Intrinsic Functions
This chapter covers the basic concepts of intrinsic functions and contains a description of each function.
1. Overview
An intrinsic function is a temporary data item, and its value is specified when the function is referenced during the execution of the statement. The name of the intrinsic function is a COBOL word.
The intrinsic functions can be divided into the six categories of Arithmetic, Statistical, Date/Time, Financial, Character-Handling, and Other, based on the service performed.
Each function can be used in statements in the procedure division by specifying its name and the necessary arguments. The function returns alphanumeric, numeric, or integer values.
Specifying Functions
A function-identifier can be specified anywhere that a data item of the same type as the function can be used. If the result of the function, including another evaluation of the same function, satisfies the argument requirements, the function can be used.
The general format of a function-identifier is as follows:

-
Arguments
Argument Description function-name-1
At least one intrinsic function name must be given for function-name-1.
argument-1
Must be an identifier, literal (except figurative constants), or arithmetic expression that satisfies the argument requirements of the function. A date field cannot be specified for argument-1.
reference-modifier
Can be specified only for alphanumeric functions.
Function Definitions and Evaluations
The following are the characteristics of functions.
-
The size of the return value for alphanumeric functions.
-
The sign of the return value and whether or not the type of the function is integer for numeric and integer functions.
-
The value returned by the functions
As such, the type and characteristics of functions are determined by the arguments of the function. The type
The evaluation of an intrinsic function is not affected by the context. Thus, function evaluation is not affected by the operations or operands outside of the function. However, the evaluation of functions may be affected by attributes of the argument.
In a statement in the procedure division, the definition of each function is evaluated at the same time that a reference modification or subscription for the identifier in the same location would be evaluated.
Function Types
An intrinsic function is a temporary data item and has the following types.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
Alphanumeric |
Belongs to class and category alphanumeric. Its return value has the USAGE DISPLAY attribute. The length of the return value is determined by the definition of the function. |
Numeric |
Belongs to class and category numeric. Its return value always has a sign. Numeric functions can only be used within an operational expression or as a source of a MOVE statement. Even though its return value can be changed into an integer through INTEGER or INTEGER-PART, numeric functions cannot be used wherever an integer must be specified. |
Integer |
Belongs to class and category numeric. Its return value always has a sign. Integer functions can only be used within an operational expression or as a source of MOVE statement. Integer functions can be used when an integer must be specified and can also have a sign. |
Arguments
An argument is a value that is used to determine the value of a function. Some functions need no argument, and others require a single or multiple arguments. There are also functions for which a variable number of arguments can be specified. A specific identifier, arithmetic expression, or integer can be specified, and function values are determined after evaluating each argument.
The types of arguments that are allowed follow. For more information about each argument of a function, refer to the function.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
Alphabetical |
An alphabetical type of elementary data item or a literal that contains only alphabetical characters. The length of the argument can be used to determine the value of the function. |
Alphanumeric |
Specifies alphabetic or alphanumeric type of elementary data item or alphanumeric literal. The length of the argument can be used to determine the value of the function. |
Integer |
Specifies an arithmetic expression whose result is always an integer. The value of an arithmetic expression that contains operational signs can be used to determine the value of the function. |
Numeric |
Specify an arithmetic expression. The value of an arithmetic expression that contains operational signs can be used to specify the value of the function. |
|
Some functions may have constraints for their arguments to obtain a meaningful value from the function. When an invalid argument is specified, the return value is undefined. |
The following is a synopsis of UPPER-CASE, an alphanumeric function which replaces each lowercase letter with an uppercase letter. This statement moves HELLO into DATA-NAME.
MOVE FUNCTION UPPER-CASE ('hello') TO DATA-NAME.
The following is an example of a numeric type function. This statement stores the result in NUM-ITEM by adding the values A, B and C using SUM.
COMPUTE NUM-ITEM = FUNCTION SUM (A B C)
Function Definitions
A function definition specifies the argument type, function type, and return value of each intrinsic function.
Argument and function types use the following abbreviated characters.
| Abbreviation | Description |
|---|---|
A |
Alphabetical |
I |
Integer |
N |
Numeric |
X |
Alphanumeric |
O |
Other types that can be specified in a function (pointer, function pointer, procedure pointer, etc.) |
The following table shows the argument, function type, and return value of each intrinsic function.
| Function | Argument | Function Type | Return Value |
|---|---|---|---|
N1 |
N |
The arccosine of N1. |
|
N1, I2 |
N |
The ratio of an annuity payment with interest N1 for a period of I2 months to the first investment of one. |
|
N1 |
N |
The arcsine of N1. |
|
N1 |
N |
The arctangent of N1. |
|
I1 |
X |
The character at the year l1 position in the collating sequence. |
|
N1 |
N |
The cosine of N1. |
|
None |
X |
The current time and difference from Greenwich mean time. |
|
I1 |
I |
The Julian date, represented by an integer value (YYYYMMDD). |
|
I1, I2 |
I |
The Julian date corresponding (YYYYMMDD) to I1 (Julian date with a windowed year, YYMMDD), which is defined by the sum of I2 and the year at the time of execution. |
|
I1 |
I |
The Julian date represented by an integer value (YYYYMMDD). |
|
I1, I2 |
I |
The Julian date corresponding (YYYYMMDD) to I1 (Julian date with a windowed year, YYMMDD), which is defined by the sum of I2 and the year at the time of execution. |
|
I1 |
I |
The factorial of I1. |
|
N1 |
I |
The greatest integer which does not exceed N1. |
|
I1 |
I |
The integer date corresponding to the Julian date (YYYYMMDD). |
|
I1 |
I |
The integer date corresponding to the Julian date (YYYYDDD). |
|
N1 |
I |
The integer part of N1. |
|
A1, N1, O1, or X1 |
I |
The length of the argument (varies based on the type of argument: national or alphanumeric character, or byte.) |
|
N1 |
N |
The natural logarithm of N1. |
|
N1 |
N |
The base 10 logarithm of N1. |
|
A1 or X1 |
X |
Replaces all letters in the argument with lowercase letters |
|
A1 ... |
X |
The maximum argument value. The function type is based on the arguments. |
|
I1 ... |
I |
The maximum argument value. The function type is based on the arguments. |
|
N1 ... |
N |
The maximum argument value. The function type is based on the arguments. |
|
X1 ... |
X |
The maximum argument value. The function type is based on the arguments. |
|
N1 ... |
N |
The arithmetic mean of the arguments. |
|
N1 ... |
N1 |
The median value of the arguments. |
|
N1 .... |
N |
The mean between the maximum and minimum values of the arguments. |
|
A1 ... |
X |
The minimum argument value. The function type is based on the arguments. |
|
I1 ... |
I |
The minimum argument value. The function type is based on the arguments. |
|
N1 ... |
N |
The minimum argument value. The function type is based on the arguments. |
|
X1 ... |
X |
The minimum argument value. The function type is based on the arguments. |
|
I1, I2 |
I |
The modulus of I2 and l1. |
|
X1 |
N |
The numeric value of a simple numeric string. |
|
X1 |
N |
The numeric value of a numeric string to which an optional comma and currency sign are appended. |
|
A1 or X1 |
I |
The ordinal position of the argument in a collating sequence. |
|
A1 ..., N1..., or X1 ... |
I |
The ordinal position of the maximum argument |
|
A1..., N1..., or X1 ... |
I |
The ordinal position of the minimum argument. |
|
N1, N2 ... |
N |
The current value of a series of amounts with a discount rate of N1 and future period-end amount of N2. |
|
I1, none |
N |
A random number. |
|
I1 ... |
I |
The maximum argument value minus the minimum argument value. The function type is based on the arguments. |
|
N1 ... |
N |
The maximum argument value minus the minimum argument value. The function type is based on the arguments. |
|
N1, N2 |
N |
The remainder of N1 divided by N2. |
|
A1 or X1 |
X |
The reverse order of the character string in the argument. |
|
N1 |
N |
The sine value of N1. |
|
N1 |
N |
The square root of N1. |
|
N1 ... |
N |
The standard deviation of the arguments. |
|
I1 ... |
I |
The sum of the arguments. The function type is based on the arguments. |
|
N1 ... |
N |
The sum of the arguments. The function type is based on the arguments. |
|
N1 |
N |
The tangent value of N1. |
|
X1 |
N |
Verifies the argument of NUMVAL |
|
X1 |
N |
Verifies the argument of NUMVAL-C. |
|
I1, I2 |
X |
Removes space padding on the left, right, or both sides of the character corresponding to I1. |
|
A1 or X1 |
X |
Replaces all letters in the arguments with uppercase letters. |
|
N1 ... |
N |
The variance of the arguments. |
|
None |
X |
The program compilation time. |
|
I1, I2 |
I |
The expanded year equivalent (YYYY) of l1 (windowed year, YY), which is defined by the sum of I2 and the year at the time of execution. |
|
For more information about the functions, refer to the section for the function. |
2. ACOS
ACOS returns the arccosine of the specified argument. The type of this function is numeric.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be a numeric value greater than or equal to -1 and less than or equal to +1.
-
Return Value
The approximation of the arccosine of the argument, which is greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to Pi.
3. ANNUITY
ANNUITY returns a numeric value; the ratio of the quarterly-based payment of an annuity for a specific period of time at a specific interest rate to the first value of one.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be a numeric value greater than or equal to 0.
Specifies an interest rate.
argument-2
Must be an integer.
Specifies a period of time.
-
Return Value
If argument-1 is 0, the value returned by the function is the approximation of the following.
1/ argument-2
For example, if argument-1 is 0 and argument-2 is 4, the approximation of 1/4 is returned.
If argument-1 is not 0, the value returned by the function is the approximation of the following.
argument-1 / (1 - (1 + argument-1) ** (- argument -2))
4. ASIN
ASIN returns the arcsine of the specified argument. The type of this function is numeric.

-
Argument
Argument Description argument-1
Must be a numeric value greater than or equal to -1 and less than or equal to +1.
-
Return Value
The approximation of the arcsine of argument-1, which is greater than or equal to -Pi/2 and less than or equal to +Pi/2.
5. ATAN
ATAN returns the arctangent of the specified argument. The type of this function is numeric.

-
Argument
Argument Description argument-1
Must be numeric.
-
Return Value
The approximation of the arctangent of argument-1, which is greater than or equal to -Pi/2 and less than or equal to +Pi/2.
6. CHAR
CHAR returns an alphanumeric character that corresponds to the position in the collating sequence specified by the argument.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be an integer.
Must be a numeric value in the collating sequence between 0 and the number of items in the sequence, up to a maximum of 256.
-
Return Value
When one or more characters are placed in the same position within collating sequence, the return value of the character is the first literal of the character within the ALPHABET clause.
|
If the current program collating sequence is not specified by an ALPHABET clause, the single-byte EBCDIC sequence will be used. |
7. COS
COS returns the cosine of the specified argument. The type of this function is numeric.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be numeric.
-
Return Value
The approximation of the COS of argument, greater than or equal to - 1 and less than or equal to + 1.
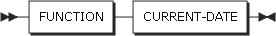
8. CURRENT-DATE
CURRENT-DATE returns a 21-digit of alphanumeric value that represents the date, time, and time difference from Greenwich mean time that are provided by the system on which the function is executed. The type of this function is alphanumeric.
-
Return Value
The returned 21-digit character represents the following, from left to right.
Character Position Description 1-4
A four-digit number that represents the year in the Gregorian calendar.
5-6
A two-digit number that represents the month, within the range of 01 - 12.
7-8
A two-digit number that represents the date, within the range of 01 - 31.
9-10
A two-digit number that represents the hours past midnight, within the range of 00 - 23.
11-12
A two-digit number that represents the minutes, within the range of 00 - 59.
13-14
A two-digit number that represents the seconds, within the range of 00 - 59.
15-16
A two-digit number that represents the hundredths of a second, within the range of 00 - 99.
If the system on which the function is executed does not support the fractional part of a second, it returns 00.
17
The following characters are used.
-
"-": In the case that the returned time is behind Greenwich mean time.
-
"+": In the case that the returned time is ahead of or equal to Greenwich mean time.
-
"0": In the case that the system on which the function is executed does not calculate local time differences.
18-19
-
If the character corresponding to the previous position (17) is "-", a two-digit numeric value is returned, within the range of 00 - 12, that represents the number of hours that the reported time is before Greenwich mean time.
-
If the character corresponding to the previous position (17) is "+", a two-digit numeric value is returned within the range of 00 - 13, that represents the number of hours that the reported time is ahead of Greenwich mean time.
-
If the character corresponding to the previous position (17) is "0", 00 is returned.
20-21
A two-digit number corresponding to the minute, within the range of 00 - 59.
Depending on whether the character corresponding to the previous position (17) is "+" or "-", this indicates the number of additional minutes. If the character in the previous position (17) is "0", 00 is returned.
-
9. DATE-OF-INTEGER
DATE-OF-INTEGER converts a date, represented as integer in the Gregorian calendar, into the Julian form (YYYYMMDD).

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
A positive integer that indicates the number of days since January 1, 1601 in the Gregorian calendar.
The valid range is from 1 to 3,067,671. This indicates the range of January 1, 1601 - Dec 31, 9999.
Returns a date corresponding to the ISO standard format for the integer specified in argument -1.
-
Return Value
A 8-character length integer in YYYYMMDD format. YYYY, MM, and DD indicate the year, month, and date respectively.
10. DATE-TO-YYYYMMDD
DATE-TO-YYYYMMDD converts argument-1 from a date represented by a two-digit year (YYMMDD) to a date represented by a four-digit year (YYYYMMDD). argument-2 is used as an argument to specify the first two digits, which is added to the year at the time of execution. The type of this function is integer.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be 0 or a positive integer less than 991,232.
The validity of the date is not checked during execution.
argument-2
Must be an integer. If this argument is omitted, it defaults to 50.
The sum of the year at the time of execution and the value of argument-2 must be less than 10,000 and greater than 1,699.
-
Return Value
The following table shows examples of the return values of the function.
Current year argument-1 argument-2 Return value 2002
851003
120
20851003
2002
851003
-20
18851003
2002
851003
10
19851003
1994
981002
-10
19891002
11. DAY-OF-INTEGER
DAY-OF-INTEGER converts a date in the Gregorian calendar into the Julian date form (YYYYDDD). The type of this function is integer.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
A positive integer that indicates the number of days since January 1, 1601 in the Gregorian calendar.
The valid range is from 1 to 3,067,671. This indicates the range of January 1, 1601 - Dec 31, 9999.
-
Return Value
A date in the Julian form corresponding to the 7-digit integer specified in argument-1. The date form is YYYYDDD, where YYYY indicates the year and DDD indicates the date in the Gregorian calendar.
12. DAY-TO-YYYYDDD
DAY-TO-YYYYDDD returns the two-digit year specified in argument-1 (YYDDD) as a four-digit year (YYYYDDD). argument-2 is used to specify the first two digits, which are added to the year at the time of execution. The type of this function is integer.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be 0 or a positive integer less than 99,367.
argument-2
Must be an integer. If this argument is omitted, it defaults to 50.
The sum of the year at the time of execution and the value of argument-2 must be less than 10,000 and greater than 1,699.
-
Return Value
The following table shows examples of the return values of the function.
Current year argument-1 argument-2 Return Value 2002
10004
-20
1910004
2002
10004
-120
1810004
2002
10004
20
2010004
2013
95005
-10
1995005
13. FACTORIAL
FACTORIAL returns the factorial value of the specified argument. The type of this function is integer.

-
Argument
Argument Description argument-1
If compiled with the ARITH(COMPAT) option, argument-1 must be an integer greater or equal to 0, and less than or equal to 28.
If compiled with the ARITH(EXTEND) option, argument-1 must be an integer greater than or equal to 0, and less than or equal to 29.
-
Return Value
If argument-1 is 0, 1 is returned. If the argument is set to a value other than 0, the factorial value of argument-1 is returned.
14. INTEGER
INTEGER returns the greatest integer that is less than or equal to the specified argument.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
A numeric value.
-
Return Value
The greatest integer that is less than the value specified in argument-1.
For example, FUNCTION INTEGER(2.5) returns 2, and FUNCTION INTEGER (-2.5) returns -3.
15. INTEGER-OF-DATE
INTEGER-OF-DATE converts a date in the standard form (YYYYMMDD) of the Gregorian calendar into the integer date form. The type of this function is integer.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be an integer in the form of YYYYMMDD.
The value can be obtained from (YYYY * 10,000) + (MM * 100) + DD.
-
YYYY: represents the year of the Gregorian calendar. This value must be an integer greater than 1,600 and less than 9,999.
-
MM: represents the month. This value must be a positive integer less than 13.
-
DD: represents the date. This value must be a positive integer less than 32. However, the specified date must be valid for the month.
-
-
Return Value
A 7-digit integer within the range of 1 - 3,067,671 that indicates the number of days since January 1, 1601 in the Gregorian calendar.
16. INTEGER-OF-DAY
INTEGER-OF-DAY returns a date in Julian form (YYYYDDD) in the Gregorian calendar as an integer date form. The function type is integer.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be an integer in the form of YYYYDDD.
The value can be obtained from (YYYY * 10,000) + DD.
-
YYYY: represents the year of Gregorian calendar. This value must be an integer greater than 1,600 and not greater than 9,999.
-
DDD: must be an integer less than 367 which is valid for the year specified.
-
-
Return Value
The return value is 7-digit integer. It is a positive integer that indicates the number of days since January 1, 1601 in the Gregorian calendar.
17. INTEGER-PART
INTEGER-PART returns the integer part of the argument specified. The type of this function is integer.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be a numeric value.
-
Return Value
If argument-1 is 0, it returns 0. Otherwise, the following occurs.
-
If the value specified in argument-1 is a positive value, the function returns the greatest integer value less than argument-1.
-
If the value specified in argument-1 is a negative value, the function returns the smallest integer value greater than argument-1.
-
18. LENGTH
LENGTH returns an integer that corresponds to the length of the argument. The type of this function is integer.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
The values that can be specified for the argument are as follows:
-
An alphanumeric literal.
-
A data item other than a two-byte character.
-
A data item defined as POINTER, PROCEDURE-POINTER or FUNCTION-POINTER.
-
An ADDRESS OF special register.
-
A LENGTH OF special register.
-
-
Return Value
A 9-digit character is returned as defined by the following rules.
-
If argument-1 is an alphanumeric literal, or the elementary data item of an alphabetic or alphanumeric value, the length of the alphanumeric character string specified in the argument is returned.
-
If argument-1 is a null-terminated literal, the length of the characters without the NULL character is returned.
-
The length of an alphanumeric data item or a literal where one-byte and two-byte characters are mixed is treated as if each byte were a one-byte character.
-
If argument-1 is an alphanumeric group item, the length of the alphanumeric value specified in argument-1 is returned regardless of the contents of the group.
-
If a data item in argument -1 describes a DEPENDING phrase in an OCCURS clause, the length of argument-1 is determined according to the contents of the data item specified in DEPENDING. If FILLER positions exist, the returned value includes the implicit positions.
-
Otherwise, this returns the number of bytes of the storage occupied by argument-1.
-
19. LOG
LOG returns a value which approximates the base e logarithm of the specified argument. The type of this function is numeric.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be a number greater than 0.
-
Return Value
The approximation of the base e logarithm of argument-1.
20. LOG10
LOG10 returns a value which approximates the base 10 logarithm of the specified argument. The type of this function is numeric.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be a number greater than 0.
-
Return Value
The approximation of the base 10 logarithm of argument-1.
21. LOWER-CASE
LOWER-CASE replaces all uppercase letters in the argument with lowercase letters. The type of the function is based on the arguments.
| Argument Type | Function Type |
|---|---|
Alphabetical |
Alphanumeric |
Alphanumeric |
Alphanumeric |

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must contain one or more alphabetical or alphanumeric characters.
-
Return Value
The function returns the lowercase letter corresponding to each uppercase letter specified as argument.
The same character string as argument-1 is returned. If argument-1 is alphabetical or alphanumeric, the uppercase letters from 'A' to 'Z' are replaced by corresponding lowercase letters within the range of 'a' to 'z'. The length of the returned string is the same as that given in argument-1.
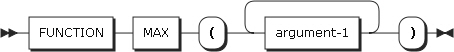
22. MAX
MAX returns the maximum value in the arguments. The type of the function is based on the arguments.
| Argument Type | Function Type |
|---|---|
Alphabetical |
Alphanumeric |
Alphanumeric |
Alphanumeric |
All arguments are integers |
Integer |
Numeric (some arguments are integers) |
Numeric |
-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be alphabetical, alphanumeric, or numeric.
All arguments must be the same type, except that the combination of alphanumeric and alphabetical is allowed.
-
Return Value
The argument specified in argument-1 that has the maximum value.
The comparison operation used to determine the maximum value is performed based on the rules for simple conditions. When two or more arguments have the same maximum value, the function returns the leftmost argument.
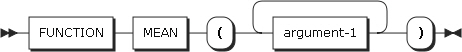
23. MEAN
MEAN returns the approximation of the arithmetic average. The type of this function is numeric.
-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be numeric.
-
Return Value
The arithmetic average of arguments. The value is the approximation of the sum of the arguments divided by the number of arguments.
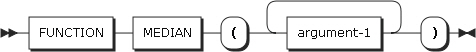
24. MEDIAN
MEDIAN returns the argument that has the middle value among the sorted list of arguments. The type of this function is numeric.
-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be numeric.
-
Return Value
The argument that has the middle value among those specified in argument-1.
25. MIDRANGE
MIDRANGE returns the approximation of the arithmetic average between the minimum and maximum values.
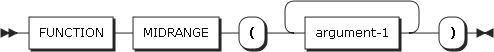
-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be numeric.
-
Return Value
The approximation of the arithmetic average between the minimum and maximum values. The maximum and minimum values are determined according to the rules for simple comparison.
26. MIN
MIN returns the minimum value in the arguments. The type of this function is based on the arguments.
| Argument Type | Function Type |
|---|---|
Alphabetical |
Alphanumeric |
Alphanumeric |
Alphanumeric |
All arguments are integer |
Integer |
Number (some parts are integer) |
Numeric |
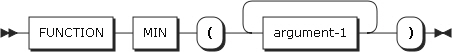
-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be alphabetical, alphanumeric, or numeric.
-
Return Value
The argument specified in argument-1 that has the minimum value.
The comparison operation used to determine the minimum value is performed according to the rules for simple conditions. When two or more argument-1s have the same minimum value, the function returns the leftmost argument.
27. MOD
MOD returns the integer value of argument-1 modulo argument -2. The type of this function is integer. The return value is an integer which has as many digits as the shorter of argument-1 and argument-2.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be an integer.
argument-2
Must be an integer, and cannot be 0.
-
Return Value
Returns the value argument-1 modulo argument-2 and is defined as follows:
argument-1 - (argument-2 * FUNCTION INTEGER (argument-1/argument-2))
The following are examples of function return values.
argument-1 argument-2 Return Value 11
5
1
-11
5
4
11
-5
-4
-11
-5
-1
28. NUMVAL
NUMVAL returns the numeric value represented by the alphanumeric character string specified by the argument. The type of this function is numeric. Leading or trailing spaces will be ignored when calculating the numeric value.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be an alphanumeric data item that contains an alphanumeric literal, or a character string which has one of the following formats.
-
space: A string of one or more spaces.
-
Number: One or more numbers.
When DECIMAL-POINT IS COMMA is specified in SPECIAL-NAMES paragraph, a comma (,) must be used in argument-1 instead of a decimal point.
The following is the format of argument-1.
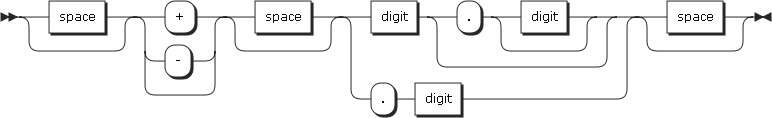
-
-
Return Value
A floating-point approximation of the value represented by argument-1. The precision of the approximation value changes based on the specified ARITH compiler option.
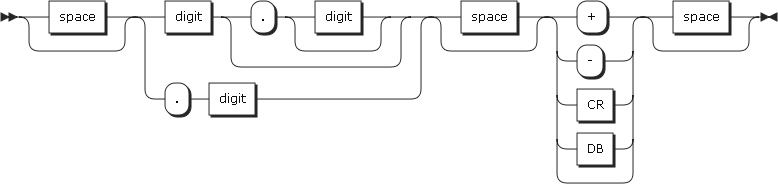
29. NUMVAL-C
NUMVAL-C returns the numeric value represented by the alphanumeric character string specified by the argument. The type of this function is numeric. Leading or trailing spaces will be ignored when calculating the numeric value.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be an alphanumeric data item that contains an alphanumeric literal, or a character string which has one of the following formats.
-
space: A string of one or more spaces.
-
cs: A currency sign (the character specified by cs can occur only once in argument-1.)
-
number: One or more numbers
argument-2
Specifies a currency string.
The following is the format of argument-1.
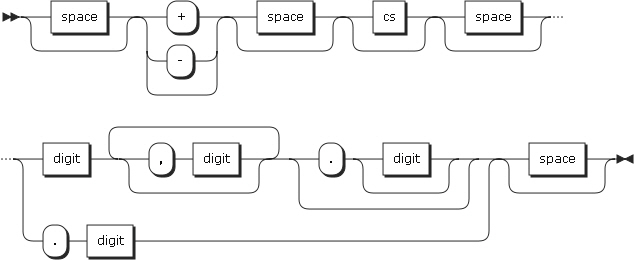
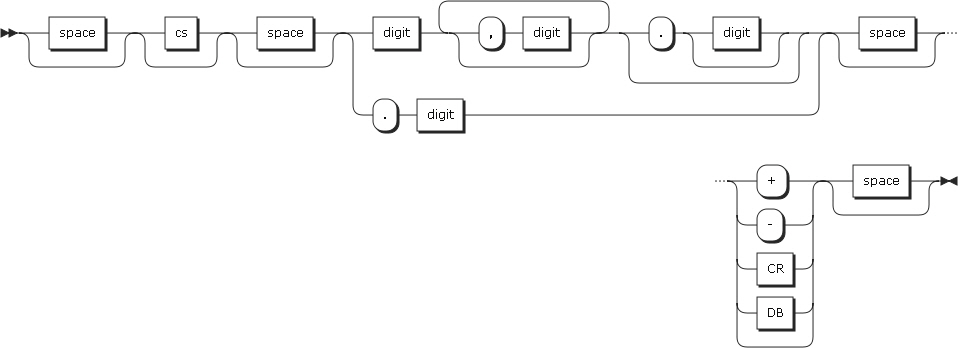
-
-
Return Value
A floating-point approximation of the value represented by argument-1.
30. ORD
ORD returns the integer value that is the ordinal position in the collating sequence. The smallest value is 1.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be an alphanumeric or alphabetic character.
-
Return Value
The ordinal position of argument-1 within the collating sequence as a three-digit integer. A value in the range from 1 to 256 is returned according to the sequence.
31. ORD-MAX
ORD-MAX returns the ordinal position of the collating sequence which contains the maximum value among the given arguments. The type of this function is integer.
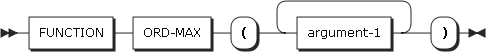
-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be alphanumeric, alphabetical, or numeric.
When more than one argument is specified, the arguments must be the same type, except that the combination of alphanumeric and alphabetical characters is allowed.
-
Return Value
The argument specified in argument-1 that has the maximum value.
The comparison operation used to determine the maximum value is performed according to the rules for simple conditions. When two or more argument-1s have the same maximum value, the function returns the leftmost argument.
32. ORD-MIN
ORD-MIN returns the ordinal position of the collating sequence which contains the minimum value among the given arguments. The type of this function is integer.
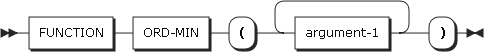
-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be alphanumeric, alphabetical, or numeric.
When more than one argument is specified, the arguments must be the same type, except that the combination of alphanumeric and alphabetical characters is allowed.
-
Return Value
The argument specified in argument-1 that has the minimum value.
The comparison operation used to determine the minimum value is performed according to the rules for simple conditions. When two or more argument-1s have the same minimum value, the function returns the leftmost argument.
33. PRESENT-VALUE
PRESENT-VALUE returns the approximation of the present value of the set of future period-end amounts specified in argument-2 by applying the discount rate specified in argument-1. The type of this function is numeric.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be a numeric value greater than -1.
argument-2
Must be numeric.
-
Return Value
The approximation of the value obtained from the following expression. (The exponent n is the number of argument-2.)
argument-2 / (1+argument-1) ** n
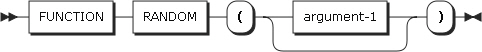
34. RANDOM
RANDOM returns a number randomly extracted from a rectangular distribution. The type of this function is numeric.
-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be 0 or a positive integer. Only values between 0 and 2,147,483,645 can generate an accurate random number.
If any subsequent reference specifies argument-1, a new random value will be generated. For a specified seed value, the random number is always the same.
If argument-1 is not given at the first reference of the function in the run unit, the initial value will be 0.
-
Return Value
A numeric value between 0 and 1.
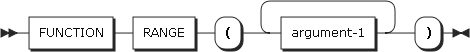
35. RANGE
RANGE returns the maximum argument value minus the minimum argument value. The type of the function is based on the arguments.
| Argument Type | Function Type |
|---|---|
All arguments are integer |
Integer |
Numeric (Some arguments are integer) |
Numeric |
-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be numeric.
-
Return Value
The value of argument-1 that has the maximum value minus the value of argument-1 that has the minimum value. The maximum and the minimum value are determined based on the rules of simple conditions.
36. REM
REM returns the remainder of the first argument divided by the second argument. The type of this function is numeric.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be numeric.
argument-2
Must be a numeric value other than 0.
-
Return Value
The remainder of argument-1 divided by argument-2. The return value is defined by the following expression.
argument-1 - (argument-2 * FUNCTION INTEGER-PART(argument-1/argument-2))
37. REVERSE
REVERSE returns a character string whose characters are the same as those of the specified argument in reverse order. The length of the argument and that of the character string are the same. The type of this function is based on the argument.
| Argument Type | Function Type |
|---|---|
Alphabetical |
Alphanumeric |
Alphanumeric |
Alphanumeric |

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be an alphabetical, alphanumeric, or national value with one or more characters.
-
Return Value
A character string whose length is the same as that of argument -1. It is a character string with the characters of argument-1 in reversed order. For example, if argument-1 is "ABC", the returned value will be "CBA".
38. SIN
SIN returns the sine of the specified argument. The type of this function is numeric.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be numeric.
-
Return Value
The approximation of the sine of argument -1. The value is greater than or equal to -1 and less than or equal to +1.
39. SQRT
SQRT returns the approximation of the square root of the specified argument. The type of this function is numeric.

-
Argument
Argument Description argument-1
Must be 0 or a positive integer.
-
Return Value
The absolute value of the approximation of the square root of argument-1.
40. STANDARD-DEVIATION
STANDARD-DEVIATION returns the approximation of the standard deviation of the argument specified. The type of this function is numeric.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be numeric.
-
Return Value
The approximation of the standard deviation of argument-1.
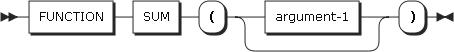
41. SUM
SUM returns the sum of the given arguments. The type of this function is determined based on the type of the arguments.
| Argument Type | Function Type |
|---|---|
All arguments are integer |
Integer |
A numeric value (may be integer) |
Numeric |
-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be numeric.
-
Return Value
The sum of all arguments.
42. TAN
TAN returns the tangent of the specified argument. The type of this function is numeric.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be numeric.
-
Return Value
The approximation of the tangent of argument-1.
43. TEST-NUMVAL
TEST-NUMVAL verifies that the contents of argument-1 conform to the specification for argument-1 of the NUMVAL function.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be an alphanumeric literal or a data item of alphanumeric.
-
Return Value
If the content of argument-1 conforms to the argument rules for the NUMVAL function, the returned value is 0
If one or more characters are in error, the returned value is the position of the first character in error.
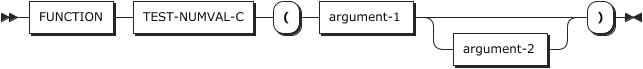
44. TEST-NUMVAL-C
TEST-NUMVAL-C verifies that the contents of argument-1 conform to the specification for argument-1 of the NUMVAL-C function.
-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be an alphanumeric literal, or a data item of alphanumeric that contains a character string in either of the following formats.
argument-2
Specifies the currency string value.
The following are the formats of argument-1.


-
Return Value
If the content of argument-1 conforms to the argument rules for the NUMVAL-C function, the returned value is 0. If one or more characters are in error, the returned value is the position of the first character in error.
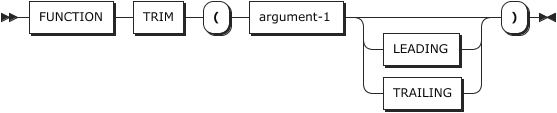
45. TRIM
TRIM removes leading spaces, trailing spaces, or both of the characters in the argument-1.
-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be alphabetic, alphanumeric, or national type.
argument-2
Must be LEADING, TRAILING, or omitted.
-
Return Value
The following are examples of returned values.
argument-1
argument-2
Return Value
" Hello, world! "
LEADING
"Hello, world! "
" Hello, world! "
TRAILING
" Hello, world!"
" Hello, world! "
"Hello, world!"
" "
""
""
""
46. UPPER-CASE
UPPER-CASE converts the lowercase letters specified in the argument into the corresponding uppercase letters. The type of this function is based on the argument.
| Argument Type | Function Type |
|---|---|
Alphabetical |
Alphanumeric |
Alphanumeric |
Alphanumeric |

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
An alphanumeric or alphabetical value that has one or more characters.
-
Return Value
Lowercase letters are replaced by their uppercase letters to return a character string that has the same length as argument-1.
If argument-1 is an alphanumeric or alphabetical value, the uppercase letters from 'A' to 'Z' are replaced by lowercase letters from 'a' to 'z'.
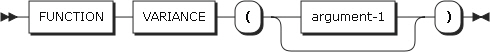
47. VARIANCE
VARIANCE returns the approximation of the variance of the specified argument. The type of this function is numeric.
-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be numeric.
-
Return Value
The approximation of the variance of argument-1.
48. WHEN-COMPILED
WHEN-COMPILED returns the program compile time provided by the system where the program was compiled. The type of this function is alphanumeric.
-
Return Value
The returned 21-digit character represents the following, from left to right.
Character Position Description 1-4
A four-digit number that represents the year in the Gregorian calendar.
5-6
A two-digit number that represents the month, within the range of 01 - 12.
7-8
A two-digit number that represents the date, within the range of 01 - 31.
9-10
A two-digit number that represents the hours past midnight, within the range of 00 - 23.
11-12
A two-digit number that represents the minutes, within the range of 00 - 59.
13-14
A two-digit number that represents the seconds, within the range of 00 - 59.
15-16
A two-digit number that represents the hundredths of a second, within the range of 00 - 99.
If the system on which the function is executed does not support the fractional part of a second, it returns 00.
17
TThe following characters are used.
-
"-": In the case that the returned time is behind Greenwich mean time.
-
"+": In the case that the returned time is ahead of or equal to Greenwich mean time.
-
"0": In the case that the system on which the function is executed does not calculate local time differences.
18-19
-
If the character corresponding to the previous position (17) is "-", a two-digit numeric value is returned, within the range of 00 - 12, that represents the number of hours that the reported time is before Greenwich mean time.
-
If the character corresponding to the previous position (17) is "+", a two-digit numeric value is returned within the range of 00 - 13, that represents the number of hours that the reported time is ahead of Greenwich mean time.
-
If the character corresponding to the previous position (17) is "0", 00 is returned.
20-21
A two-digit number corresponding to the minute, within the range of 00 - 59.
Depending on whether the character corresponding to the previous position (17) is "+" or "-", this indicates the number of additional minutes. If the character in the previous position (17) is "0", 00 is returned.
This function returns the time of compilation of the program that contains the function. For subprograms which belong to other programs, this returns the time of compilation of the subprogram.
-
49. YEAR-TO-YYYY
YEAR-TO-YYYY converts a two-digit year of argument-1 to a four-digit year. The function expands the year to the sum of the value specified in argument-2 and the year at the time of execution. The type of this function is integer.

-
Arguments
Argument Description argument-1
Must be a positive integer less than 100.
argument-2
Must be an integer. If omitted, the default value is 50.
-
Return Value
The following table shows examples of return values of the function.
Current Year argument-1 Value argument-2 Value Return Value 1995
4
23
2004
1995
4
-15
1904
2008
98
23
1998
2008
98
-15
1898