1. WRITE
The WRITE statement writes a record to an output file.
A sequential file must be open in OUTPUT or EXTEND mode.
An indexed file or relative file must be open in OUTPUT, I-O, or EXTEND mode.
-
Format 1
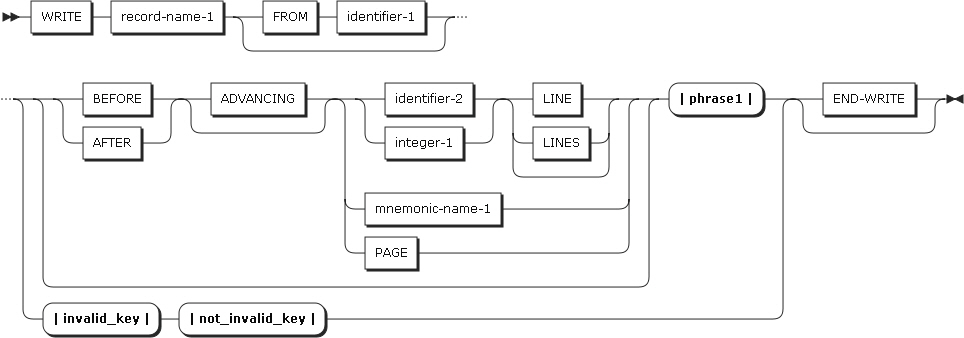 WRITE Statement Format 1
WRITE Statement Format 1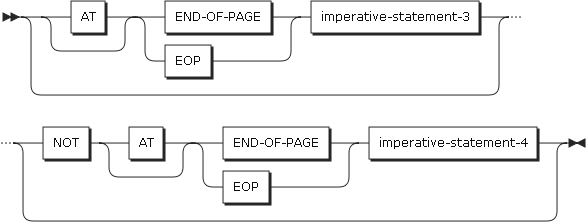 WRITE Statement Format 1 - phrase1
WRITE Statement Format 1 - phrase1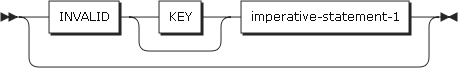 WRITE Statement Format 1 - invalid_key
WRITE Statement Format 1 - invalid_key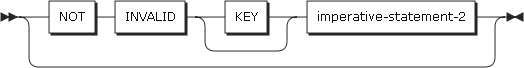 WRITE Statement Format 1 - not_invalid_key
WRITE Statement Format 1 - not_invalid_key -
Format 2
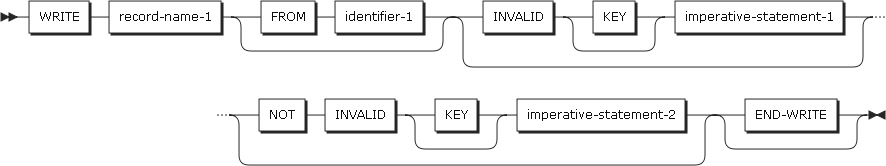 WRITE Statement Format 2
WRITE Statement Format 2 -
Format 3
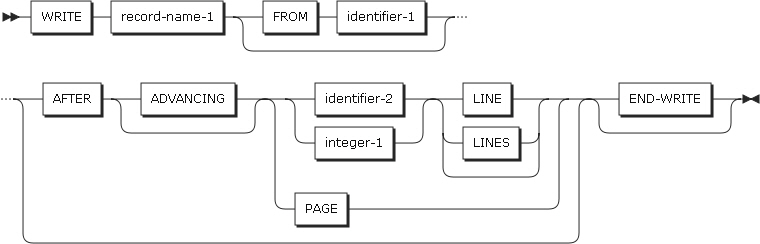 WRITE Statement Format 3
WRITE Statement Format 3
The following items are specified in the statement.
-
record-name-1
-
Must be described in the FD entry in the data vision.
-
record-name-1 can be qualified, but must not be related to a sort or merge file.
-
-
FROM phrase
-
The execution result of the WRITE statement with the FROM phrase is the same as executing the following statements.
MOVE identifier-1 TO record-name-1. WRITE record-name-1.
-
-
identifier-1
-
identifier-1 references any of the following.
-
An entry in the working-storage section, the local-storage section, or the linkage section.
-
A record description for another opened file.
-
An alphanumeric function.
-
-
identifier-1 must be a valid sending item whose record-name-1 can be a receiving item according to the rules for a MOVE statement.
-
identifier-1 and record-name-1 must not reference the same storage area. After executing the WRITE statement, the information of identifier-1 is still valid.
-
-
identifier-2
Must be an integer data item.
-
ADVACING phrases
The ADVANCING phrase adjusts the position of the output record on the page.
-
ADVANCING phrase rules
If the ADVANCING phrase is specified, the following rules must apply.
-
If BEFORE ADVANCING is specified, the line is printed first, and then the page is advanced.
-
If AFTER ADVANCING is specified, the page is advanced, and then the line is printed.
-
If identifier-2 is specified, the page is advanced as many lines as are specified in identifier-2. identifier-2 must be an integer data item.
-
If integer-1 is specified, the page is advanced as many lines as are specified in integer-1.
-
The value in integer-1 or identifier-2 can be zero.
-
If PAGE is specified, the record is printed before or after the page is advanced to the next logical page, based on the specification of the BEFORE or AFTER phrase.
-
If mnemonic-name is specified, a skip to channels (from channel 1 to 12) or space suppression occurs. mnemonic-name must be described in the SPECIAL-NAMES paragraph.
If the ADVANCING phrase is specified in the WRITE statement, or the LINAGE clause exists in the file, a carriage control character is created to be added to the record. If the ADVANCING phrase is omitted, actions are performed as if AFTER ADVANCING 1 LINE has been specified.
-
-
LINAGE-COUNTER rules
If the LINAGE clause is described on the file, the LINAGE-COUNTER special register is modified according to the following rules whenever the WRITE statement is executed.
-
If ADVANCING PAGE is specified, LINAGE-COUNTER is 1.
-
If ADVANCING identifier-2 or integer-1 is specified, LINAGE-COUNTER increases by the value in identifier-2 or integer-1.
-
If the ADVANCING phrase is omitted, LINAGE-COUNTER increases by 1.
-
If the device is positioned on a new page, LINAGE-COUNTER is 1.
-
-
-
END-OF-PAGE phrases
-
If the END-OF-PAGE phrase is specified, and the logical end of the page is reached by the WRITE statement, the statement specified in imperative-statement-3 of the phrase is executed. If the END-OF-PAGE phrase is specified, the FD entry must contain a LINAGE clause.
-
An END-OF-PAGE condition occurs if a record line or space is printed in the footing area of the page body. In other words, an END-OF-PAGE condition occurs if the value of the LINAGE-COUNTER special register is greater than or equal to the value specified in the WITH FOOTING phrase of the LINAGE clause.
-
An automatic page overflow condition occurs if the WRITE statement cannot be completed within the current page body, and it has to continue to the next page.
-
If an END-OF-PAGE condition or an automatic page overflow condition occurs, and the END-OF-PAGE phrase is described, and the statement specified in imperative-statement-3 is executed.
-
-
INVALID KEY phrases
-
An invalid key condition occurs in the following cases.
-
For indexed files, a sequential access is specified and the file is opened in OUTPUT mode, and the value of the prime record key is not larger than that of the previous record key.
-
For indexed files, the file is opened in I-O or OUTPUT mode, and the value of the prime record key is equal to that of the existing record.
-
For relative files, random or dynamic access is specified, and RELATIVE KEY is identical to that of the existing record.
-
-
-
END-WRITE phrases
-
Explicitly indicates the end of the WRITE statement.
-
In each I-O mode, the WRITE statement functions as follows:
-
Sequential files
-
The greatest record length of sequential files is determined when the file is created, and is never changed.
-
Execution of the WRITE statement has no effect on the file position indicator.
-
If the FILE STATUS clause is specified in the file control entry, the file status key is updated after the WRITE statement is executed.
-
-
Indexed files
-
Before executing the WRITE statement for indexed files, the prime record key (the data item which is defined as RECORD KEY in the file control entry) must be set to any value. The value must be unique in the file.
-
If ACCESS IS SEQUENTIAL is specified in the file control entry, records must be written in the order of RECORD KEY values.
-
-
Relative files
-
If ACCESS IS SEQUENTIAL is specified in the file control entry, the first record is written as relative record number 1, the second record written as relative record number 2, the third record written as relative record number 3, and so on. If RELATIVE KEY is described in the file control entry, the relative number of the written record is stored in RELATIVE KEY.
-
If ACCESS IS RANDOM or ACCESS IS DYNAMIC is specified in the file control entry, the RELATIVE KEY must have the specified value before the WRITE statement is executed. After the WRITE statement is executed, the record is stored at the relative record number in the file.
-