: true if each bit state (on or off) in the bit pattern is not the same as that in an input field.
-
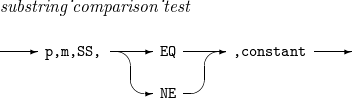
substring_ comparison_test
Relational expression for comparing a string constant and a CH field value at p-th to (p + m - 1)th bytes of an input record.
The comparison is performed as follows:
-
If m is greater than the length of the string constant, the input field value will be searched for the constant. If not, the string constant will be searched for the input field value.
The following operators are available.
-
EQ: true if the string constant and the input field value match is found.
-
NE: true if the string constant and the input field value match is not found.
-
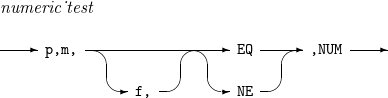
numeric_test
Relational expression for deciding whether a field (input record’s p-th to (p + m - 1)th bytes) is a numeric type.
x1y1...xmym
If the field is expressed as a previous hexadecimal value and the operator is EQ, the expression result is as follows:
-
When f is CSF (or FS) or FORMAT=CSF (or FS) is specified, the result is true if x1=…=xm=3 and 0≤y1,…,ym≤9 or false if not.
-
When f is ZD or FORMAT=ZD is specified, the result is true if x1=…=xm-1=3, xm∈{3,4,5,7}, and 0≤y1,…,ym≤9 or false if not.
-
When f is PD or FORMAT=PD is specified, the result is true if 0≤x1,…,xm≤9, 0≤y1,…,ym-1≤9, and ym∈{C,D,F} or false if not.
If the operator is NE, the result is contrary to that when the operator is EQ.
-
-
Example
The following includes records in which bytes 5 through 12 are greater than bytes 13 through 20 or bytes 105 through 108 are less than 1000.
INCLUDE COND=(5,8,GT,13,8,|,105,4,LE,1000),FORMAT=CSF
The following includes records in which bytes 11 through 16 contain the string OK or bytes 21 through 23 contain the string J69.
INCLUDE FORMAT=SS,COND(11,6,EQ,C'OK',OR,21,3,EQ,C'J69')
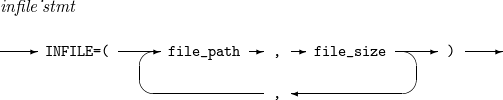
8. INFILE
Sets an input file’s path and expected size.
The details of INFILE are as follows:
-
Syntax
 INFILE
INFILE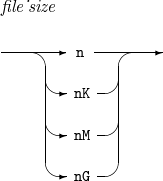
-
Component
Component Description file_path
Input file path.
file_size
Expected input file size.
-
Example
The following sets the input file’s path and expected size to IN and 1 MB respectively.
INFILE=(IN,1M)
9. INREC, OUTREC
Reformats input records into new records with a specified format. INREC is performed before SORT, MERGE, and COPY operations. OUTREC is performed after the operations.
The details of INREC and OUTREC are as follows:
-
Syntax
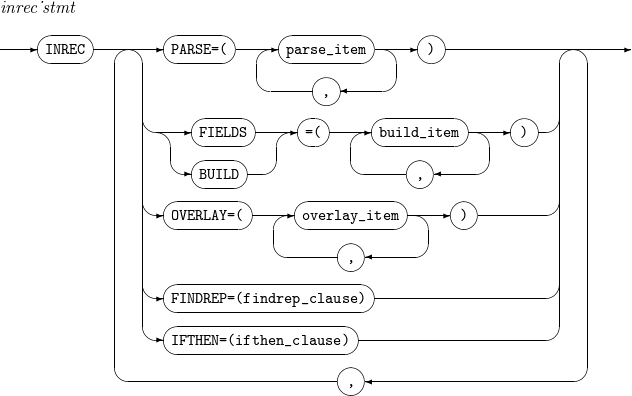 INREC
INREC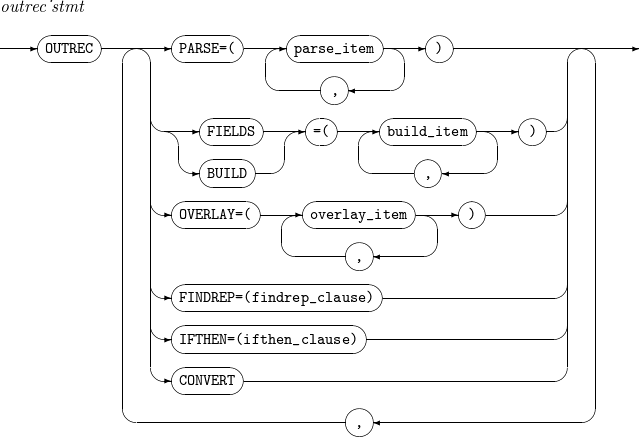 OUTREC
OUTREC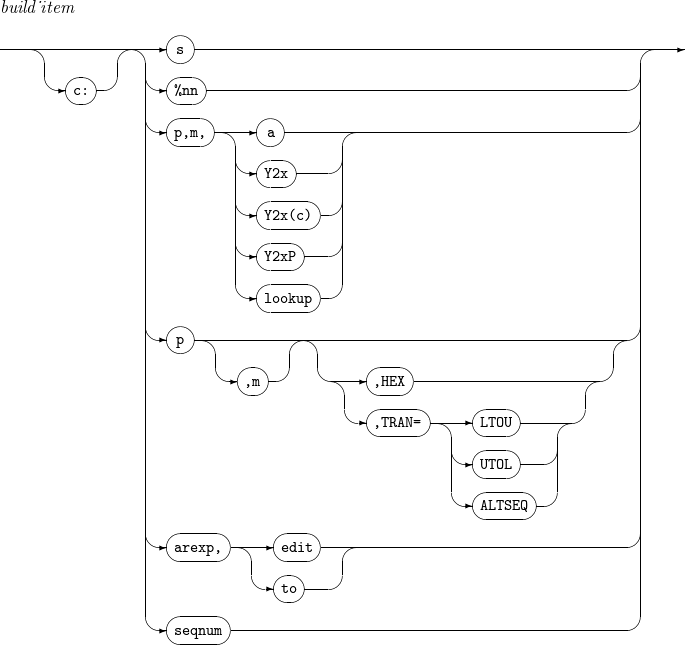
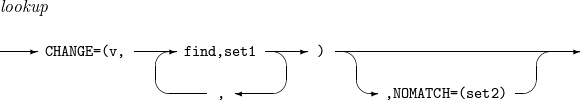

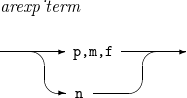
 INREC, OUTREC - build_item
INREC, OUTREC - build_item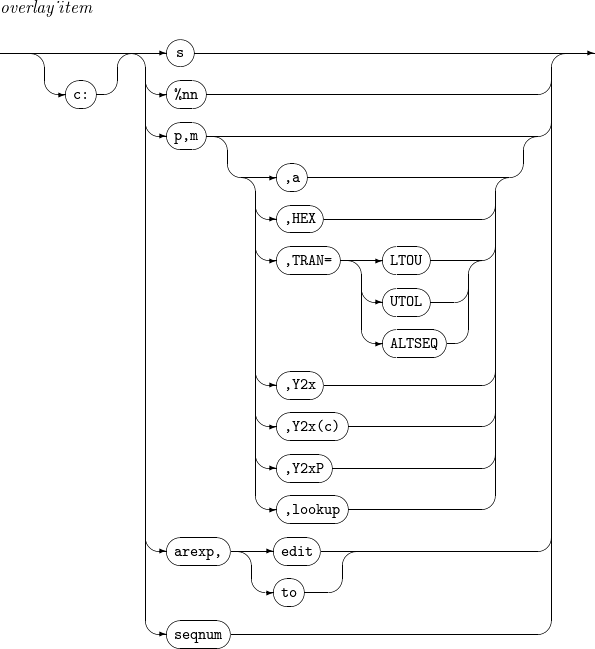 INREC, OUTREC - overlay_item
INREC, OUTREC - overlay_item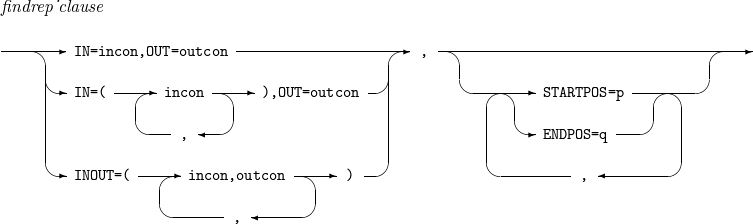 INREC, OUTREC - findrep_clause
INREC, OUTREC - findrep_clause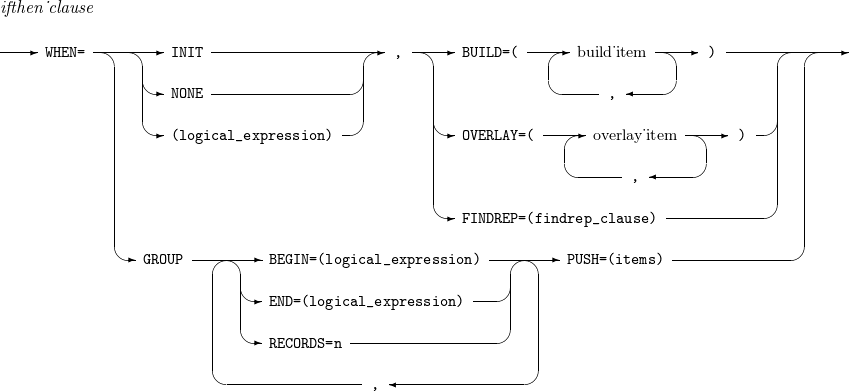 INREC, OUTREC - ifthen_clause
INREC, OUTREC - ifthen_clause -
Component
Component Description PARSE
Refer to parse_item.
CONVERT
Converts a variable-length input record to a fixed-length output record.
c
Field position.
Unused spaces followed by the separation field are padded with blanks. For example, specifying 30:C’Tmax' pads the columns 1 through 29 with blanks and inserts 'Tmax' into the columns 30 through 33. Specifying 20:5,1 pads the columns 1 through 19 with blanks and inserts the input field’s byte 5 into the column 20.
s
Outputs one of the following separation fields.
-
nX: n blanks (X'20'). If n is not specified, the default value is 1.
-
nZ: n nulls (X'00'). If n is not specified, the default value is 1.
-
nC'…': n strings enclosed in single quotation marks. If n is not specified, the default value is 1.
-
nX'…': n hexadecimal strings enclosed in single quotation marks. If n is not specified, the default value is 1.
-
DATE=(abcd): current date in the format of C’adbdc', where a,b,c∈{M,D,Y,4} and d is a delimiter.
-
M: month (01-12)
-
D: day (01-31)
-
Y: last two digits of a year
-
4: four-digit year (0001-9999)
-
-
&DATE=(abcd): same as DATE=(abcd).
-
DATE or &DATE: same as DATE=(MDY/).
-
DATENS=(abc): current date in the format of C’abc', where a,b,c∈{M,D,Y,4}.
-
M: month (01-12)
-
D: day (01-31)
-
Y: last two digits of a year
-
4: four-digit year (0001-9999)
-
-
&DATENS=(abc): same as DATENS=(abc).
-
n/: n record delimiters. If n is not specified, the default value is 1.
%nn
Specifies the parsed field of the %nn label.
p,m
Specifies field position (p) and length (m).
The last field’s length can be omitted. If the length is omitted, the last field ends at the end of the record.
a
Specifies field alignment.
The following values are available.
-
H: Halfword aligned
-
F: Fullword aligned
-
D: Doubleword aligned
HEX
Converts a value into a hexadecimal value. For example, a string AB is converted into C1C2.
TRAN= [ LTOU | UTOL | ALTSEQ ]
-
If TRAN=LTOU, lowercase letters are converted to uppercase letters. If TRAN=UTOL, uppercase letters are converted to lowercase letters.
-
If TRAN=ALTSEQ, a defined ALTSEQ table is converted.
lookup
Finds a specific string in a field, and then converts the field value according to the result.
-
v: length of the changed field value.
-
find: string to find in the format of C’x1…xn', X’x1…xn' or B’x1…xn'.
-
set1: new value of the field if the string have been found. The new value is a constant in the format of C’x1…xn' or X’x1…xn', or a field in the format of p, m.
-
set2: new value of the field if it failed to find the string. The new value is a constant in the format of C’x1…xn' or X’x1…xn', or a field in the format of p, m.
arexp
Operation result.
arexp_term
Operand.
-
p,m,f: field position, length, and format.
-
n: integer value.
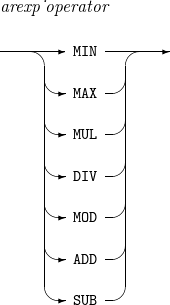
arexp_operator
Operator.
The result of each operator is as follows:
-
MIN: value of an operand with the smallest value.
-
MAX: value of an operand with the greatest value.
-
MUL: product of the operands.
-
DIV: value of dividing the left operand by the right operand.
-
MOD: remainder of dividing the left operand by the right operand.
-
ADD: sum of the operands.
-
SUB: value of subtracting the right operand from the left operand.
Operators' priority is as follows:
-
MIN, MAX
-
MUL, DIV, MOD
-
ADD, SUB
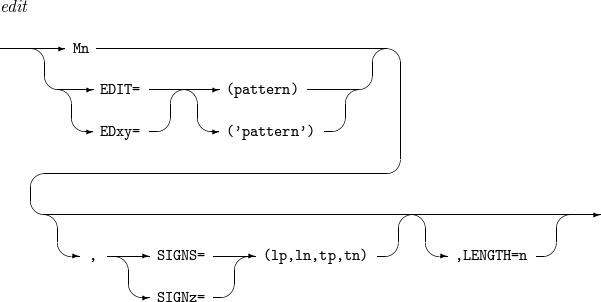
edit
Changes a field with a desired format and length. For more information, refer to [app_mask].
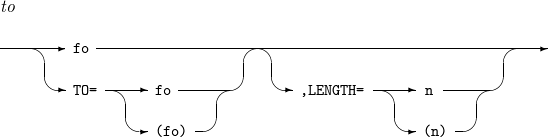
to
Changes a field with a desired format (fo) and length (n).
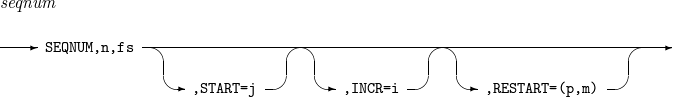
seqnum
Outputs sequence numbers according to defined rules.
-
n: Specifies the number of digits for the sequence number.
-
fs: Specifies the string format used to represent the sequence number.
-
START=j: Sets the starting value of the sequence number to j. If omitted, START defaults to 1.
-
INCR=i: Sets the increment value of the sequence number to i. If omitted, INCR defaults to 1.
-
RESTART=(p,m): Resets SEQNUM to 1 when the specified field does not match the corresponding field of the previous record.
findrep_clause
Finds incon in a record and changes it to outcon.
-
incon: string to find in the format of C’x1…xn', nC’x1…xn', X’x1…xn', or nX’x1…xn'.
-
outcon: string to output in the format of C'', C’x1…xn', nC’x1…xn', X’x1…xn', or nX’x1…xn'.
-
p: search start position.
-
q: search end position.
WHEN=INIT, [ BUILD | OVERLAY | FINDREP ]
Performs BUILD, OVERLAY, or FINDREP operations on all input records. An IFTHEN clause that includes WHEN=INIT is processed before other IFTHEN clauses.
WHEN=(logical_expression), [ BUILD | OVERLAY | FINDREP ]
Performs BUILD, OVERLAY, or FINDREP operations on input records that meet the specific condition (logical_expression).
WHEN=GROUP
[,BEGIN=(logical_expression) |
,END=(logical_expression) |
,RECORDS=n]
,PUSH=(items)
The BEGIN, END, and RECORDS operations are applied to all input records. When the specified conditions are met, records are assigned to or released from a GROUP.
-
BEGIN=(logical_expression): Assigns a GROUP starting from the record that satisfies the logical_expression.
-
END=(logical_expression): Releases the GROUP after the record that satisfies the logical_expression.
-
RECORDS=n: Ends the GROUP when the number of records in a single GROUP reaches n.
-
PUSH=(items): Overlays the values specified in items when the record belongs to a GROUP. The available item types are as follows:
-
c:p,m: Overlays the value corresponding to p,m from the first record of the GROUP at position c.
-
c:ID=n: Represents a GROUP ID of length n and overlays the current GROUP ID at position c.
-
c:SEQ=n: Represents the record sequence within a GROUP with length n and overlays the current record sequence at position c.
-
-
-
Example
The following two examples have the same result.
INREC FIELDS=(10,3,20,8) SORT FIELDS=(5,6,CH,A)
OUTREC FIELDS=(10,3,20,8) SORT FIELDS=(21,6,CH,A)
The first example reformats bytes 10 through 12 and bytes 20 through 27 of each input record into a new record with the length of 11 bytes, and then sorts the new records based on their bytes 5 through 10 in ascending order. The second example sorts input records based on bytes 21 through 26, and then reformats the result records in the same way as in the first example.
The following performs INREC and OUTREC.
INREC FIELDS=(14,4, 6,3) SORT FIELDS=(1,4,A, 5,3,A), FORMAT=AC OUTREC FIELDS=(3X, 1,4,H, 13:1,3, 5,2, 4X'61', X'0A')
Input record: ABCDE567LMNOP1234
The results are as follows:
-
The result of performing INREC
Classification Description Bytes 1 through 4
Bytes 14 through 17 of the input record ('1234')
Bytes 5 through 7
Bytes 6 through 8 of the input record ('567')
-
Result of performing OUTREC
Classification Description Bytes 1 through 3
Space characters (20 20 20 in HEX)
Byte 4
NULL padded for halfword alignment (00 in HEX)
Bytes 5 through 8
Bytes 1 through 4 of the INREC result ('1234')
Bytes 9 through 12
Space characters (20 20 20 20 in HEX)
Bytes 13 through 15
Bytes 1 through 3 of the INREC result ('123')
Bytes 16 through 17
Bytes 5 through 6 of the INREC result ('56')
Bytes 18 through 21
0x61 ('aaaa')
Byte 22
Carriage return (0A in HEX)
-
9.1. parse_item
The details of parse_item are as follows.
-
Syntax
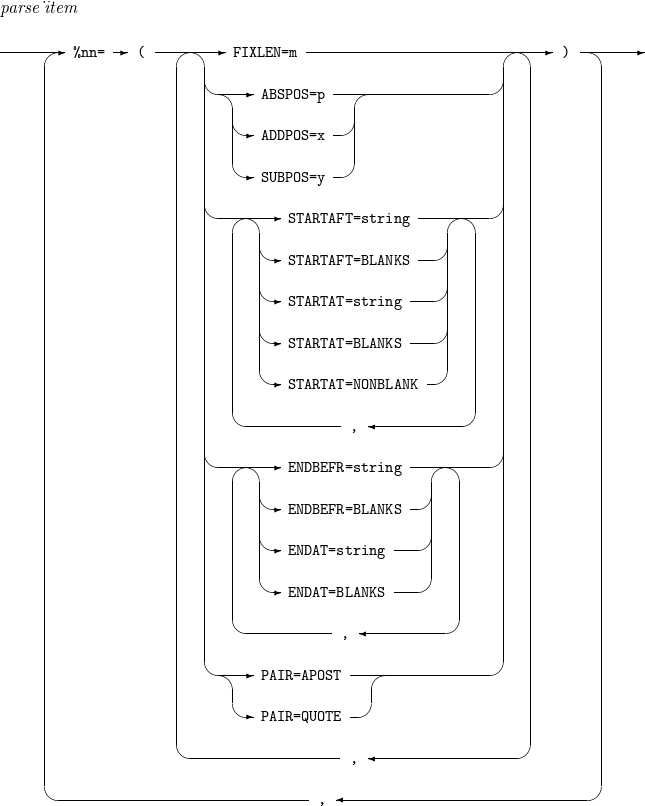 INREC, OUTREC - parse_item
INREC, OUTREC - parse_item -
Component
Component Description %nn
Converts variable-length input records into fixed-length output records.
Parsed fields can be used wherever (p,m) is specified in BUILD or OVERLAY.
FIXLEN=m
Specifies the length of the parsed field. This attribute must be specified for all parsed fields.
ABSPOS=p
Specifies the absolute starting position p for parsing in the input record.
ADDPOS=x
Increases the parsing start position in the input record by x.
SUBPOS=y
Decreases the parsing start position in the input record by y.
STARTAFT
-
STARTAFT=string: The parsed field starts after the first occurrence of string in the input record.
-
STARTAFT=BLANKS: The parsed field starts after the first sequence of spaces from the beginning of the input record.
STARTAT
-
STARTAT=string: The parsed field starts at the first occurrence of string in the input record, including the string.
-
STARTAT=BLANKS: The parsed field starts at the first sequence of spaces from the beginning of the input record.
-
STARTAT=NONBLANK: The parsed field starts at the first non-space character from the beginning of the input record.
ENDBEFR
-
ENDBEFR=string: The parsed field ends before the first occurrence of string in the input record.
-
ENDBEFR=BLANKS: The parsed field ends before the first sequence of spaces from the beginning of the input record.
ENDAT
-
ENDAT=string: The parsed field ends at the first occurrence of string in the input record, including the string.
-
ENDAT=BLANKS: The parsed field ends at the first sequence of spaces from the beginning of the input record, including the spaces.
PAIR
-
PAIR=APOST: Text enclosed in apostrophes (') is not treated as BLANKS or strings.
-
PAIR=QUOTE: Text enclosed in quotation marks (") is not treated as BLANKS or strings.
-
10. INSERT
Inserts a specified file into a script.
The details of INSERT are as follows:
-
Syntax
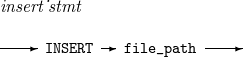 INSERT
INSERT -
Component
Component Description file_path
Path of a file to be inserted into a script.
-
Example
The following inserts the ins.scr file into a script.
INSERT ins.scr
11. MEMORY
Sets the memory size used when performing operations.
The details of MEMORY are as follows:
-
Syntax
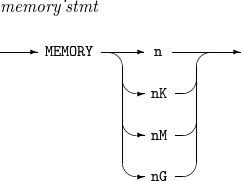 MEMORY
MEMORY -
Component
Component Description n
Memory size in n bytes.
nK
Memory size in n KB.
nM
Memory size in n MB.
nG
Memory size in n GB.
-
Example
The following sets 64 MB memory.
MEMORY 64M
The following set 1 GB memory.
MEMORY 1G
12. MODS
Registers a function as User Exit Function by using a ProSort script.
|
For more information about User Exit Function, refer to User Exit Function. |
The details of MODS are as follows:
-
Syntax
 MODS
MODS -
Component
Component Description func_name
Function name to register.
lib_path
Path of library file to dynamically refer to.
lib_type
Either C for COBOL functions or N for non-COBOL function.
-
Example
The following registers the exit_none and exit_insert functions as User Exit Function E15 and E32 respectively. The lib_exit.so library file is referred to dynamically.
MODS E15 = (exit_none, /path/lib_exit.so, N), E32 = (exit_insert, /path/lib_exit.so, N)
13. OPTION
Sets values of options such as USE_ALTERNATIVE_TP_TYPE.
The details of OPTION are as follows:
-
Syntax
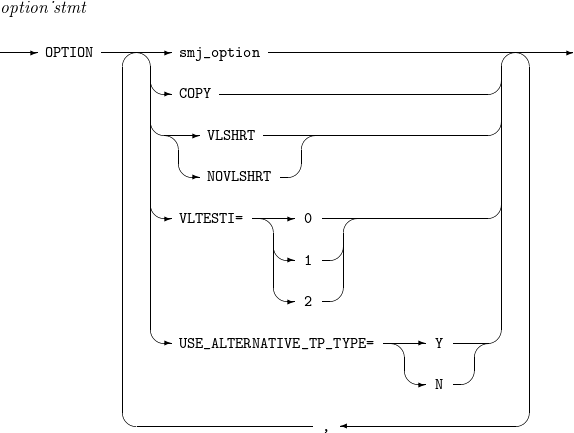 OPTION
OPTION -
Component
Component Description EQUALS
Guarantees to preserve the original sequence of records that have the same key field.
NOEQUALS
Does not guarantee to preserve the original sequence of records that have the same key field.
SKIPREC=n
Skips the first n input records and passes the remaining records to E15 user exit or a routine that processes an INCLUDE or OMIT statement. Refer to SORT and COPY Operation Procedure (with User Exit Function).
STOPAFT=n
Passes up to the first n input records to a routine that processes an INREC statement if the INREC statement exists or a routine that processes a SORT or COPY statement if an INREC statement does not exist. Refer to SORT and COPY Operation Procedure (with User Exit Function).
[ CENTURY | CENTWIN | Y2PAST ] = [ s | f ]
Supplements the first two-digit year value for Y2x fields because the fields have only the last two-digit year value. CENTURY and CENTWIN are the same as Y2PAST.
Y2PAST can have a value with one of the following types.
-
s: sliding century window. An integer between 0 and 100. A Y2x field value is interpreted as a value between (the current year - s) and (the current year - s + 99).
-
f: fixed century window. An integer between 1000 and 3000. A Y2x field value is interpreted as a value between f and (f + 99).
COPY
Performs the COPY operation.
MSGPRT
Messages to output. Only syntax-checked. (Alias: PRINT)
VLSHRT
Action to take when a field specified in a SORT, MERGE, FILTER (INCLUDE, OMIT), or SUM operation does not exist or only a part of it exists in an input record.
For more information, refer to Example.
NOVLSHRT
An error message is displayed and ProSort terminates when a field specified in a SORT, MERGE, FILTER (INCLUDE, OMIT), or SUM operation does not exist or only a part of it exists in an input record.
If both VLSHRT and NOVLSHRT are not specified, NOVLSHRT is used.
VLTESTI=(0 | 1 | 2)
Action to take when a field specified in a reformat (INCLUDE, OMIT) operation does not exist or only a part of it exists in an input record.
The following describes each option:
-
0: In INCLUDE or OMIT operations, the full range of all specified fields must exist in the input record. Otherwise, an error occurs. If the VLTESTI option is not specified, the operation behaves as if VLTESTI=0 were specified.
-
1: For INCLUDE operations, if the specified field does not exist in the input record or exists only partially, the record is not output. For OMIT operations, if the specified field does not exist in the input record or exists only partially, the record is output.
-
2: In INCLUDE or OMIT operations, if the specified field does not exist in the input record or exists only partially, the relational expression is evaluated as false.
USE_ALTERNATIVE_ TP_TYPE
How to express the TP positive numbers. For more information, refer to Miscellaneous.
-
-
Example
When VLSHRT is specified, each operation behaves as follows.
-
SORT, MERGE
If a specified field does not exist or only a part of it exists in an input record, binary zeros are padded.
SORT FIELDS=(1,2,CH,A) Input: A B AA BB Output: A AA B BB
-
INCLUDE, OMIT
If a specified field does not exist or only a part of it exists in an input record, the relational expression is regarded as false.
INCLUDE COND=(1,2,CH,EQ,C'AA') Input: A AA B BB Output: AA
-
SUM
If a specified field does not exist or only a part of it exists in an input record, the record is excluded from a SUM operation.
SORT FIELDS=(1,1,CH,A) SUM FIELDS=(2,2,ZD) Input: A03 A04 B B05 C Output: A07 B05
-
14. OUTFIL
Outputs new records created by applying a condition to records resulting from a SORT, MERGE, or COPY operation. Its alias is OUTFILE.
The details of OUTFIL are as follows:
-
Syntax
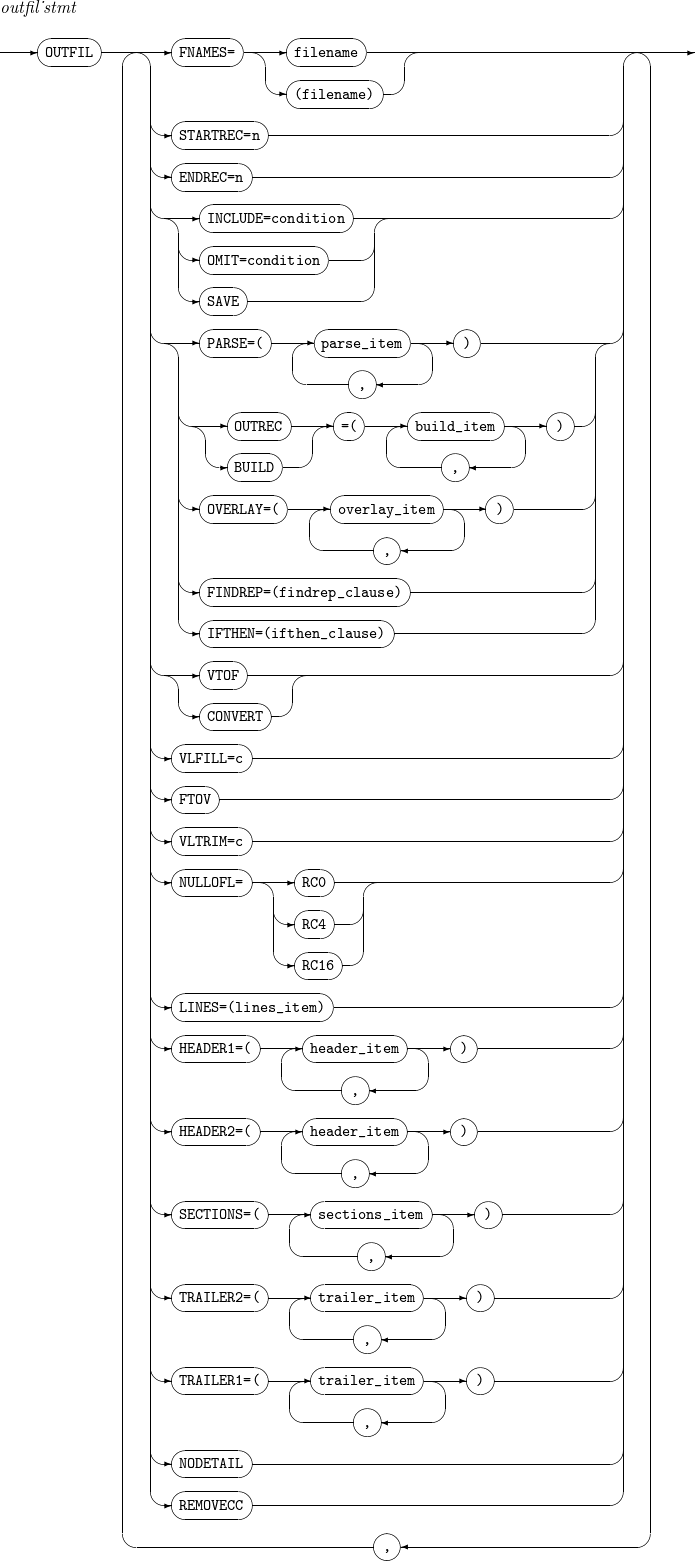 OUTFIL
OUTFIL -
Component
Component Description filename
File name to output.
STARTREC=n
Outputs result records from the n-th record.
ENDREC=n
Outputs result records to the n-th record.
INCLUDE=condition
Outputs result records that meet the condition. For more information, refer to INCLUDE, OMIT.
OMIT=condition
Does not output result records that meet the condition. For more information, refer to INCLUDE, OMIT.
SAVE
Outputs records that are not outputted for any other OUTFIL with INCLUDE or OMIT.
OUTREC or BUILD
Refer to INREC, OUTREC.
OVERLAY
Refer to INREC, OUTREC.
FINDREP
Refer to INREC, OUTREC.
IFTHEN
Refer to INREC, OUTREC.
VTOF or CONVERT
Converts a variable-length input record to a fixed-length output record.
VLFILL=c
Character (c) with which an input record is right-padded if a specific field does not exist or only a part of it exists in the input record.
FTOV
Converts a variable-length input record to a fixed-length output record.
VLTRIM=c
Trailing character (c) to remove from a result record. The number of the characters can be one or more.
NULLOFL= [ RC0 | RC4 | RC16 ]
Action to take when there is no operation result record.
-
RC0: set the return value to 1, and then continue with the next operation.
-
RC4: set the return value to 4, and then continue with the next operation.
-
RC16: stop the operation and return 16.
LINES=n
Number of lines (n) displayed in one page of a report.
HEADER1
Report header. For more information, refer to header_item.
HEADER2
Page header. For more information, refer to header_item.
SECTIONS
Adds a header or trailer whenever the data defined in a section changes. Multiple sections can be defined with sections_item. For more information, refer to sections_item.
TRAILER2
Page trailer. For more information, refer to trailer_item.
TRAILER1
Report trailer. For more information, refer to trailer_item.
NODETAIL
Outputs a report that includes result records without data records.
REMOVECC
Outputs result records without ANSI control characters.
-
-
Example
The following is an example that records in which bytes 15 through 20 are AAA are outputted to the file AAA, the records in which bytes 15 through 200 are BBB are outputted to the file BBB, and the remaining records are outputted to the file UNKNOWN.
OUTFIL INCLUDE=(15,6,AC,EQ,C'AAA'), FNAMES=AAA OUTFIL INCLUDE=(15,6,AC,EQ,C'BBB'), FNAMES=BBB OUTFIL SAVE, FNAME=UNKNOWN
14.1. header_item
The details of header_item are as follows:
-
Syntax
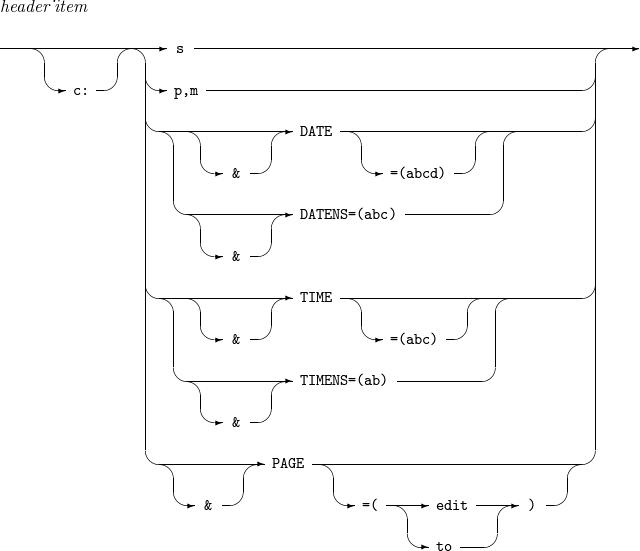 OUTFIL - header_item
OUTFIL - header_item -
Component
Component Description s
Count to repeat a string in the format of n’xx…x'.
p,m
Input field position (p) and length (m).
DATENS=(abc)
Date in the format of abc. a, b, and c can be one of M, D, Y, and 4. Each value cannot be defined multiple times.
-
M: month (01-12)
-
D: day (01-31)
-
Y: last two digits of a year
-
4: four-digit year (0001-9999)
For example, DATENS=(DMY) expresses June 3, 2009 as 030609.
DATE=(abcd)
Date in the format of abcd.
-
abc: same as abc for DATENS.
-
d: delimiter added between each token (year, month, and day).
For example, DATE=(4MD-) expresses June 3, 2009 as 2009-06-03.
TIMENS=(ab)
Time in the format of ab (either 12 or 24).
If ab is 24, time is expressed as hhmmss (24-hour clock).
-
hh: hour (00-23)
-
mm: minute (00-59)
-
ss: second (00-59)
For example, 4:15:37 p.m. is expressed as 161537.
If ab is 12, time is expressed as hhmmss xx (12-hour clock).
-
hh: hour (00-23)
-
mm: minute (00-59)
-
ss: second (00-59)
-
xx: either am or pm.
For example, 4:15:37 p.m. is expressed as 041537 pm.
TIME=(abc)
Time in the format of abc.
-
ab: same as ab for TIMENS.
-
c: delimiter added between each token (hour, minute, and second).
For example, TIME=(12.) expresses 4:15:37 p.m. as 04.15.37 pm.
PAGE
Page number. For information about 'edit' and 'to', refer to INREC, OUTREC.
-
14.2. sections_item
The details of sections_item are as follows:
-
Syntax
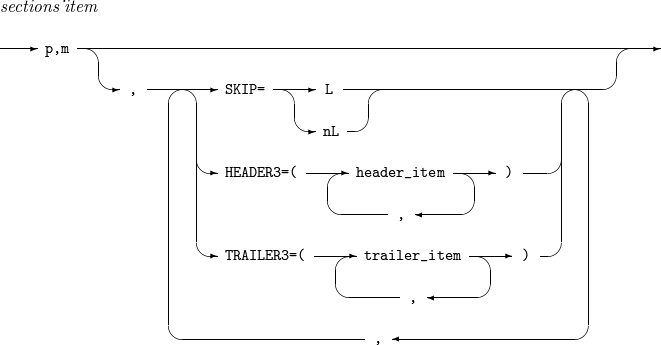 OUTFIL - sections_item
OUTFIL - sections_item -
Component
Component Description p,m
Position (p) and length (m) of a section field in an output record.
Before outputting the first record, the first section header is outputted. If the section field value of a current record is different from that of the previous record, the previous section trailer and the current section header are outputted. After outputting the last record, the last section trailer is outputted.
SKIP=L
Outputs one empty line between sections.
SKIP=nL
Outputs n empty lines between sections.
HEADER3
Section header. For more information, refer to header_item.
TRAILER3
Section trailer. For more information, refer to trailer_item.
14.3. trailer_item
The details of trailer_item are as follows:
-
Syntax
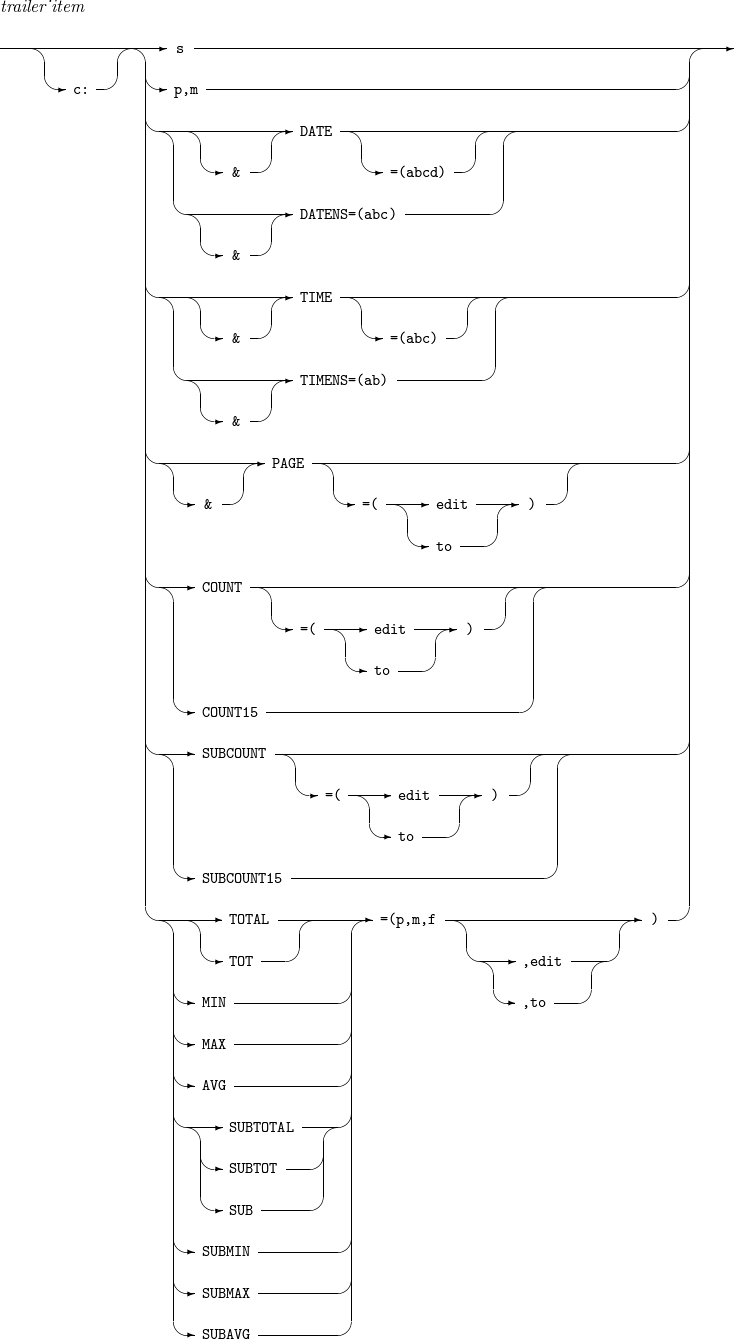 OUTFIL - trailer_item
OUTFIL - trailer_item -
Component
Component Description s
Refer to header_item.
p,m
Refer to header_item.
DATENS=(abc)
Refer to header_item.
DATE=(abcd)
Refer to header_item.
TIMENS=(ab)
Refer to header_item.
TIME=(abc)
Refer to header_item.
PAGE
Refer to header_item.
COUNT
-
For report trailers
Total number of output records.
-
For page/section trailers
Number of records displayed in a current page/section.
For information about 'edit' and 'to', refer to INREC, OUTREC. If both 'edit' and 'to' are not specified, an 8-digit integer is outputted.
COUNT15
Same as COUNT except that the count is a 15-digit integer.
SUBCOUNT
-
For report trailers
Total number of output records.
-
For page/section trailers
Accumulated number of records displayed up to a current page/section.
For information about 'edit' and 'to', refer to INREC, OUTREC. If both 'edit' and 'to' are not specified, an 8-digit integer is outputted.
SUBCOUNT15
Same as SUBCOUNT except that a 15-digit integer is output instead of an 8-digit integer.
TOTAL or TOT
A field at bytes p through (p + m - 1) of each output recor is used as an aggregate field.
-
For report trailers
Total of aggregate fields in the specified format (f) of all output records.
-
For page/section trailers
Total of aggregate fields in the specified format (f) of records displayed in a current page/section.
For information about 'edit' and 'to', refer to INREC, OUTREC.
MIN
A field at bytes p through (p + m - 1) of each output record is used as an aggregate field.
-
For report trailers
Minimum value among aggregate fields in the specified format (f) of all output records.
-
For page/section trailers
Minimum value among aggregate fields in the specified format (f) of records displayed in a current page/section.
For information about 'edit' and 'to', refer to INREC, OUTREC.
MAX
A field at bytes p through (p + m - 1) of each output record is used as an aggregate field.
-
For report trailers
Maximum value among aggregate fields in the specified format (f) of all output records.
-
For page/section trailers
Maximum value among aggregate fields in the specified format (f) of records displayed in a current page/section.
For information about 'edi’t and 'to', refer to INREC, OUTREC.
AVG
A field at bytes p through (p + m - 1) of each output record is used as an aggregate field.
-
For report trailers
Average value of aggregate fields in the specified format (f) of all output records.
-
For page/section trailers
Average value of aggregate fields in the specified format (f) of records displayed in a current page/section.
For information about 'edit' and 'to', refer to INREC, OUTREC.
[ SUBTOTAL | SUBTOT | SUB ]
A field at bytes p through (p + m - 1) of each output record is used as an aggregate field.
-
For report trailers
Total value of aggregate fields in the specified format (f) of all output records.
-
For page/section trailers
Total value of aggregate fields in the specified format (f) of records displayed up to a current page/section.
For information about 'edit' and 'to', refer to INREC, OUTREC.
SUBMIN
A field at bytes p through (p + m - 1) of each output record is used as an aggregate field.
-
For report trailers
Minimum value among aggregate fields in the specified format (f) of all output records.
-
For page/section trailers
Minimum value among aggregate fields in the specified format (f) of records displayed up to a current page/section.
For information about 'edit' and 'to', refer to INREC, OUTREC.
SUBMAX
A field at bytes p through (p + m - 1) of each output record is used as an aggregate field.
-
For report trailers
Maximum value among aggregate fields in the specified format (f) of all output records.
-
For page/section trailers
Maximum value among aggregate fields in the specified format (f) of records displayed up to a current page/section.
For information about 'edit' and 'to', refer to INREC, OUTREC.
SUBAVG
A field at bytes p through (p + m - 1) of each output record is used as an aggregate field.
-
For report trailers
Average value of aggregate fields in the specified format (f) of all output records.
-
For page/section trailers
Average value of aggregate fields in the specified format (f) of records displayed up to a current page/section.
For information about 'edit' and 'to', refer to INREC, OUTREC.
-
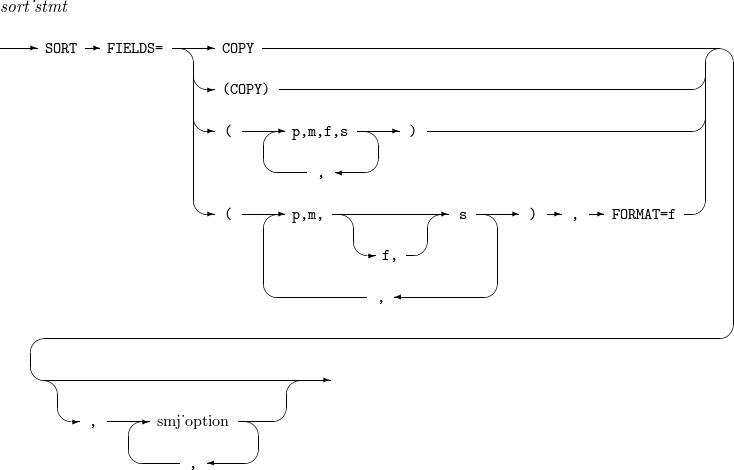
15. SORT, MERGE
Performs a sort, copy, or merge operation. SORT and MERGE statements consist of a field list and options. If all the fields have the same format, it needs to set the format only once after the field list.
The details of SORT and MERGE are as follows:
-
Syntax
 SORT
SORT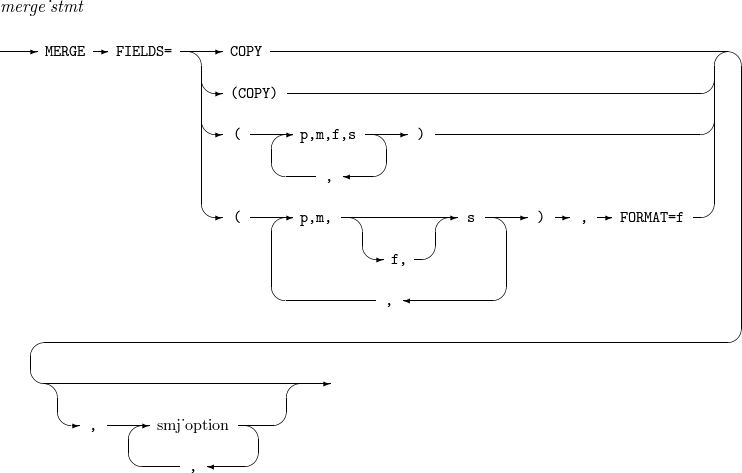 MERGE
MERGE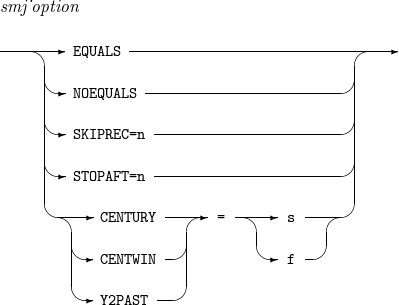 SORT, MERGE - smj_option
SORT, MERGE - smj_option -
Component
Component Description COPY
Performs a COPY operation instead of a SORT operation.
p,m,f,s
Position (p), length (m), and format (f) of a field in each input record, and a sorting order (s).
If f is omitted, the format set in the FORMAT option is used. s can be set to either A (ascending order) or D (descending order).
smj_option
Refer to OPTION.
-
Example
The following sorts records based on 8-byte ZD fields at byte 3 in ascending order and 6-byte AC fields at byte 40 in descending order.
SORT FIELDS=(3,8,ZD,A,40,6,AC,D)
The following sorts records based on 8-byte ZD fields at byte 3 in ascending order and 6-byte AC fields at byte 40 in descending order. Since EQUALS is used, records with the same key field are sorted in the original order (stable sort).
SORT FIELDS=(3,8,ZD,A,40,6,AC,D), EQUALS
The following sorts records based on 8-byte ZD fields at byte 3 in ascending order and 6-byte AC fields at byte 40 in descending order. Since SKIPREC and STOPAFT are used, only records 101 through 300 are sorted.
SORT FIELDS=(3,8,ZD,A,40,6,AC,D), SKIPREC = 100, STOPAFT = 200
The following merges records based on 4-byte ZD fields at byte 25 and 8-byte ZD fields at byte 48 in ascending order.
MERGE FIELDS=(25,4,A,48,8,A),FORMAT=ZD
The following examples only copy records to output.
MERGE FIELDS=COPY
SORT FIELDS=COPY
16. SUM
Outputs one of sorted or merged records that have the same key field. Specified fields (summary fields) of the records are added and the sum is outputted.
The details of SUM are as follows:
-
Syntax
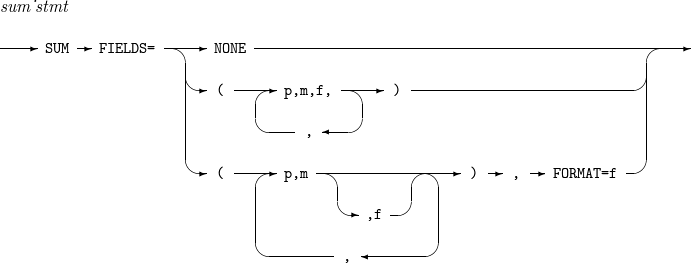 SUM
SUM -
Component
Component Description NONE
Performs a SORT or MERGE operation and then outputs one of the records that have the same key field.
p,m,f
Position (p), length (m), and format (f) of a summary field in each input record.
Only one of the records that have the same key field is outputted. Summary fields in the format of f of the records are added, and the sum in the format of f is outputted in bytes p through (p + m -1) of the output record. If f is omitted, the format set in the FORMAT option is used.
-
Example
The following specifies an 8-byte packed decimal field at byte 21 and a 4-byte fixed-integer field at byte 11 as summary fields.
SUM FIELDS=(21,8,PD,11,4,FI)
The following only eliminates duplicate records.
SUM FIELDS=NONE
The following specifies an 8-byte ZD field at byte 41 and a 4-byte ZD field at byte 49 as summary fields.
SUM FIELDS=(41,8,49,4),FORMAT=ZD