OSI
This chapter describes the key features of the [OSI] menu, which manages OpenFrame OSI, in OpenFrame Manager.
1. Overview
[OSI] allows users to view OpenFrame/OSI status, manage system resources and their status, and view OSI messages and terminal information.
To start OSI, click [OSI] at the top menu area and select the desired menu form the navigation pane.
The following describes the menus in the navigation pane.
| Menu | Description |
|---|---|
Provides the status of each region in OSI.
|
|
Allows users to view and modify system resources.
|
|
Allows users to view and modify the status of active resources.
|
|
Displays OSI message queues. |
|
Displays active dependent regions of the OSI region. |
2. Region
For the submenus under Region, refer to the description of each section.
2.1. Region Status
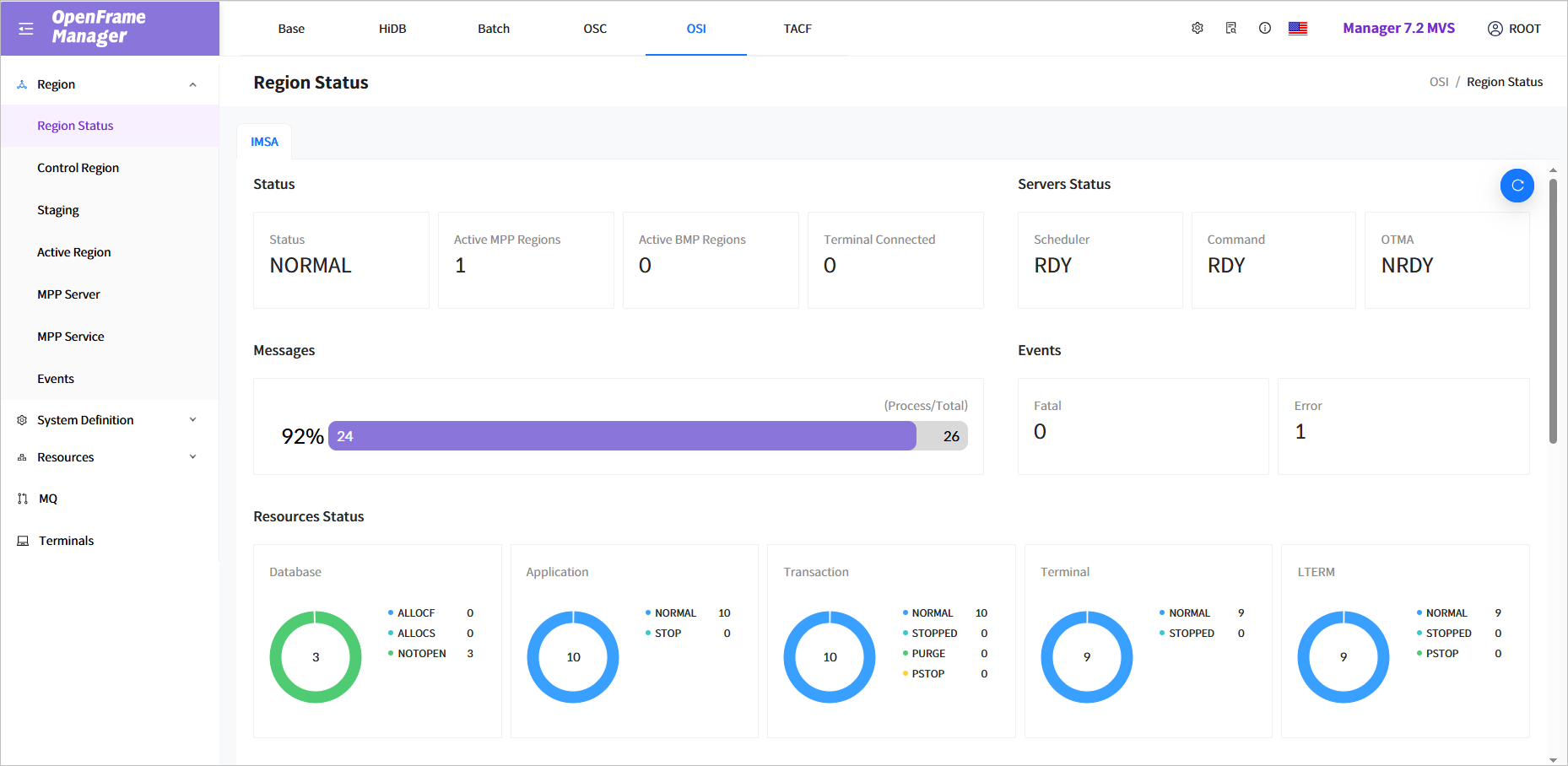
Click [Region] > [Region Status] from the navigation pane to display general information about a region.
The following describes each item.
-
Status
Displays the basic information of a region based on the IMS ID.
Item Description Status
Current status of the region.
-
INIT: Initial state.
-
NORMAL: Normal state where transactions can be processed.
-
NEEDNRE: The control region server is running but has not received the ‘/NRE’ command.
-
NEEDNREQ: The control region was terminated with the ‘/CHECKPOINT DUMPQ’ or ‘/CHECKPOINT PURGE’ command and has not received the ‘/NRE’ command.
-
NEEDERE: The control region server is running but has not received the ‘/ERE’ command.
-
DOINGRST: The control region is in the process of a RESTART operation.
-
NEEDSTDC: The control region has restarted but has not received the DC command.
-
CHEFREEZ: The control region was terminated with the ‘/CHECKPOINT FREEZE’ command.
-
CHEDUMPQ: The control region was terminated with the ‘/CHECKPOINT DUMPQ’ command.
-
CHEPURGE: The control region was terminated with the‘/CHECKPOINT PURGE’ command.
-
DOINGFRE: The control region is in the process of performing a ‘/CHECKPOINT FREEZE’ operation.
-
DOINGDMP: The control region is in the process of a ‘/CHECKPOINT DUMPQ’ command.
-
DOINGPUR: The control region is in the process of a ‘/CHECKPOINT PURGE’ operation.
-
SHUTDOWN: The control region has shut down normally.
-
UNKNOWN: The status of the control region is unknown.
Active MPP Regions
Number of active MPP regions.
Active BMP Regions
Number of active BMP regions.
Terminal Connected
Number of connected terminals.
-
-
Servers Status
Displays the status of major system servers.
Item Description Scheduler
Displays the current status of the schedule server in the OSI control region.
-
RDY: The server is ready to run.
-
NRDY: The server is not started.
-
RUNNING: The server is processing.
Command
Displays the current status of the command server in the OSI control region.
-
RDY: The server is ready to run.
-
NRDY: The server is not started.
-
RUNNING: The server is processing.
OTMA
Displays the current status of the OTMA server in the OSI.
-
RDY: The server is ready to run.
-
NRDY: The server is not started.
-
RUNNING: The server is processing.
-
-
Messages
Displays statistics for the OSI message queue, including throughput rate, the number of processed message, and total messages.
-
Events
The number of Fatal and Error events that occurred during OSI operation.
-
Resources Status
Displays the status of runtime resources. Currently supported resources include databases, applications, transactions, terminals, and LTERMs.
-
Database
Item Description STARTED
Number of databases currently running.
ALLOCF
Number of databases that failed to allocate.
ALLOCS
Number of databases that have successfully allocated but not yet used.
DBR
Number of databases in Database Recovery (DBR) state.
STOPPED
Number of stopped databases.
-
Application
Item Description NORMAL
Number of available applications.
STOP
Number of stopped applications.
-
Transaction
Item Description NORMAL
Number of available transactions.
STOP
Number of stopped transactions.
-
Terminal
Item Description NORMAL
Number of available terminals.
STOP
Number of stopped terminals.
-
LTERM
Item Description NORMAL
Number of LTERMs in normal state.
STOPPED
Number of stopped LTERMs.
PURGE
Number of LTERMs in PURGE state.
PSTOP
Number of LTERMs in PSTOP state.
-
-
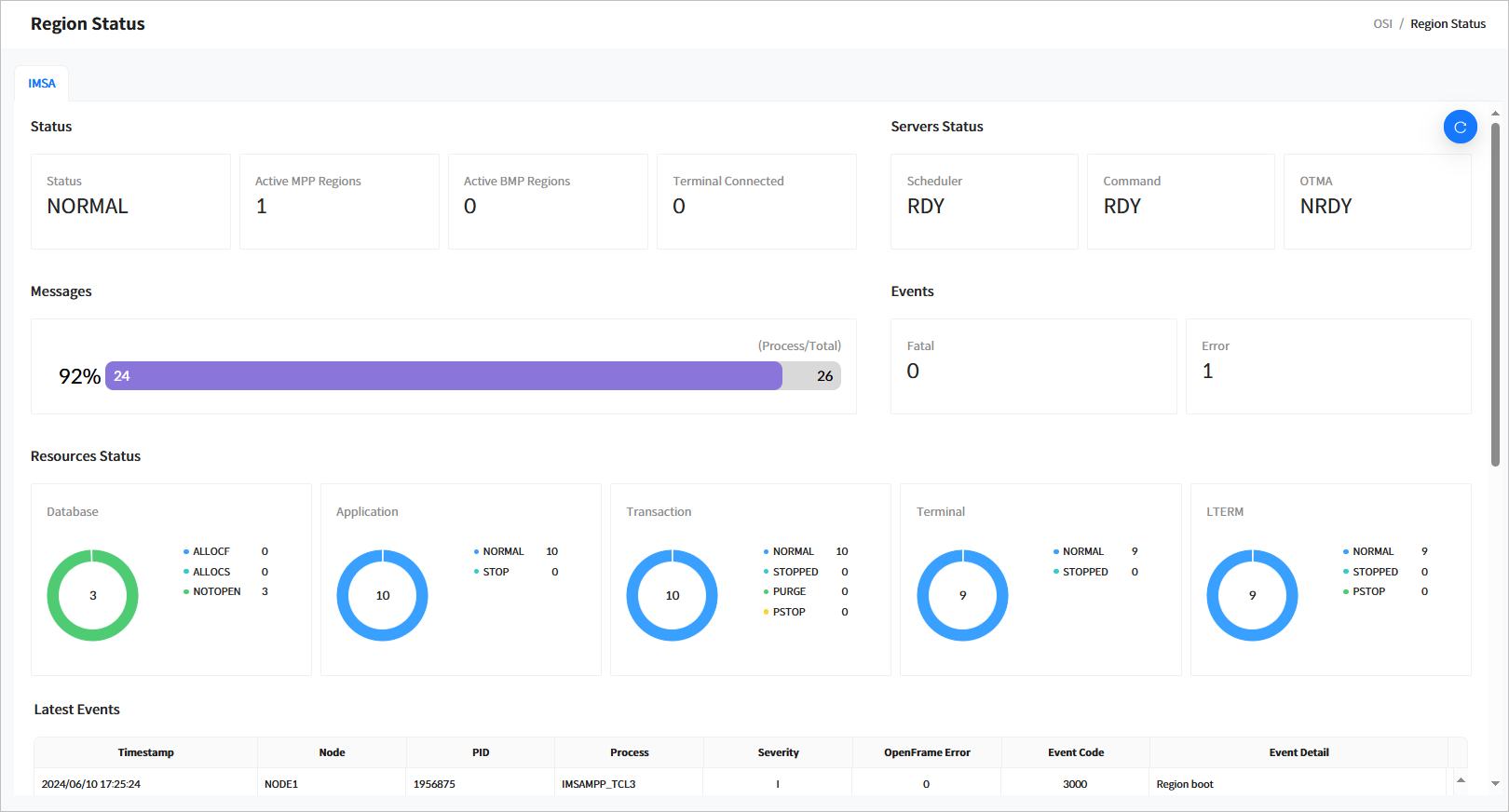
Last Events
Displays a list of the most recent 20 events in OSI. The following describes each item.
Item Description Timestamp
Timestamp when the event occurred.
Node
Node name.
PID
ID of the process where the event occurred.
Process
Name of the process where the event occurred.
Severity
Severity level of the event.
OpenFrame Error
OpenFrame error code if the event is an error. This will be indicated only if the error code can be verified.
Event Code
OSI event code. For more details about event codes, refer to OpenFrame OSI Administrator’s Guide.
Event Detail
Detailed description of the event.
2.2. Control Region
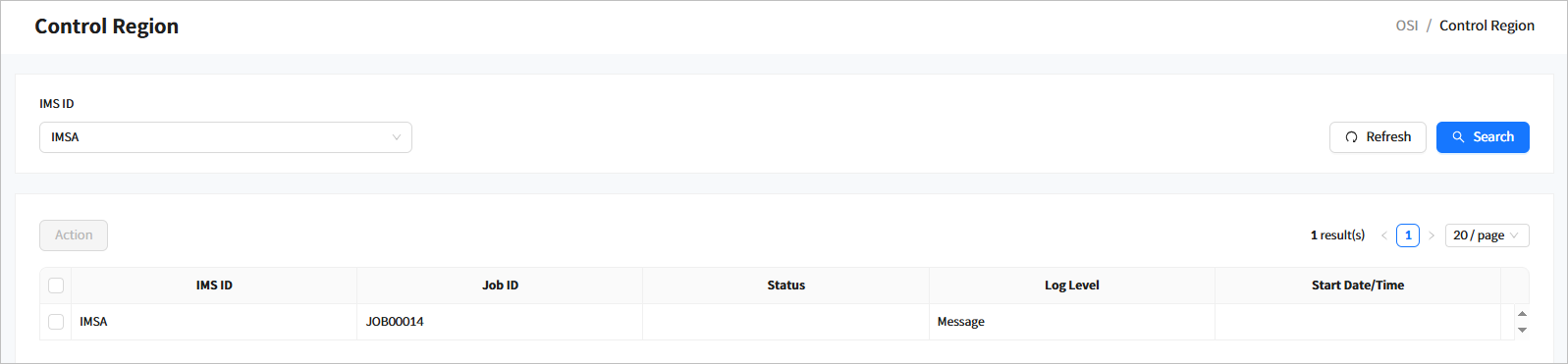
Click [Region] > [Control Region] from the navigation pane to move to the Control Region page. In this page, you can view and modify the status of the control region in OSI.
When you enter the search criteria and click the [Search] button, the search results are displayed. Click the [Refresh] button above the list to refresh the list.
-
Search Conditions
The following describes the control region search conditions.
Item Description IMS ID
IMS ID to search for.
-
Search Results
The following describes the search result columns.
Column Description IMS ID
IMS ID.
Job ID
ID of the job that started the control region.
Status
Current status of the control region.
Log Level
Current log level of the region.
Start Date/Time
Date and time when the control region was started.
2.2.1. Changing Control Region Status
You can change the status of control region by selecting the check box next to a control region in the list and clicking the [Action] button.
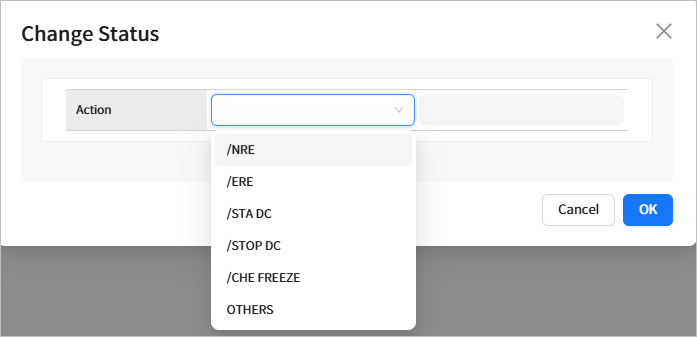
The following statuses can be changed.
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
NRE |
Performs ‘NORMAL RESTART’. |
ERE |
Performs ‘EMERGENCY RESTART’. |
STA DC |
Starts a data communication (DC). |
STOP DC |
Stops a data communication (DC). |
CHE FREEZE |
Performs ‘CHECKPOINT FREEZE’. |
OTHERS |
Other commands that can be run. For more information on related commands, refer to OpenFrame OSI Administrator’s Guide. |
2.3. Staging
Click [Region] > [Staging] from the navigation pane to go to the Staging page. In this page, you can view the current staging library information of the OSI region.
When you enter the search criteria and click the [Search] button, the search results are displayed. Click the [Refresh] button above the list to refresh the list.
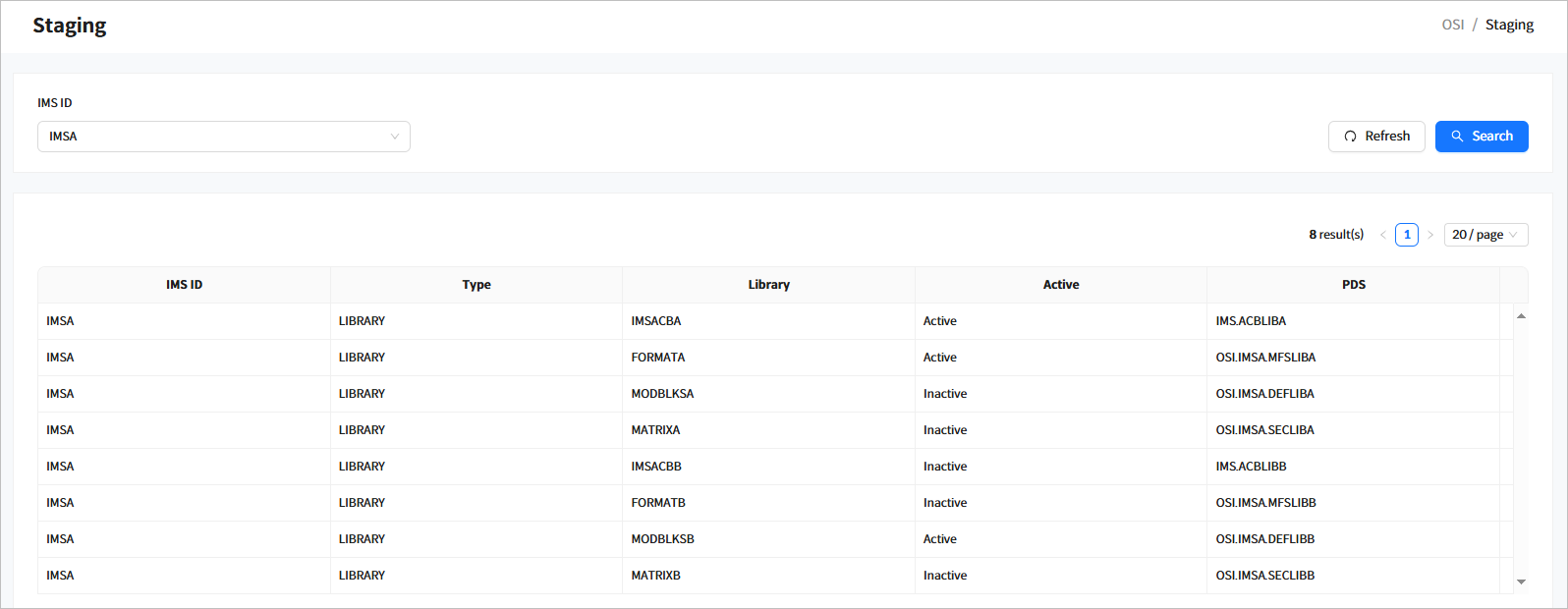
-
Search Conditions
The following describes the staging search conditions.
Item Description IMS ID
IMS ID to search for.
-
Search Results
The following describes the search result columns.
Column Description IMS ID
IMS ID.
Type
Staging target. Currently, only ‘LIBRARY’ is supported.
Library
Name of the staging target.
Active
Status of the staging library (Active or Inactive).
PDS
PDS name of the library.
2.4. Active Region
Displays dependent regions currently in operation in the OSI region.
When you enter the search criteria and click the [Search] button, the search results are displayed. Click the [Refresh] button above the list to refresh the list.
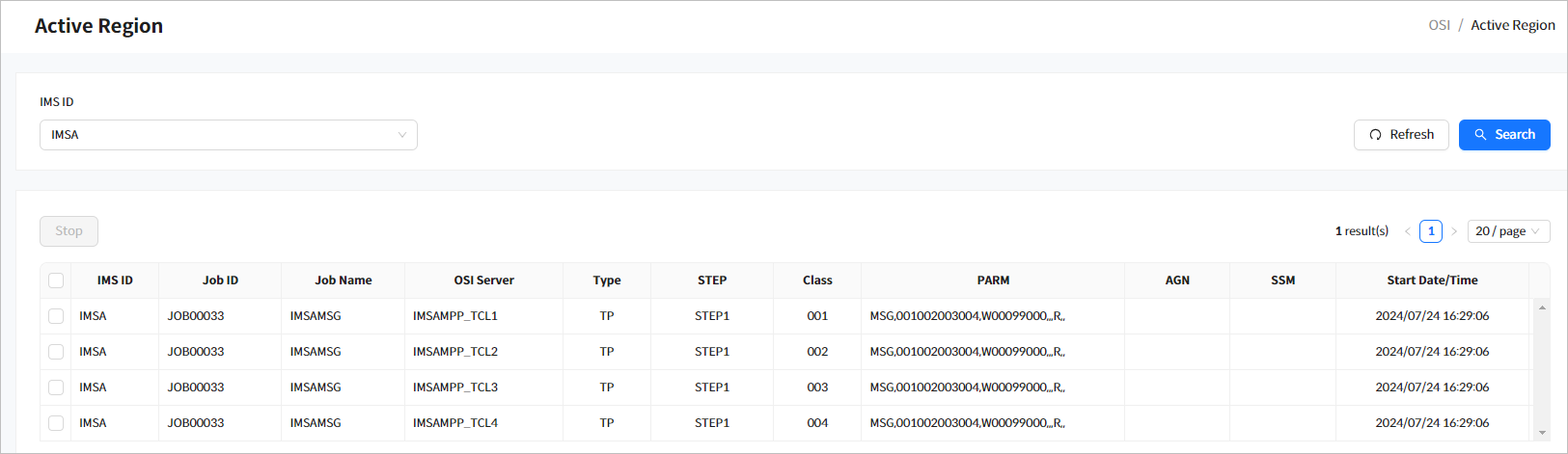
-
Search Conditions
The following describes the active region search conditions.
Item Description IMS ID
IMS ID to search for.
-
Search Results
he following describes the search result columns.
Column Description IMS ID
IMS ID.
Job ID
ID of the job that started the dependent region.
Job Name
Name of the job that started the dependent region.
OSI Server
Actual server name of the dependent region in OSI.
Type
Type of dependent region.
-
TP: MPP region
-
BATCH: BMP region
Step
Step name of the job that started the dependent region.
Class
For MPP regions, the class name of the transactions.
PARM
PARM parameter of the JCL when the dependent region was started.
AGN
AGN parameter of the JCL when the dependent region was started.
SSM
SSM parameter of the JCL when the dependent region was started.
Start Date/Time
Date and time when the dependent region was started.
-
2.5. MPP Server
Click [Region] > [MPP Server] from the navigation pane to check the current status of active MPP servers in the OSI region.
When you enter the search criteria and click the [Search] button, the search results are displayed. Click the [Refresh] button above the list to refresh the list.
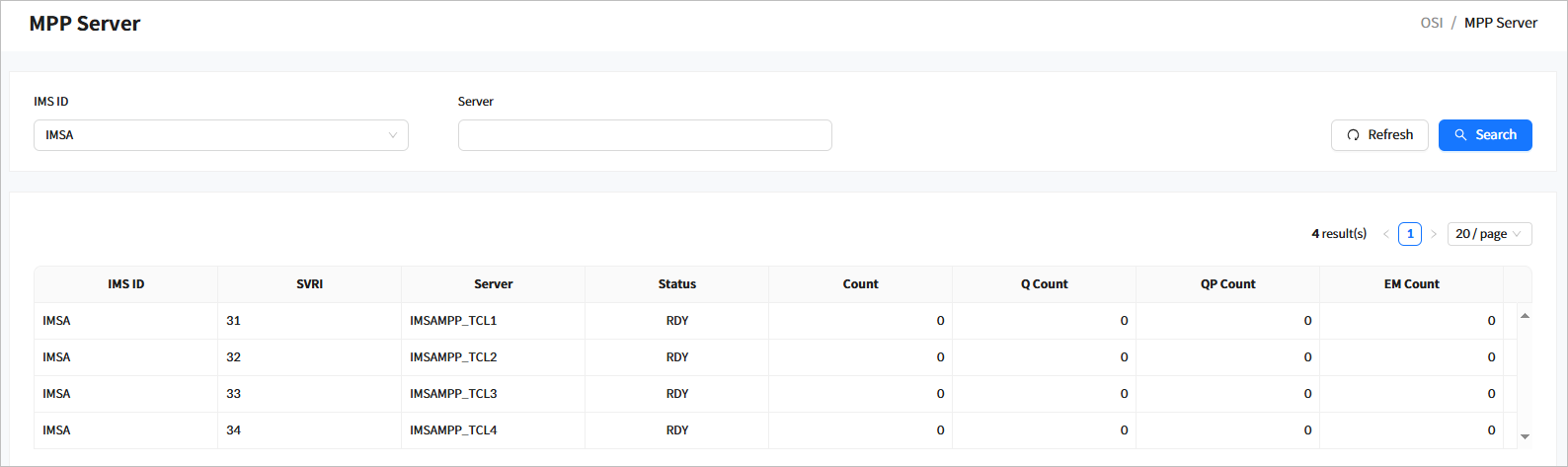
-
Search Conditions
The following describes the MPP server search conditions.
Item Description IMS ID
IMS ID to search for.
Server
Transaction class of the MPP server.
-
Search Results
The following describes the search result columns.
Column Description IMS ID
IMS ID.
SVRI
Index of the MPP server in OSI.
Server
Name of the MPP server in OSI.
Status
Current status of the MPP server.
-
RDY: The server is active.
-
NRDY: The server is inactive.
Count
Number of messages processed by the MPP server.
Q Count
Number of messages queued for processing in the MPP server.
QP Count
Number of messages deleted while queued in the MPP server.
EM Count
Number of messages returned due to exceeding the maximum queuing limit.
-
2.6. MPP Service
Click [Region] > [MPP Service] from the navigation pane to check the transaction status of the currently running MPP server in the OSI region.
When you enter the search criteria and click the [Search] button, the search results are displayed. Click the [Refresh] button above the list to refresh the list.
-
Search Conditions
The following describes the MPP service search conditions.
Item Description IMS ID
IMS ID to search for.
Server
Transaction class of the MPP server.
Transaction
Transaction of the MPP server.
-
Search Results
The following describes the search result columns.
Column Description IMS ID
IMS ID.
Server
Transaction class name.
Transaction
Transaction name.
Count
Number of messages processed by the transaction.
SVC Avg.
Average time taken to perform the transaction.
Status
Current status of the transaction.
-
RDY: Transaction is ready.
-
NRDY: Transaction is not ready.
Q Count
Number of messages queued for processing by the transaction.
Q Avg.
Average waiting time for messages queued for processing.
-
2.7. Events
Click [Region] > [Events] from the navigation pane to check major events in the OSI region.
When you enter the search criteria and click the [Search] button, the search results are displayed. Click the [Refresh] button above the list to refresh the list.
-
Search Conditions
The following describes the event search conditions.
Item Description IMS ID
IMS ID to search for.
Severity
Severity level of the event.
-
FATAL: An event where a severe error occurred.
-
ERROR: An event where an error occurred.
-
INFO: An informational event.
-
-
Search Results
The following describes the search result columns.
Column Description IMS ID
IMS ID.
Timestamp
Timestamp when the event occurred.
Node
Node name.
PID
ID of the process where the event occurred.
Process
Name of the process where the event occurred.
Severity
Severity level of the event.
OpenFrame Error
OpenFrame error code if the event is an error. This will be indicated only if the error code can be verified.
Event Code
OSI event code. For more details about event codes, refer to OpenFrame OSI Administrator’s Guide.
Details
Detailed description of the event.
3. System Definition
This function manages system resources to operate the OSI system. OSI supports the following resources:
3.1. Database
Click [System Definition] > [Database] from the navigation pane to manage databases (DBDs) among system resources.
When you enter the search criteria and click the [Search] button, the search results are displayed. Click the [Refresh] button above the list to refresh the list.
-
Search Conditions
The following describes the DBD search conditions.
Item Description IMS ID
IMS ID to search for.
DBD
DBD name.
-
Search Results
The following describes the search result columns.
Column Description IMS ID
IMS ID.
DBD
DBD name.
Access
Access type of the DBD.
Residential
Indicates whether the DBD is resident.
Registered Date/Time
Date and time when the DBD was created.
Updated Date/Time
Date and time when the DBD information was updated.
-
Buttons
You can manage DBDs using the following buttons above the list.
Button Description [Add]
Adds a new DBD.
[Delete]
Delete the selected DBD.
3.1.1. Database Details
Click a specific DBD from the list in the System Definition > Database page ([OSI] - System Definition - Database) to go to the Database Details page.
Click the [<] icon to return to the previous page.
The following describes each item.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
IMS ID |
IMS ID. |
DBD |
DBD name. |
Access |
Access type of the DBD. |
Residential |
Indicates whether the DBD is resident. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
Registered Date/Time |
Date and time when the DBD was created. |
Updated Date/Time |
Date and time when the DBD information was updated. |
3.2. Application
Click [System Definition] > [Application] from the navigation pane to manage applications among system resources.
When you enter the search criteria and click the [Search] button, the search results are displayed. Click the [Refresh] button above the list to refresh the list.
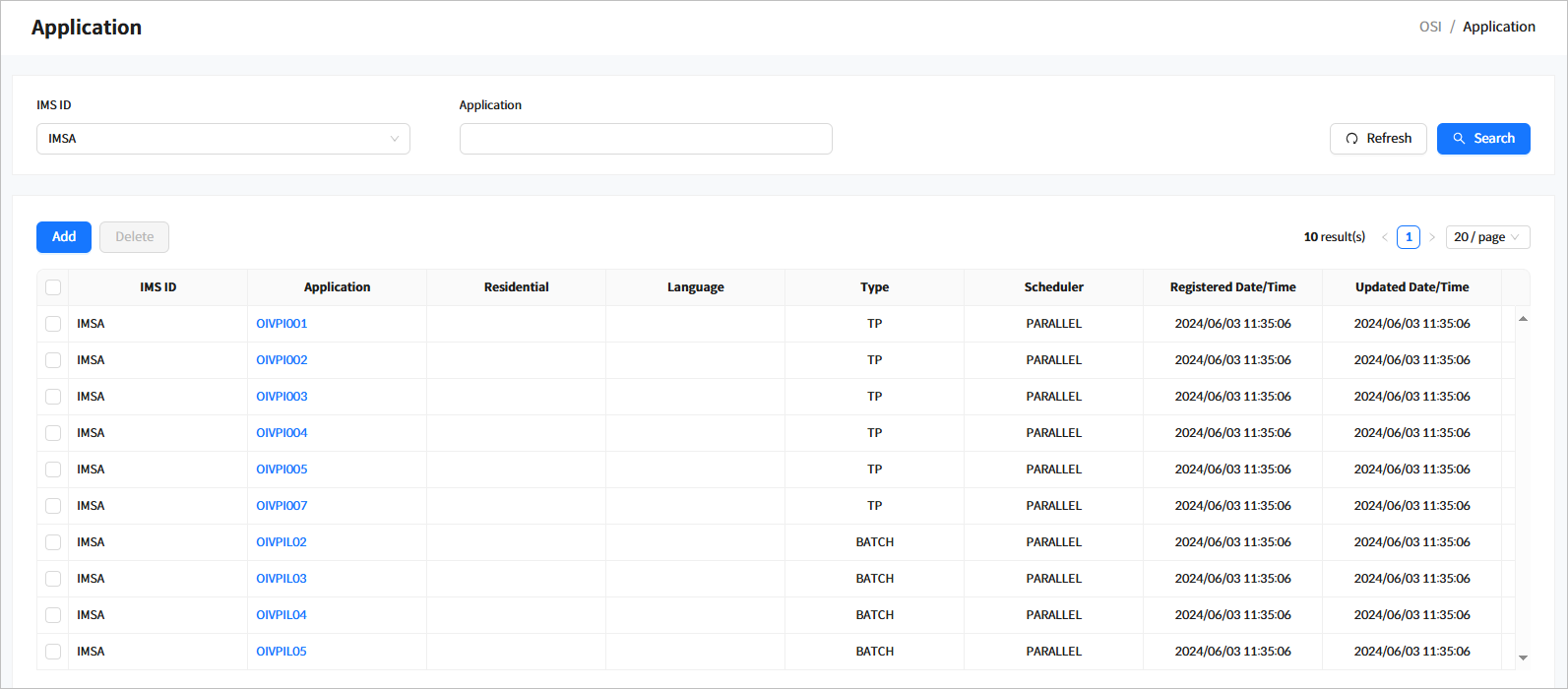
-
Search Conditions
The following describes the application search conditions.
Item Description IMS ID
IMS ID to search for.
Application
Application name.
-
Search Results
The following describes the search result columns.
Column Description IMS ID
IMS ID.
Application
Application name.
Residential
Indicates whether the application is resident. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility)
Language
Language type of the application.
Type
Program type of the application.
Scheduler
Schedule type of the application.
Registered Date/Time
Date and time when the application was created.
Updated Date/Time
Date and time when the application was updated.
-
Buttons
You can manage applications using the following buttons above the list.
Button Description [Add]
Adds an application.
[Delete]
Deletes the selected application.
3.2.1. Application Details
Click a specific application from the list in the System Definition > Application page ([OSI] - System Definition - Application) to go to the Application Details page.
Click the [<] icon to return to the previous page.
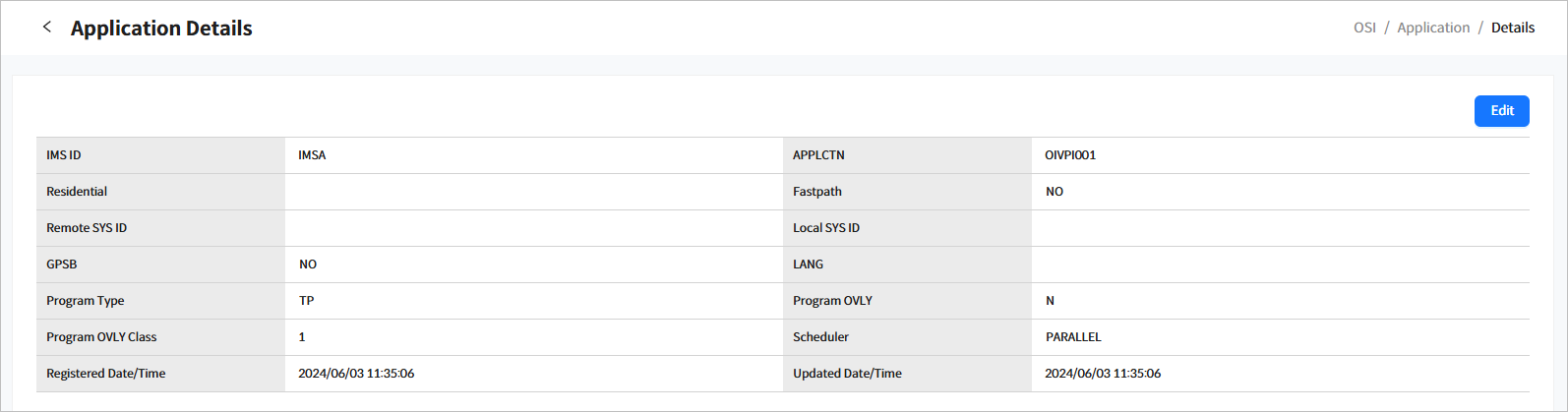
The following describes each item.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
IMS ID |
IMS ID. |
APPLCTN |
Application name. |
Residential |
Indicates whether the application is resident. |
Fastpath |
Indicates whether it is a FastPath application. |
Remote SYS ID |
Remote system ID. |
Local SYS ID |
Local system ID. |
GPSB |
GPSB name. |
LANG |
Language of the application program. |
Program Type |
Application type.
|
Program OVLY |
OVLY of the application. |
Program OVLY Class |
OVLY class of the application. |
Scheduler |
Indicates whether messages can be processed simultaneously in MPP or BMP.
|
Registered Date/Time |
Date and time when the application resource was registered. |
Updated Date/Time |
Date and time when the application resource was last updated. |
3.3. Transaction
Click [System Definition] > [Transaction] from the navigation pane to manage transactions among system resources.
When you enter the search criteria and click the [Search] button, the search results are displayed. Click the [Refresh] button above the list to refresh the list.
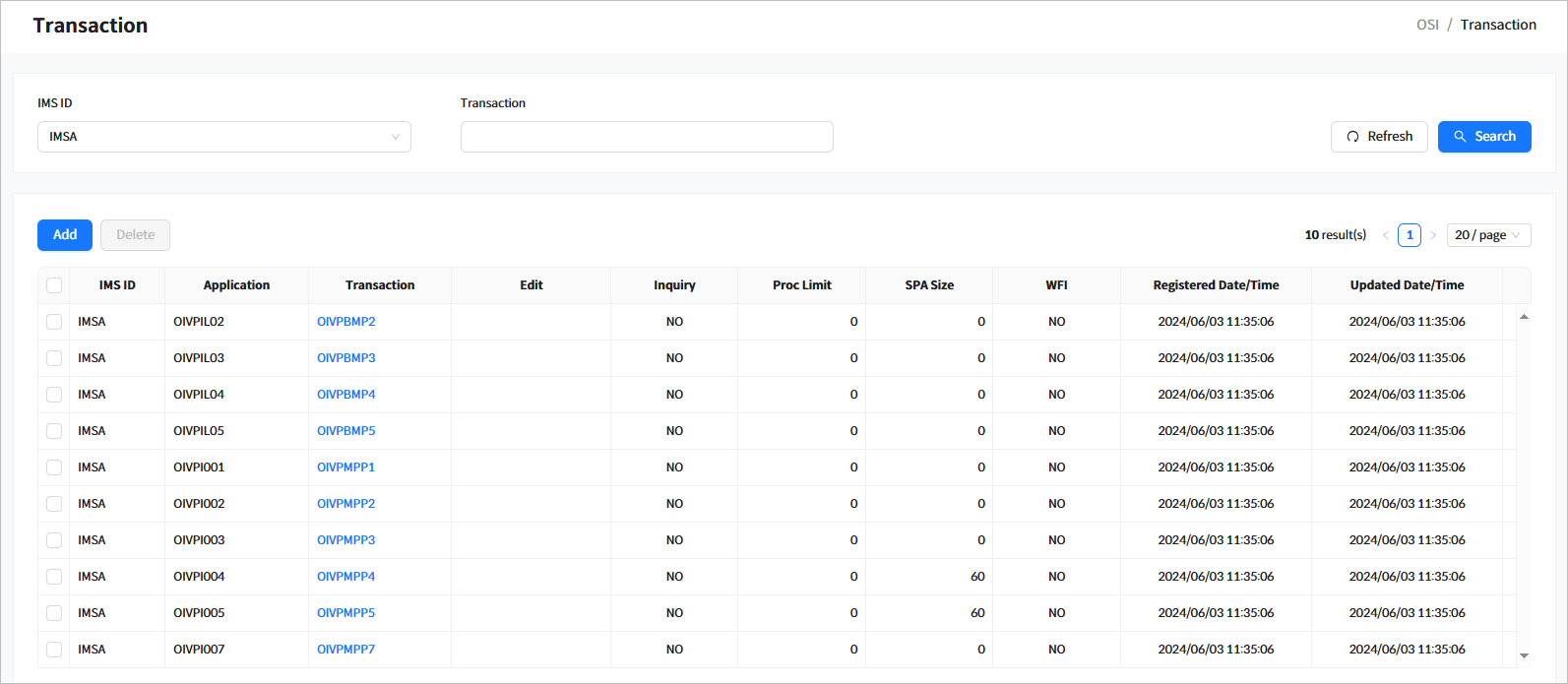
-
Search Conditions
The following describes the transaction search conditions.
Item Description IMS ID
IMS ID to search for.
Transaction
Transaction code.
-
Search Results
The following describes the search result columns.
Column Description IMS ID
IMS ID.
Application
Application name of the transaction.
Transaction
Transaction name
Edit
Edit name of the transaction.
Inquiry
Indicates whether the transaction is for inquiry purposes.
Proc Limit
Number of process limits for the transaction.
SPA Size
SPA size of the transaction.
WFI
Indicates whether the transaction is WFI.
Registered Date/Time
Date and time when the transaction was created.
Updated Date/Time
Date and time when the transaction information was updated.
-
Buttons
You can manage transactions using the following buttons above the list.
Button Description [Add]
Adds a transaction.
[Delete]
Deletes the selected transaction.
3.3.1. Transaction Details
Click a specific transaction from the list in the System Definition > Transaction page ([OSI] - System Definition - Transaction) to go to the Transaction Details page.
Click the [<] icon to return to the previous page.
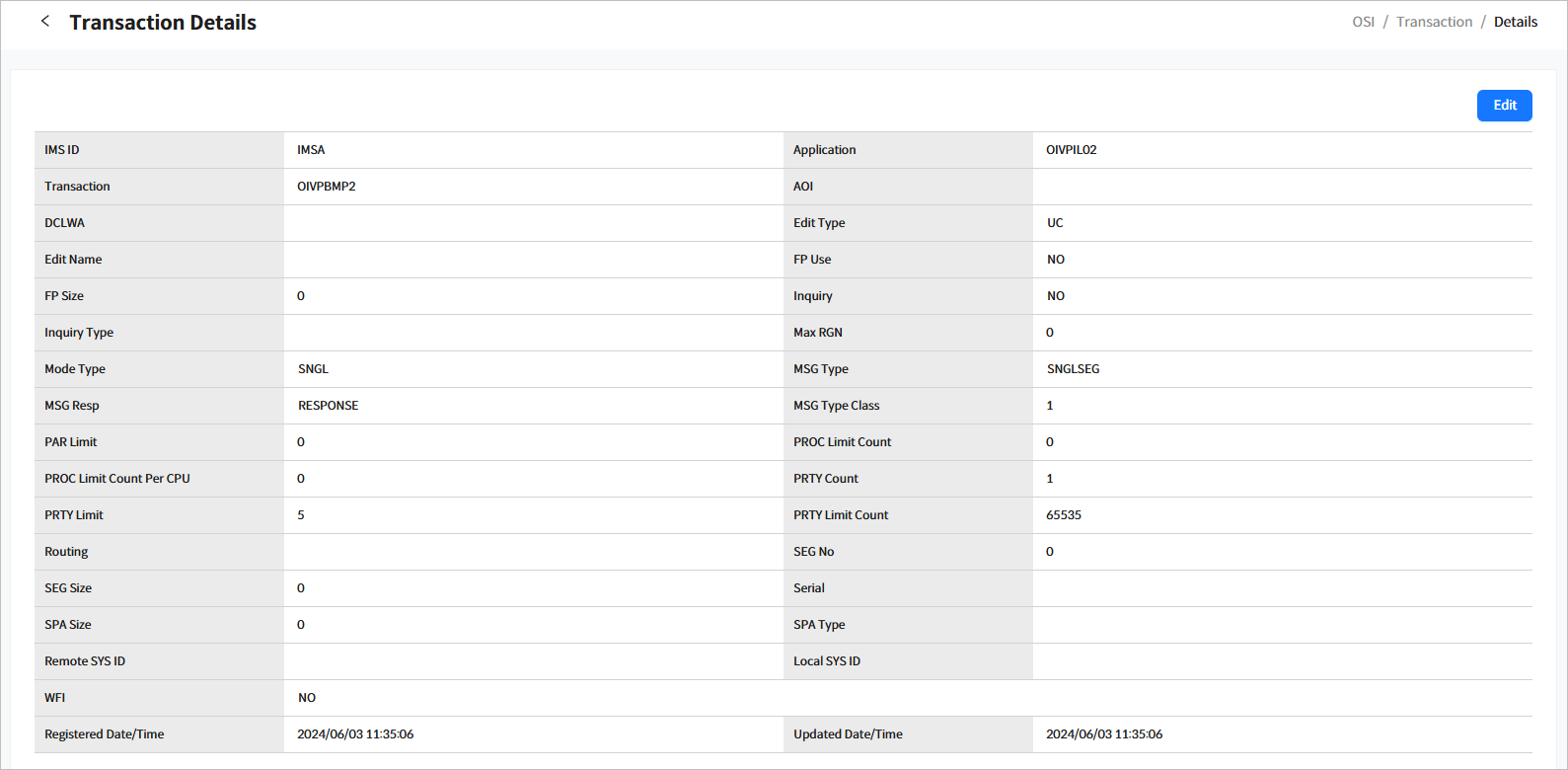
The following describes each item.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
IMS ID |
IMS ID. |
Application |
Application name. |
Transaction |
Transaction name. |
AOI |
Indicates whether to use Automated Operator Interface (AOI). (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
DCLWA |
Indicates whether to use Data Communication Log Write Ahead (DCLWA). (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
Edit Type |
Specifies whether to convert the input data to uppercase.
|
Edit Routine Name |
Edit routine name. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
FP Use |
Indicates if FastPath is used. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
FP Size |
Buffer size for performing a FastPath. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
Inquiry |
Indicates whether the transaction is for inquiry purposes. If set to YES, HiDB’s ISRT, DLET, and REPL commands cannot be issued. |
Inquiry Type |
Specifies whether to recover during NRE or ERE. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
Max RGN |
Maximum number of regions for MPP. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
Mode Type |
Specifies whether to process the database for each message or apply changes at the end of the program. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
MSG Type |
Type of transaction code. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
MSG Resp |
Indicates whether a response was returned for the transaction input. |
MSG Type Class |
Transaction class. |
PAR Limit |
Maximum value when SCHDTYPE in the application is PARALLEL. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
PROC Limit Count |
Maximum number of messages that can be processed in a single transaction. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
PROC Limit Count Per CPU |
Maximum time that can be used per CPU within a transaction. |
PRTY Count |
Parameter that specifies the scheduling priority of the transaction. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
PRTY Limit |
Parameter that specifies the scheduling priority of the transaction. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
PRTY Limit Count |
Parameter that specifies the scheduling priority of the transaction. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
Routing |
Parameter that specifies routing information in multiple OSI systems. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
SEG No |
Maximum number of segments that a GU message can retrieve in the application. |
SEG Size |
Size of the segments that a GU message can retrieve in the application. |
Serial |
Indicates whether the processing order of transactions can be specified. |
SPA Size |
Application size for SPA area. |
SPA Type |
Indicates whether to truncate the SPA area length if it is small when switched to another transaction. |
Remote SYS ID |
SYSID parameter of the remote system. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
Local SYS ID |
SYSID parameter of the local system. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
WFI |
Indicates whether it is a wait-for-input (WFI) transaction. |
Registered Date/Time |
Date and time when the transaction was registered. |
Updated Date/Time |
Date and time when the transaction was last updated. |
3.4. Terminal
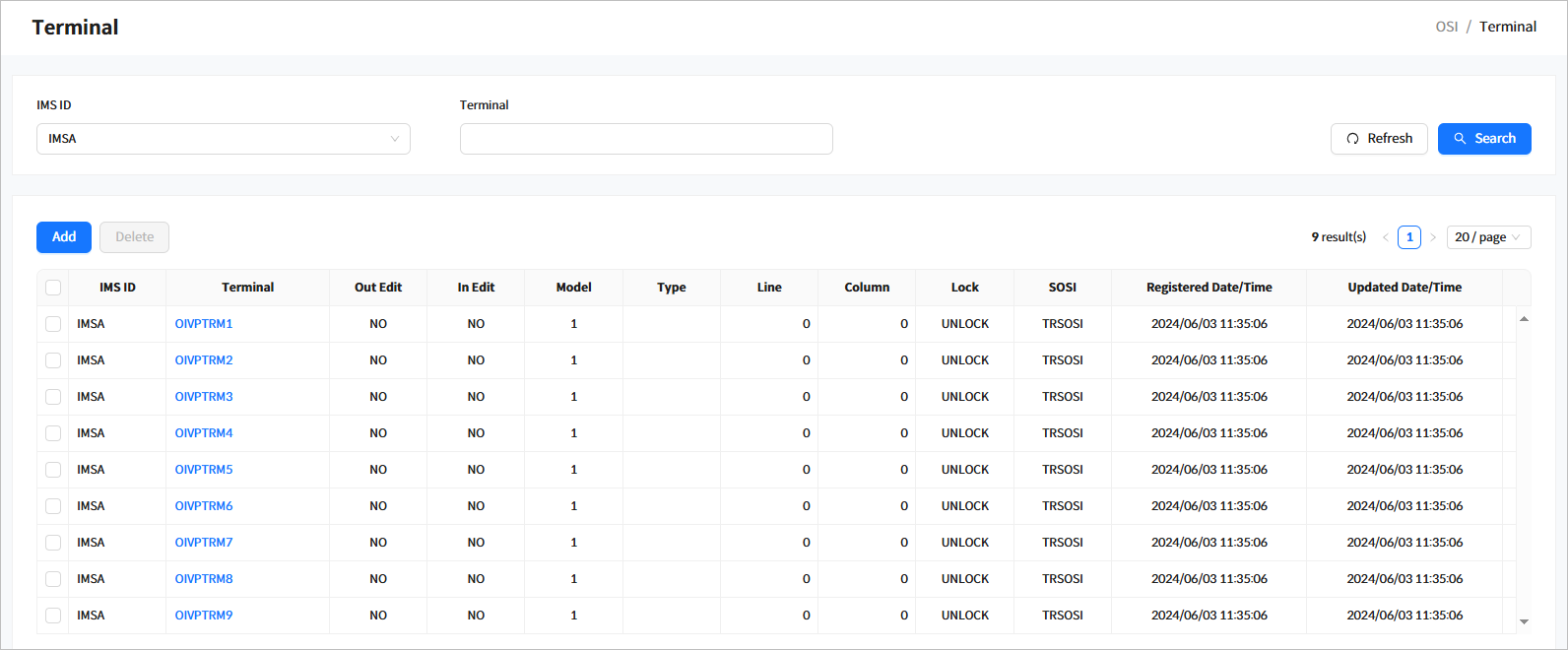
Click [System Definition] > [Terminal] from the navigation pane to manage terminals among system resources.
When you enter the search criteria and click the [Search] button, the search results are displayed. Click the [Refresh] button above the list to refresh the list.
-
Search Conditions
The following describes the terminal search conditions.
Item Description IMS ID
IMS ID to search for.
Terminal
Terminal name.
-
Search Results
The following describes the search result columns.
Column Description IMS ID
IMS ID.
Terminal
Terminal name.
Out Edit
Indicates whether the terminal output can be edited.
In Edit
Indicates whether the terminal input can be edited.
Model
Model type of the terminal.
Type
Type of the terminal.
Line
Line size of the terminal.
Column
Column size of the terminal.
Lock
Lock type of the terminal.
SOSI
SOSI type of the terminal.
Registered Date/Time
Date and time when the terminal was created.
Updated Date/Time
Date and time when the terminal was last updated.
-
Buttons
You can manage terminals using the following buttons above the list.
Button Description [Add]
Adds a terminal.
[Delete]
Deletes the selected terminal.
3.4.1. Terminal Details
Click a specific terminal from the list in the System Definition > Terminal page ([OSI] - System Definition - Terminal) to go to the Terminal Details page.
Click the [<] icon to return to the previous page.
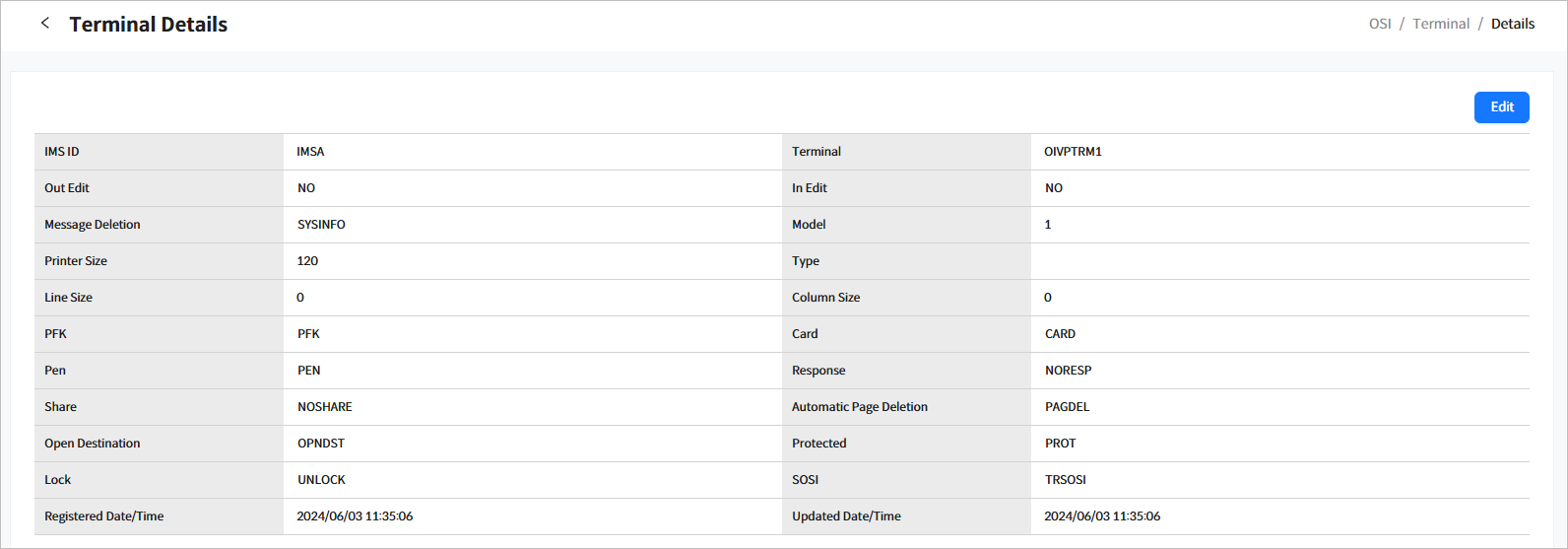
The following describes each item.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
IMS ID |
IMS ID. |
Terminal |
Terminal name. |
Out Edit |
Name of the module to be used for output processing. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
In Edit |
Name of the module to be used for input processing. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
Message Deletion |
Parameter that specifies whether message deletion is allowed on the terminal. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
Model |
Terminal model. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
Printer Size |
Print location at the printer. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
Type |
Terminal type. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
Line Size |
Line size of the 3270 display terminal. |
Column Size |
Column size of the 3270 display terminal. |
PFK |
Type of program function key (PFK). (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
Card |
Indicates whether CARD is available. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
Pen |
Indicates whether PEN is available. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
Response |
Response to the transaction. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
Share |
Indicates whether the printer is shared in VTAM. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
Automatic Page Deletion |
Specifies whether automatic page deletion is allowed in the terminal. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
Open Destination |
Specifies whether the IMS ‘/OPNDST’ command can be set. |
Protected |
Protected mode for each message. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
Lock |
Specifies whether a lock can be set on the keyboard after MFS data transmission. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
SOSI |
Specifies whether MFS data is trans Shift-out (SO) or Shift-in (SI) is applied during MFS input. (Not supported by OSI but maintained for compatibility) |
Registered Date/Time |
Date and time when the terminal was created. |
Updated Date/Time |
Date and time when the terminal was last updated. |
3.5. LTERM
Click [System Definition] > [LTERM] from the navigation pane to manage logical terminals (LTERM) among system resources.
When you enter the search criteria and click the [Search] button, the search results are displayed. Click the [Refresh] button above the list to refresh the list.
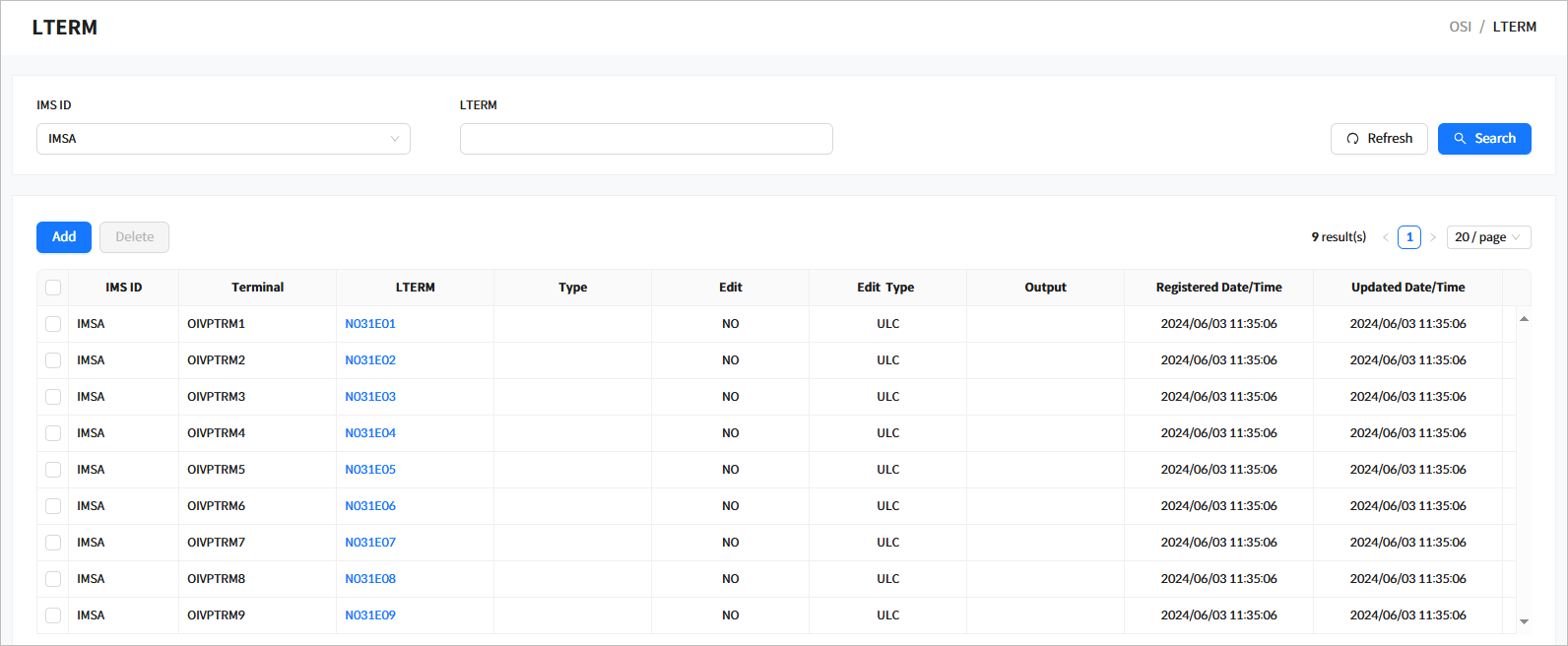
-
Search Conditions
The following describes the LTERM search conditions.
Item Description IMS ID
IMS ID to search for.
LTERM
LTERM name.
-
Search Results
The following describes the search result columns.
Column Description IMS ID
IMS ID.
Terminal
Terminal name of the LTERM.
LTERM
LTERM name.
Type
Type of LTERM.
Edit
Specifies whether the LTERM can be edited.
Edit Type
Edit type of the LTERM. (UC or ULC).
Output
Output terminal name of the LTERM.
Registered Date/Time
Date and time when the LTERM was created.
Updated Date/Time
Date and time when the LTERM information was updated.
-
Buttons
You can manage LTERMs using the following buttons above the list.
Button Description [Add]
Adds a LTERM.
[Delete]
Deletes the selected LTERM.
3.5.1. LTERM Details
Click a specific LTERM from the list in the System Definition > LTERM page ([OSI] - System Definition - LTERM) to go to the LTERM Details page.
Click the [<] icon to return to the previous page.
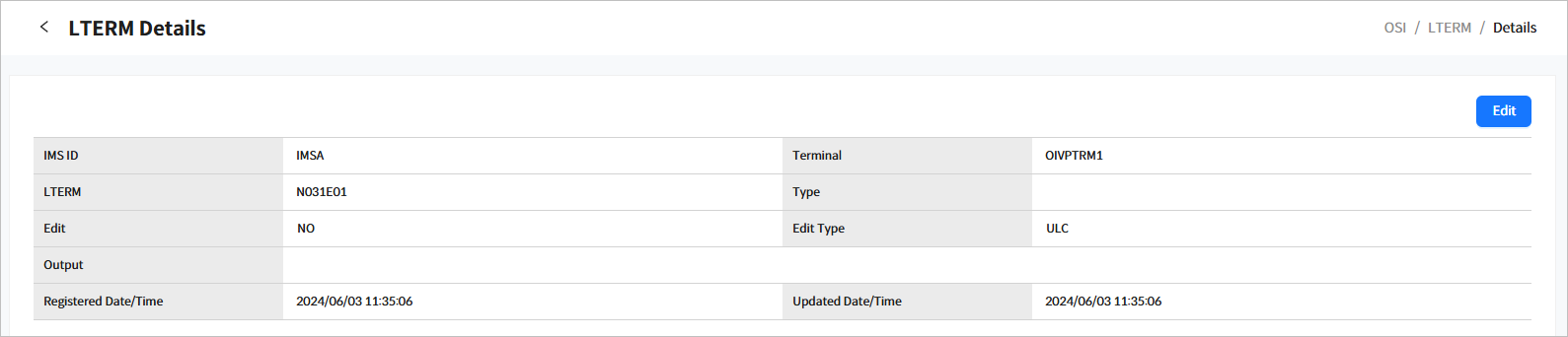
The following describes each item.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
IMS ID |
IMS ID. |
Terminal |
Terminal name of the LTERM. |
LTERM |
LTERM name. |
Type |
Type of LTERM. |
Edit |
Specifies whether the LTERM can be edited. |
Edit Type |
Edit type of the LTERM (UC or ULC). |
Output |
Output terminal name of the LTERM. |
Registered Date/Time |
Date and time when the LTERM was created. |
Updated Date/Time |
Date and time when the LTERM information was updated. |
4. Resources
You can use the Resources menu to manage runtime system resources required for operating the OSI system. OSI supports the following runtime system resources.
4.1. Database
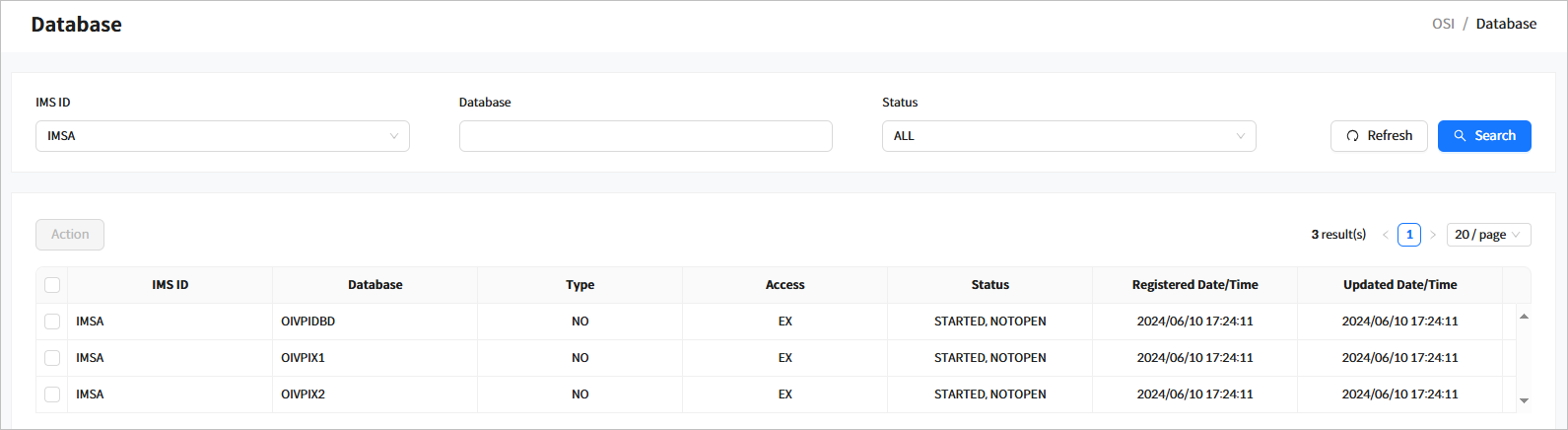
Click [Resources] > [Database] from the navigation pane to manage databases among runtime system resources.
When you enter the search criteria and click the [Search] button, the search results are displayed. Click the [Refresh] button above the list to refresh the list.
-
Search Conditions
The following describes the database search conditions.
Item Description IMS ID
IMS ID to search for.
Database
Database name.
Status
Database status.
-
Search Results
The following describes the search result columns.
Column Description IMS ID
IMS ID.
Database
Database name.
Type
Indicates whether the database is resident.
Access
Access type of the database.
Status
Status of the database.
Registered Date/Time
Date and time when the database was created.
Updated Date/Time
Date and time when the database status was updated.
-
Buttons
You can manage databases using the following buttons above the list.
Button Description [Action]
Executes the imscmd for the selected item.
-
/STA DB
-
/STOP DB
-
/DBR DB
-
4.1.1. Changing Resource Database Status
You can change the database status by selecting the check box next to a database in the list and clicking the [Action] button.
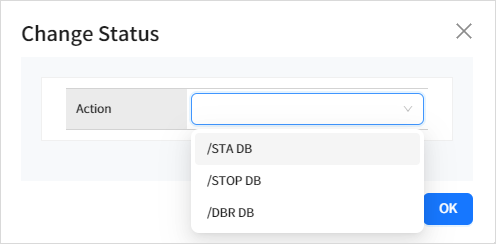
The following statuses can be changed.
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
STA DB |
Allows transactions to access the database. |
STOP DB |
Prevents programs from accessing the database. |
DBR DB |
Blocks transactions or programs from accessing the database. |
4.2. Application
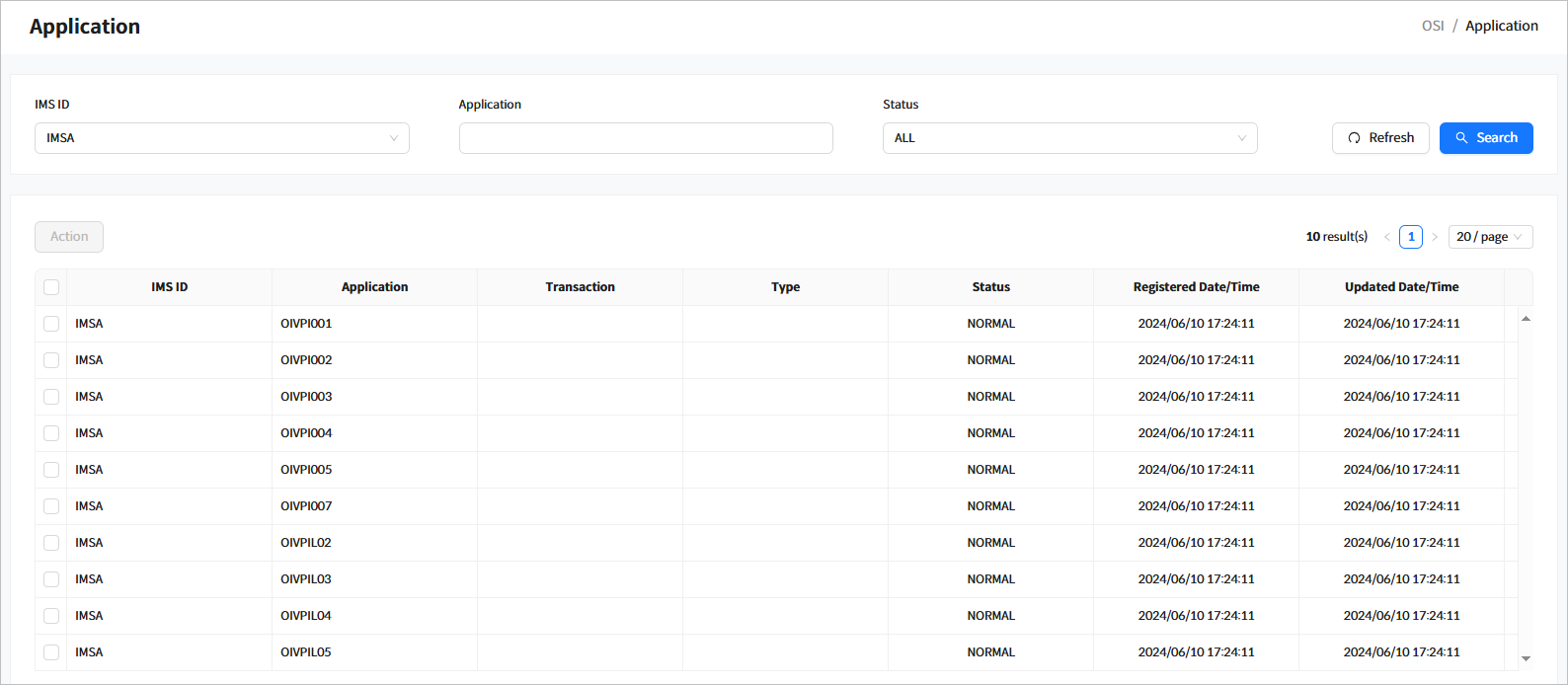
Click [Resources] > [Application] from the navigation pane to manage applications among runtime system resources.
When you enter the search criteria and click the [Search] button, the search results are displayed. Click the [Refresh] button above the list to refresh the list.
-
Search Conditions
The following describes the application search conditions.
Item Description IMS ID
IMS ID to search for.
Application
Application name.
Status
Application Status.
-
Search Results
The following describes the search result columns.
Column Description IMS ID
IMS ID.
Application
Application name.
Transaction
Transaction name of the application.
Type
Type of the application’s program.
Status
Status of the application.
Registered Date/Time
Date and time when the application was created.
Updated Date/Time
Date and time when the application status was last updated.
-
Buttons
You can manage applications using the following buttons above the list.
Button Description [Action]
Executes the imscmd for the selected item.
-
/STA PGM
-
/STOP PGM
-
4.2.1. Changing Resource Application Status
You can change the application status by selecting the check box next to an application in the list and clicking the [Action] button.
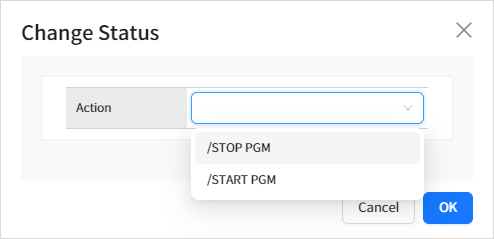
The following statuses can be changed.
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
STOP PGM |
Stops the PGM (application). |
START PGM |
Starts the PGM (application). |
4.3. Transaction
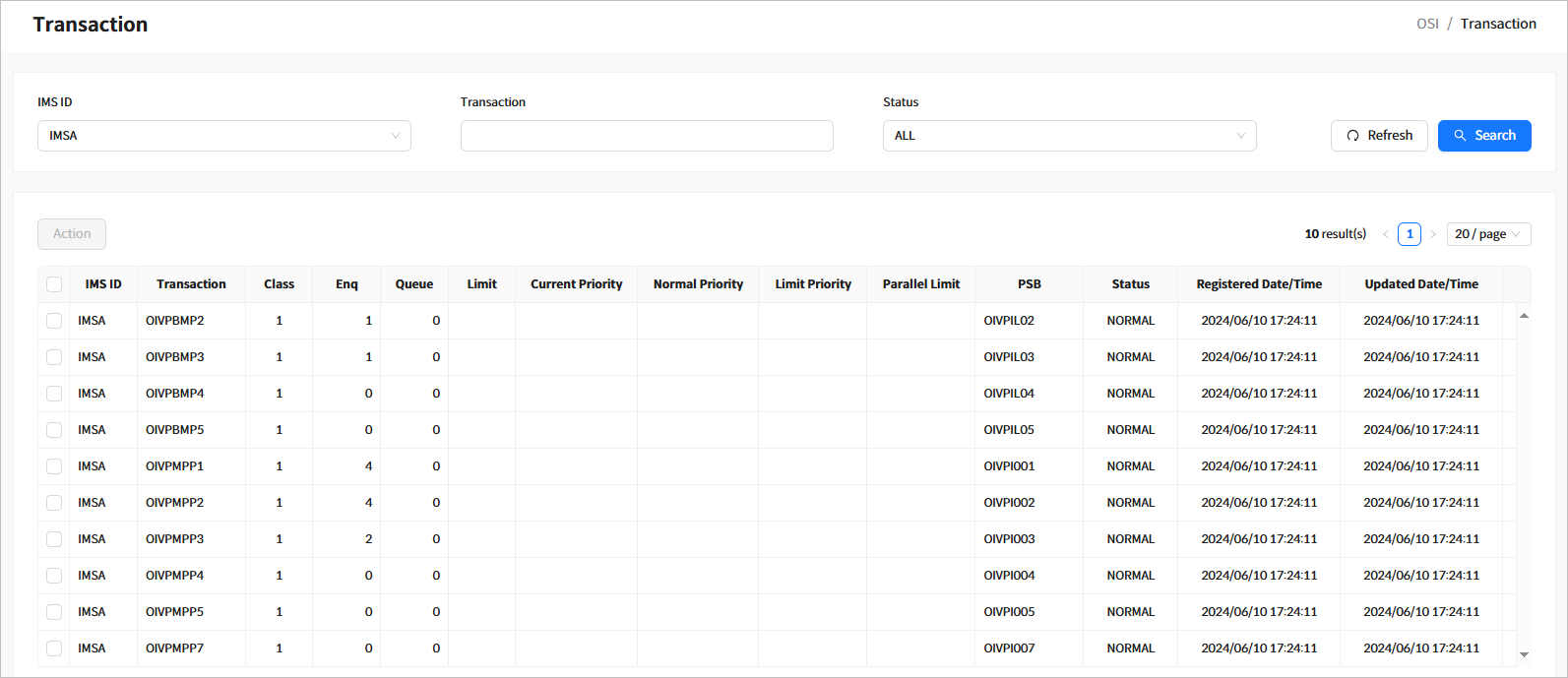
Click [Resources] > [Transaction] from the navigation pane to manage transactions among runtime system resources.
When you enter the search criteria and click the [Search] button, the search results are displayed. Click the [Refresh] button above the list to refresh the list.
-
Search Conditions
The following describes the transaction search conditions.
Item Description IMS ID
IMS ID to search for.
Transaction
Transaction code.
Status
Transaction status.
-
Search Results
The following describes the search result columns.
Column Description IMS ID
IMS ID.
Transaction
Transaction name.
Class
Class of the transaction.
Enq
Number of enqueues for the transaction.
Queue
Number of queues for the transaction.
Limit
Number of limits for the transaction. (Currently not supported)
Current Priority
Current priority of the transaction. (Currently not supported)
Normal Priority
Normal priority of the transaction. (Currently not supported)
Limit Priority
Limit priority of the transaction. (Currently not supported)
Parallel Limit
Number of parallel limits of the transaction. (Currently not supported)
PSB
PSB (application) name of the transaction.
Status
Status of the transaction.
Registered Date/Time
Date and time when the transaction was created.
Updated Date/Time
Date and time when the status of the transaction was last changed.
-
Buttons
You can manage transactions using the following buttons above the list.
Button Description [Action]
Executes the imscmd for the selected item.
-
/START TRAN
-
/STOP TRAN
-
/PSTOP TRAN
-
/PURGE TRAN
-
4.3.1. Changing Resource Transaction Status
You can change the transaction status by selecting the check box next to a transaction in the list and clicking the [Action] button.
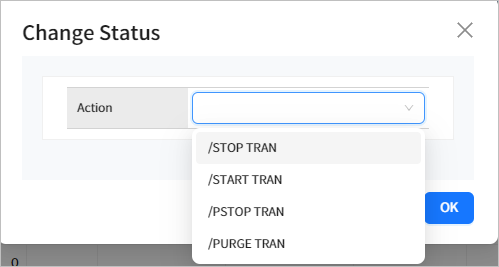
The following statuses can be changed.
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
STOP TRAN |
Stops the transaction. |
START TRAN |
Starts the transaction. |
PSTOP TRAN |
Stops the message scheduling for a specific transaction. |
PURGE TRAN |
Stops the transaction queueing. |
4.4. Terminal
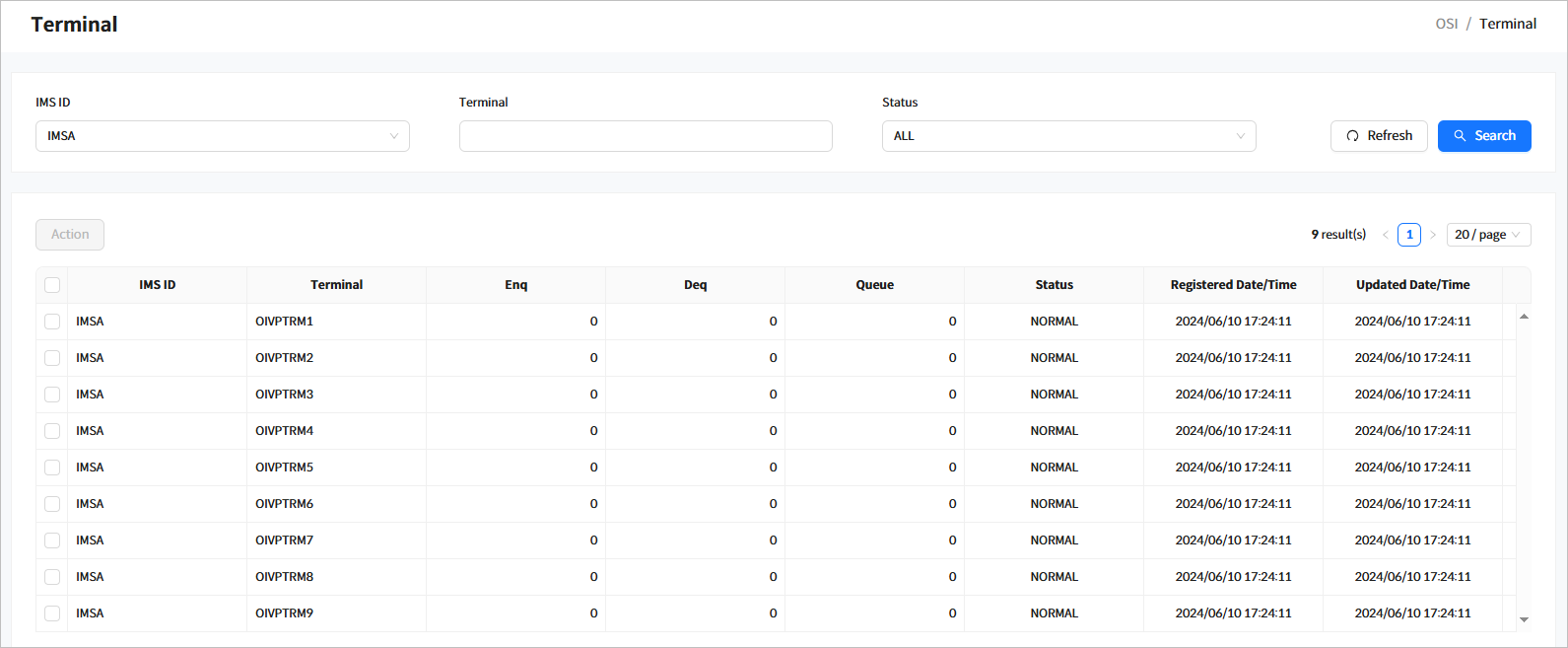
Click [Resources] > [Terminal] from the navigation pane to manage terminals among runtime system resources.
When you enter the search criteria and click the [Search] button, the search results are displayed. Click the [Refresh] button above the list to refresh the list.
-
Search Conditions
The following describes the terminal search conditions.
Item Description IMS ID
IMS ID to search for.
Terminal
Terminal name.
Status
Terminal Status.
-
Search Results
The following describes the search result columns.
Column Description IMS ID
IMS ID.
Terminal
Terminal name.
Enq
Number of enqueues for the terminal.
Deq
Number of dequeues for the terminal.
Queue
Number of queues for the terminal.
Status
Status of the terminal.
Registered Date/Time
Date and time when the terminal was created.
Updated Date/Time
Date and time when the status of the terminal was last changed.
-
Buttons
You can manage terminals using the following buttons above the list.
Button Description [Action]
Executes the imscmd for the selected item.
-
/START NODE
-
/STOP NODE
-
/OPN NODE
-
/CLS NODE
-
4.4.1. Changing Resource Terminal Status
You can change the terminal status by selecting the check box next to a terminal in the list and clicking the [Action] button.
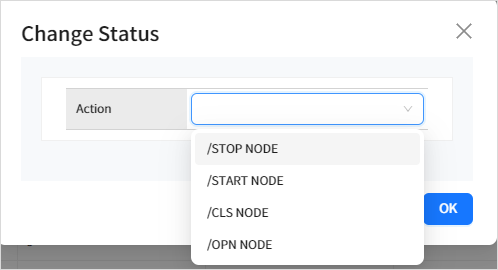
The following statuses can be changed.
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
STOP NODE |
Sets the terminal to be stopped and logged off. |
START NODE |
Enables the terminal to log on. |
CLS NODE |
Disconnects the node from OSI. |
OPN NODE |
Connects the VTAM terminal to the OSI system. |
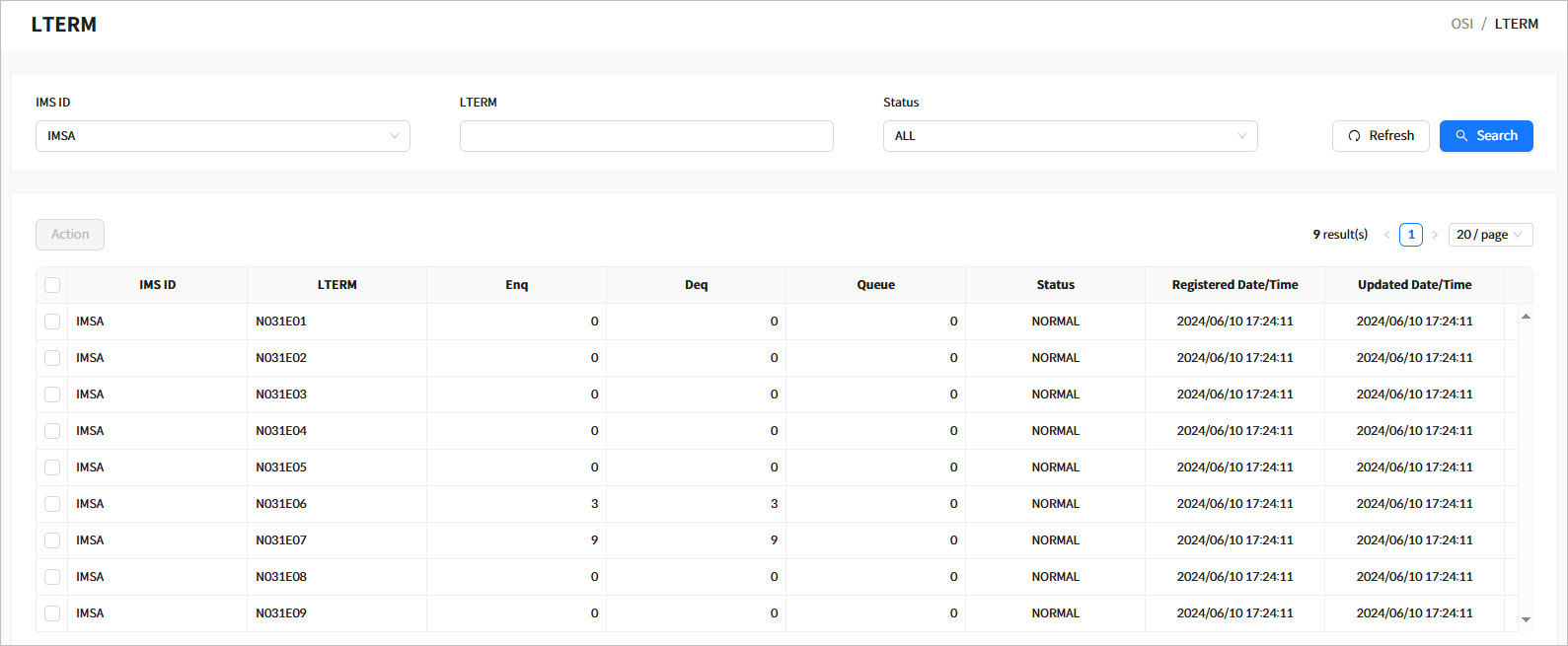
4.5. LTERM
Click [Resources] > [LTERM] from the navigation pane to manage logical terminals (LTERM) among runtime system resources.
When you enter the search criteria and click the [Search] button, the search results are displayed. Click the [Refresh] button above the list to refresh the list.
-
Search Conditions
The following describes the LTERM search conditions.
Item Description IMS ID
IMS ID to search for.
LTERM
LTERM name.
Status
LTERM status.
-
Search Results
The following describes the search result columns.
Column Description IMS ID
IMS ID.
LTERM
LTERM name.
Enq
Number of enqueues for the LTERM.
Deq
Number of dequeues for the LTERM.
Queue
Number of queues for the LTERM.
Status
Status of the LTERM.
Registered Date/Time
Date and time when the LTERM was created.
Updated Date/Time
Date and time when the status of the LTERM was last updated.
-
Buttons
You can manage LTERMs using the following buttons above the list.
Button Description [Action]
Executes the imscmd for the selected item.
-
/START LTERM
-
/STOP LTERM
-
/PSTOP LTERM
-
4.5.1. Changing Resource LTERM Status
You can change the LTERM status by selecting the check box next to a LTERM in the list and clicking the [Action] button.
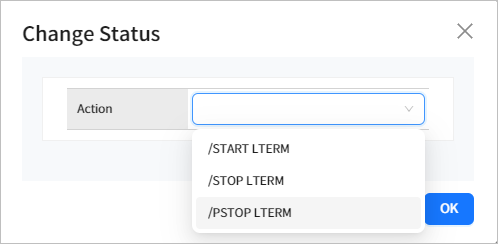
The following statuses can be changed.
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
START LTERM |
Sets the LTERM to be started and resets the states such as STOP and PSTOP. |
STOP LTERM |
Sets the LTERM to be stopped and stops sending to or receiving from the LTERM. |
PSTOP LTERM |
Stops sending to or receiving from a specific LTERM. |
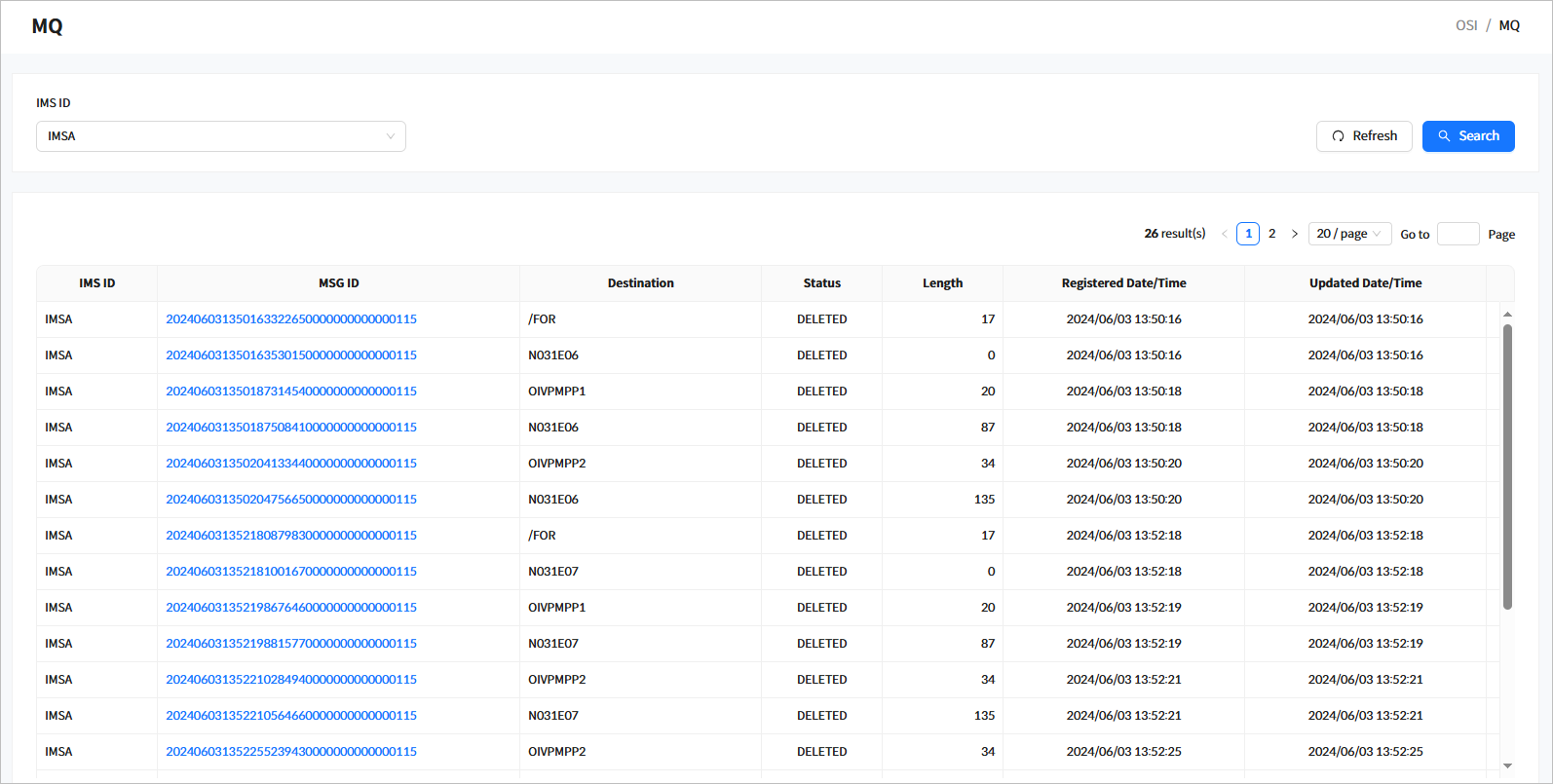
5. MQ
Click [MQ] from the navigation pane to view the OSI message queues (hereafter MQ).
When you enter the search criteria and click the [Search] button, the search results are displayed. Click the [Refresh] button above the list to refresh the list.
-
Search Conditions
The following describes the MQ search conditions.
Item Description IMS ID
IMS ID to search for.
-
Search Results
The following describes the search result columns.
Column Description IMS ID
IMS ID.
MSG ID
Message ID.
Destination
Destination of the message.
Status
Status of the message.
Length
Length of the message data.
Registered Date/Time
Date and time when the message was created.
Updated Date/Time
Date and time when the message status was changed.
5.1. MQ Details
Click a specific MSG ID from the list in the MQ page ([OSI] - MQ) to go to the MQ Details page.
Click the [<] icon to return to the previous page.
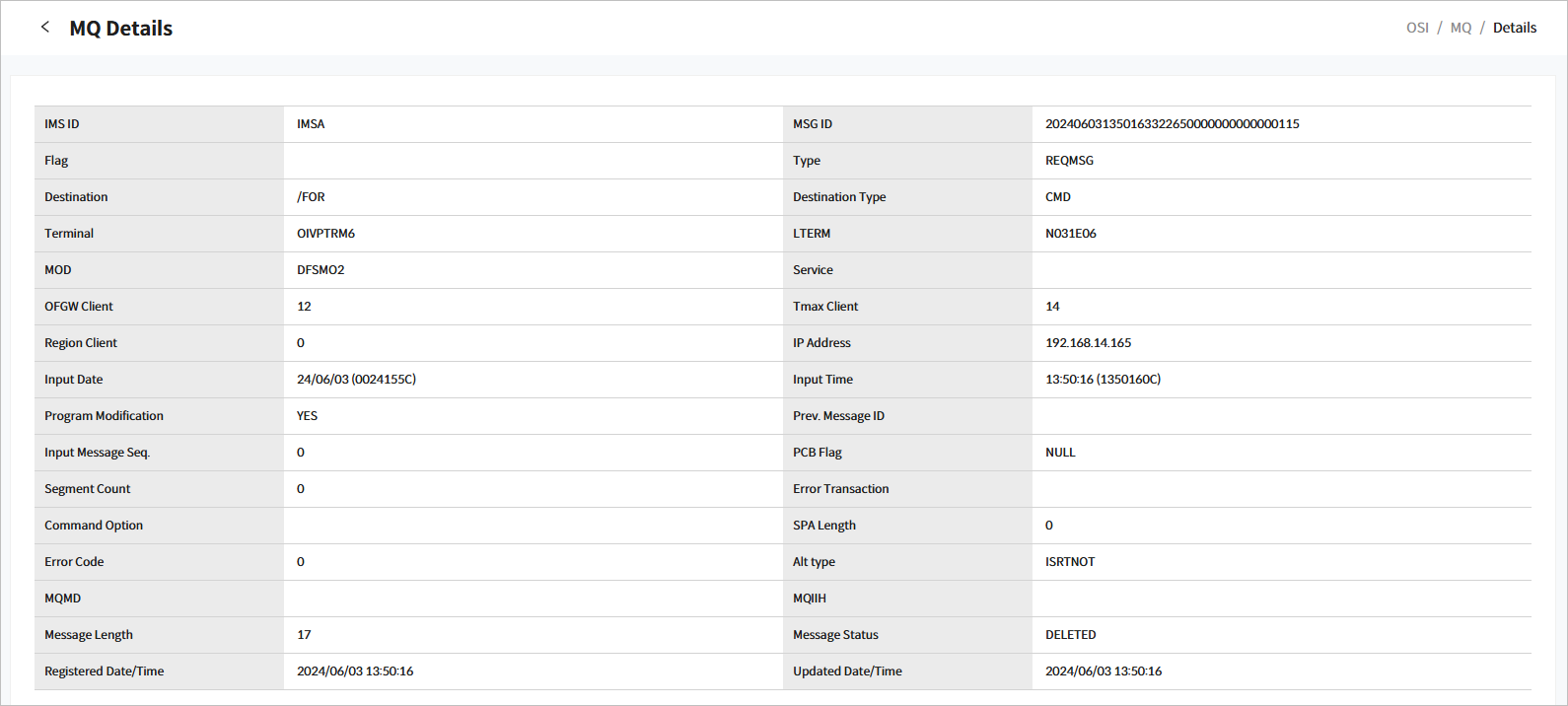
The following describes each item.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
IMS ID |
IMS ID. |
MSG ID |
Message ID. |
Flag |
Flag of the message. |
Type |
Message type. |
Destination |
Destination of the message. |
Destination Type |
Destination type of the message. |
Terminal |
Terminal of the message source. |
LTERM |
LTERM of the message source. |
MOD |
MOD name of the message. |
Service |
Service name of the message’s destination. |
OFGW Client |
OFGW client ID of the message source. |
Tmax Client |
Tmax client ID of the message source. |
Region Client |
Region client ID of the message source. |
IP Address |
IP address of the message source. |
Input Date |
Date when the message was input into the IO-PCB. |
Input Time |
Time when the message was input into the IO-PCB. |
Program Modification |
MOD setting flag for the message. |
Prev. Message ID |
Previous message ID used in the message’s AL-PCB. |
Input Message Seq. |
Sequence of the message. |
PCB Flag |
PCB flag of the message. |
Segment count |
Number of segments in the message. |
Error Transaction |
Transaction code where the message error occurred. |
Command Option |
Command option of the message. |
SPA Length |
SPA length of the message. |
Error Code |
Error code of the message. |
Alt Type |
Alt message flag of the message. |
MQMD |
MQMD of the message. |
MQIIH |
MQIIH of the message. |
Message Length |
Length of the message. |
Message Status |
Current status of the message. |
Registered Date/Time |
Date and time when the message was created. |
Updated Date/Time |
Date and time when the message was last modified. |
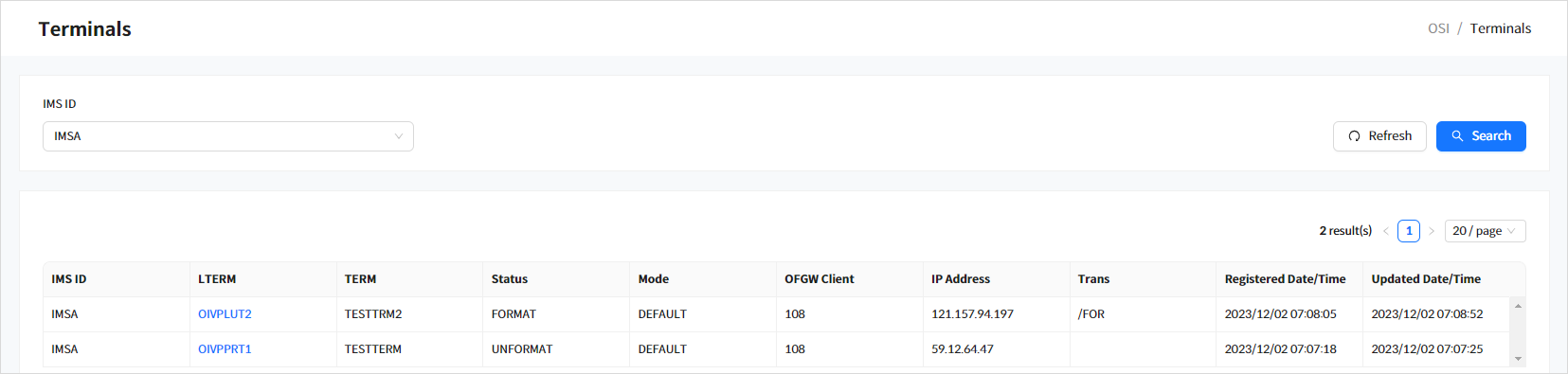
6. Terminals
Click [Terminals] from the navigation pane to view the dependent regions currently running in the OSI region.
When you enter the search criteria and click the [Search] button, the search results are displayed. Click the [Refresh] button above the list to refresh the list.
-
Search Conditions
The following describes the terminal search conditions.
Item Description IMS ID
IMS ID to search for.
-
Search Results
The following describes the search result columns.
Column Description IMS ID
IMS ID.
LTERM
LTERM name of the connected terminal.
TERM
Terminal name.
Status
Status of the terminal.
-
FORMAT: Initial state.
-
UNFORMAT: Logged-in state.
Mode
Modes of the terminal.
-
DEFAULT: Default mode.
-
PRINTER: Printer mode.
OFGW Client
Client ID of the OpenFrame GW.
IP Address
IP address from which the terminal is connected.
Trans
Last transaction performed by the terminal.
Registered Date/Time
Date and time when the terminal was connected.
Updated Date/Time
Date and time the terminal information was last updated.
-
6.1. Terminals Details
Click a specific 'LTERM' from the list in the [Terminals] page ([OSI] - Terminals) to go to the Terminal Details page.
Click the [<] icon to return to the previous page.
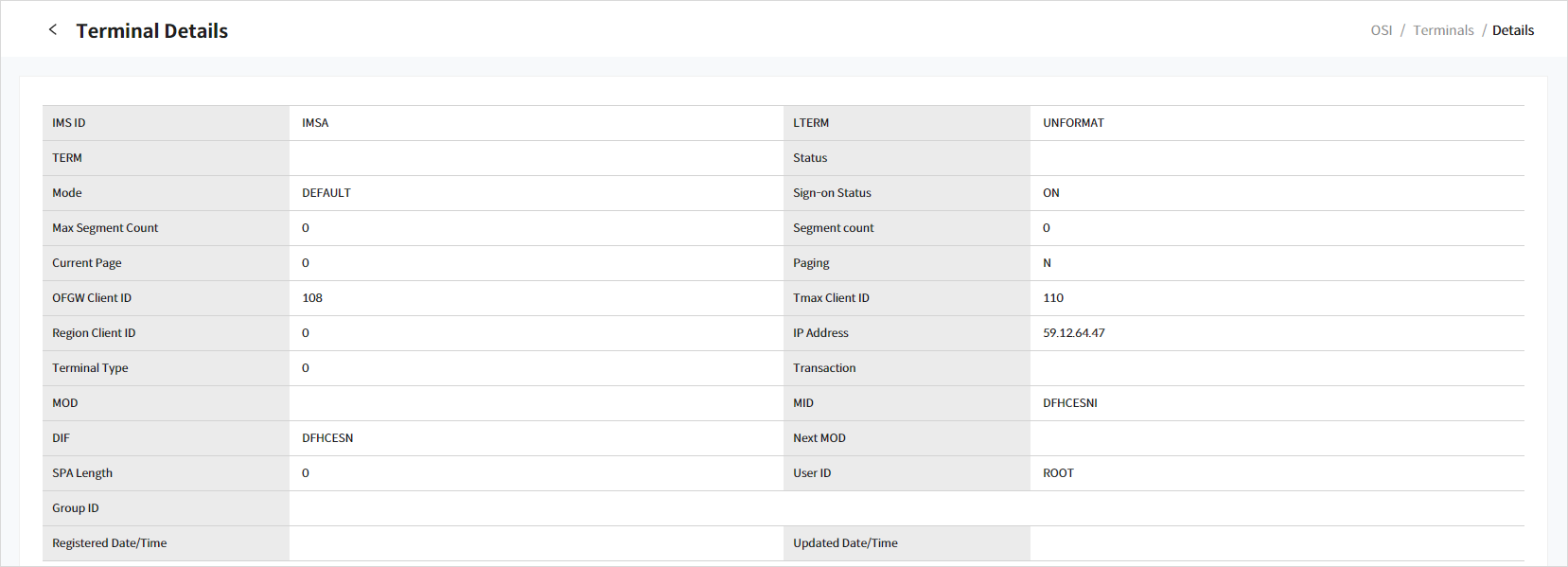
The following describes each item.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
IMS ID |
IMS ID. |
LTERM |
LTERM name of the connected terminal. |
TERM |
Terminal name. |
Status |
Status of the terminal.
|
Mode |
Modes of the terminal.
|
Sign-on Status |
TACF Sign-on status for the terminal.
|
Max Segment Count |
Maximum number of segments. |
Current Page |
Current page number of the terminal. |
Paging |
Indicates whether paging is currently enabled. |
OFGW Client |
Client ID of the OpenFrame GW. |
Tmax Client ID |
Client ID of the terminal. |
Region Client ID |
Client ID of the connected region. |
IP Address |
IP address from which the terminal is connected. |
Terminal Type |
Types of the terminal.
|
Transaction |
Last transaction performed by the terminal. |
MOD |
Current Message Output Descriptor (MOD) value of the terminal. |
MID |
Current Message Input Descriptor (MID) value of the terminal. |
DIF |
Device Input Format (DIF) value of the terminal. |
Next MOD |
MOD for the next transaction. |
SPA Length |
Length of the SPA. |
User ID |
ID of the user. |
Group ID |
ID of the group. |
Registered Date/Time |
Date and time when the terminal was connected. |
Updated Date/Time |
Date and time when the terminal information was last updated. |