1. ASSIGN Statement
The assignment statement evaluates an expression and assigns a result value to one or more target variables. If a target or pseudo variable attributes are different from source attributes, data conversion will be required.
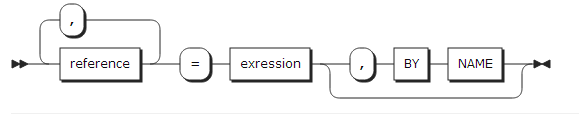
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
reference |
A target or pseudo variable. |
expression |
A source expression. |
BY NAME |
An option used in a structure assignment. For more information, refer to "Assignment Execution". |
Compound Assignment Statement
A compound assignment statement uses compound assignment operations.

| Component | Description |
|---|---|
reference |
Target variable or pseudo variable. |
compound operator |
Operator to apply to the source and target before the assignment is made. Compound operators that can be used in an assignment statement are:
|
expression |
Expression of the source. |
The following are examples of executing compound assignment statements.
X += 5; ==> X = X + 5; X *= Y - 1; ==> X = X * (Y - 1);
Target Variables
Target variables can be elements, arrays, structures, or pseudo variables.
-
Array
-
A target variable must be an array of scalars or structures. A source must be a scalar expression or an expression with the same number of dimensions and the same bounds as a target.
-
-
Structure
-
If BY NAME is specified, each target and source must be a structure.
-
If BY NAME is not specified, each target must be a structure and each source must be a scalar or a structure that is the same as a target.
-
If BY NAME is not specified and a source is described as a NULL string("") then:
-
all targets will be padded with '00’X.
-
all numeric targets will 0.
-
all character and graphic targets will be padded with blanks.
-
-
Assignment Execution
-
Array
-
All array operands (of sources and targets) must have the same number of dimensions and the same bounds.
-
An array assignment is expanded into a loop as follows:
DO I1 = LBOUND( target-variable, 1 ) to HBOUND( target-variable, 1 ); DO I2 = LBOUND( target-variable, 2 ) to HBOUND( target-variable, 2 ); ... DO IN = LBOUND( target-variable, N ) to HBOUND( target-variable, N ); generated element assignment ; END;
-
N is the number of dimensions of a target. In the generated element assignment, I1 through IN are used as subscripts. If a source is scalar, subscripts will not be used.
-
-
Structure
-
If BY NAME is not specified:
-
All operands must be the same structure, not an array. The member of a structure can be an array.
-
An assignment will be executed on each member. If the number of members is n, assignments will be executed n times.
-
If a member is an aggregate, assignments will be executed on all members of the member.
-
-
If BY NAME is specified:
-
The same name as the name of a target structure member will be searched from a source from the first member. The members will be direct children of the structure, not children of a child of the structure.
-
A search will be repeated until a same name is found.
-
If a searched member is a structure or an array of structures, an assignment with the BY NAME option will be executed.
-
If a searched member is a scalar or an array of scalars, an element assignment will be executed.
-
The above steps will be repeated for following members.
-
-
The following is an example of a structure assignment using BY NAME:
DCL 1 ONE, DCL 1 TWO, DCL 1 THREE 2 PART1, 2 PART1, 2 PART1, 3 RED, 3 BLUE, 3 RED, 3 ORANGE, 3 GREEN, 3 BLUE, 2 PART2, 3 RED, 3 BROWN, 3 YELLOW, 2 PART2, 2 PART2, 3 BLUE, 3 BROWN, 3 YELLOW, 3 GREEN; 3 YELLOW; 3 GREEN;
-