The ALLOCATE statement allocates storage for controlled variables. Controlled parameters can also be allocated. An ALLOCATE statement can describe the array bounds and string length of a controlled variable.
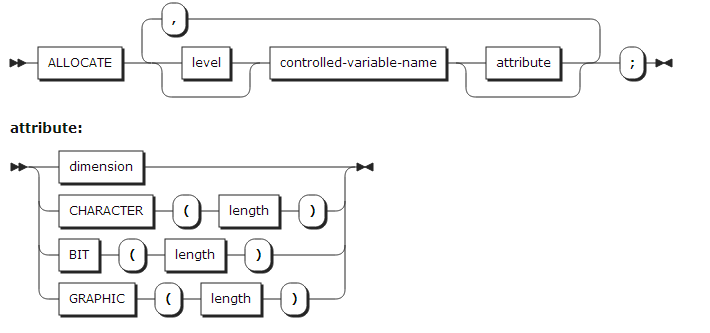
Array bounds and string lengths are evaluated when an ALLOCATE statement is executed.
-
An ALLOCATE statement or a DECLARE or DEFAULT statement must specify required size and string length information.
-
If the DIMENSION attribute or a string length are specified in an ALLOCATE statement, they will override attributes specified during a variable declaration.
-
If a bound or string length is specified as an asterisk (*) in an ALLOCATE statement, the information of the current generation will be used. If there is no current generation, the information will be undefined and a program error will occur.
-
The DIMENSION attribute specified in an ALLOCATE statement must match the number of declared dimensions. That is, n DIMENSION attributes must be specified for an n-dimensional array.
-
The BIT, CHARACTER, and GRAPHIC attributes must be the same as the attributes declared in a DECLARE statement.
The following example uses an ALLOCATE statement:
DCL X(M,N) CHAR(L) CTL; M = 10; N = 5; L = 100; ALLOCATE X(5,5) CHAR(200);