Introduction
This chapter describes the JCA specification and WebTJCA.
1. Overview
WebTJCA is a library package that functions as a resource adapter as specified in JCA (J2EE Connector Architecture) of J2EE. This library can be used to communicate with Tmax.
Since the existing WebT ran as a single application or used JEUS to communicate with Tmax, a specific configuration or API was needed to communicate with Tmax.
WebTJCA implements the JCA specification so that users can request services from Tmax without having to consider WebT.
2. JCA
JCA is a standard framework for accessing resources in Enterprise Information Systems (EIS). These can include ERP systems, legacy applications, etc.
Before JCA was supported, a custom driver was used to connect to an EIS. The driver implemented separate interfaces for each vendor’s EIS or WAS (web application server). When using a custom driver, various interfaces and development methods must be considered according to the driver, and some products are incompatible with one another.
This situation is called an N*M problem. An N*M problem requires code level modifications, which severe restrict portability and expandability in a J2EE environment. To solve this problem, the JCA specification defines the interface and interoperability between the resource adapter and a WAS. Any WAS and resource adapter can connect with one another as long as they comply with the JCA standard. Providing the standard architecture for the custom drivers of each EIS vendor has mitigated the N*M connection problem to N+M.
|
To download the connector 1.5 specification, use the link http://java.sun.com/j2ee/connector/download.html. |
2.1. JCA Architecture
The following shows the JCA architecture.
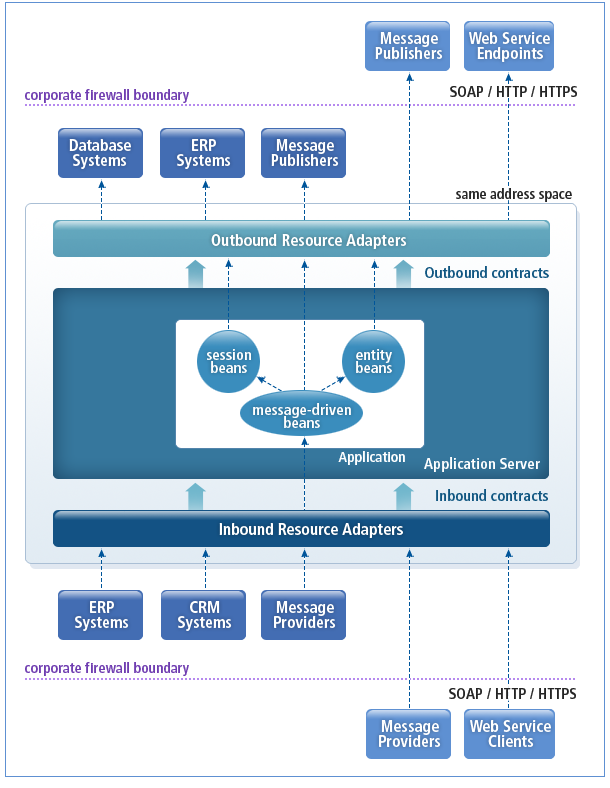
-
Outbound Communication
When a web application server sends a service request to EIS, this is called outbound communication.
The JCA specification provides the Common Client Interface (CCI), which is used by application developers for EIS-related applications. All resource adapters must implement both the CCI and Service Provider Interface (SPI) specifications.
-
Inbound Communication
When an EIS sends a service request to a web application server, this is called inbound communication.
The JCA 1.5 specification supports both inbound and outbound communications between a web application server and an EIS.
The following shows the inbound communication structure.
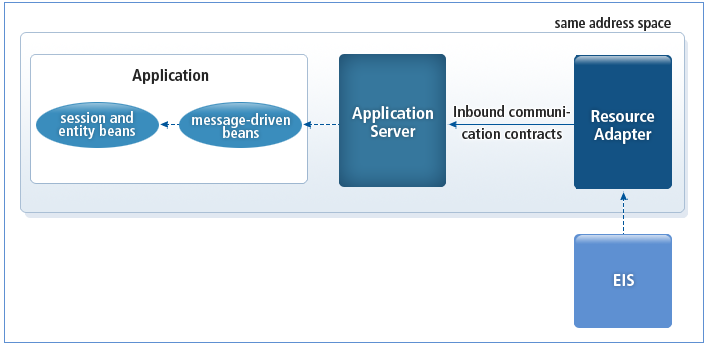 Inbound Communication
Inbound Communication
2.2. WebTJCA
WebTJCA, a library that implements the JCA specification, is deployed in WebT*.jar. This library also includes the components of the existing WebT library, ensuring backward compatibility. WebTJCA supports both outbound and inbound communication.
-
Outbound communication
Developers must use WebT*.jar and deploy it to the web application server by creating a resource adapter defined in ra.xml, along with configuration files specific to the web application server vendor.
Developers can write applications using the CCI to send service requests.
-
Inbound communication
Developers must use WebT*.jar and deploy it to the web application server by creating a resource adapter defined in ra.xml, along with configuration files specific to the web application server vendor.
Developers must implement a message-driven bean (MDB) to handle EJB calls during the message reception process.