Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of the system and describes its process and service types.
1. Overview
The TCP/IP thread gateway (hereafter TCPGWTHR) plays the role of an interface between non-Tmax clients (non-Tmax servers) and Tmax. A non-Tmax client and the gateway communicate with each other through TCP/IP, and the gateway and Tmax system through Tmax.
The gateway can run either as a server or a client depending on where the request for the connection, not service, started. When the gateway is running as a server, it is using a remote connection. Otherwise, it is using a gateway (thread) connection. Regardless of which side initiated the connection request, both sides can request for a service as long as a connection has been established.
Connection is made by allocating a handler thread to a client which allows the user to add an arbitrary protocol between the client and thread. A Tmax service can send a request to a client either by internally finding an idle thread connected to the client in a round robin fashion, or using a thread connected to the client. The gateway is included in and managed by Tmax.
The previous version of TCP/IP gateway simply sent and received requests/responses by connecting to multiple number of remote channels in a single process. However, TCPGWTHR can be used in various environments and users can add arbitrary protocols to it. Since RCA (Raw Client Agent) connects to Tmax as a client, it can request services to Tmax, but not to RCA. In contrast, TCPGWTHR supports two-way service requests.
The following is the operating structure of TCPGWTHR.
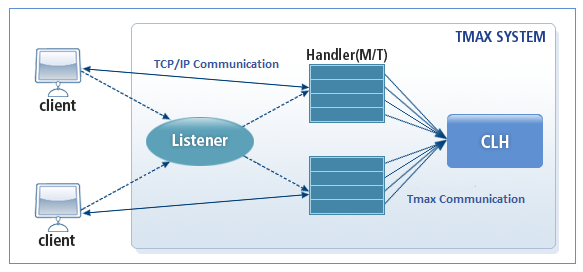
In the server mode, TCPGWTHR is composed of the listener and handler processes. In the client mode, it is composed of the client shared memory management process (hereafter Clishm) and the handler process.
-
Listener Process
This process is needed when TCPGWTHR runs as a server. The listener listens through the given port and forwards any incoming connection requests to the handler process. Since the listener process is connected to a Tmax system, it starts and shuts down with the Tmax system.
-
Handler Process
This process handles actual requests by accessing a non-Tmax client (non-Tmax server). It distributes the socket received from the listener thread to allocate a thread to process the request, or a specific thread can process the request by connecting to a non-Tmax client (non-Tmax server).
Many threads exist in the handler process. Each thread is connected to a remote server. As a server, TCPGWTHR receives a socket from the listener process, and each thread in the handler process connects with the remote server when it runs as a client. A connected thread can receive a request from a non-Tmax client or can make a request to a Tmax service.
Each handler process can generate up to a maximum of 50 threads.
-
Clishm Process
This process is used instead of the listener process in the client mode to initialize the shared memory. Since the Clishm process is connected to a Tmax system, it starts and shuts down with the Tmax system.
2. Service Types
2.1. Server Mode
In the server mode, a client connection is established using the following 2 methods.
-
Shared method
-
Dedicated method
Client Connection (Shared Method)
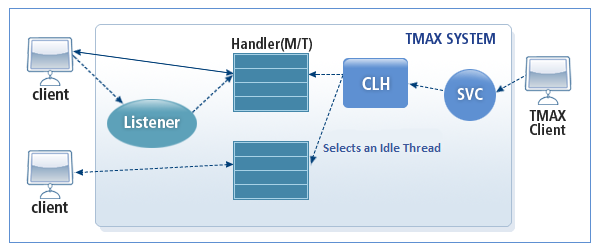
A listener process is required when running in the server mode. The listener process receives connection requests from a non-Tmax client and evenly distributes the requests to handler processes in a round robin fashion.
When a Tmax service calls a gateway service, the request is sent to an idle thread of the handler process connected to the client in a round robin fashion.
The following is the operating structure of TCPGWTHR when the client is connected using the shared method in the server mode.
The following is a sample configuration in the Tmax environment file for connecting a client using the shared method in the server mode.
*SERVER
tcpgwlsn SVGNAME = svg1, MIN = 1, MAX = 1,
SVRTYPE = CUSTOM_GATEWAY, RESTART = N,
CLOPT = "-- -P 1029 -N 3 -k 98765"
tcpgwhdr1 SVNAME = svg1, MIN = 3, MAX = 3, SCHEDULE = RR,
SVRTYPE = CUSTOM_GATEWAY, CPC = 10, TARGET = tcpgwhdr,
CLOPT = "-- -P 1029 -N 10 -s –L tcpgwlsn"
*SERVICE
svcgw SVRNAME = tcpgwhdr1
Client Connection (Dedicated Method)
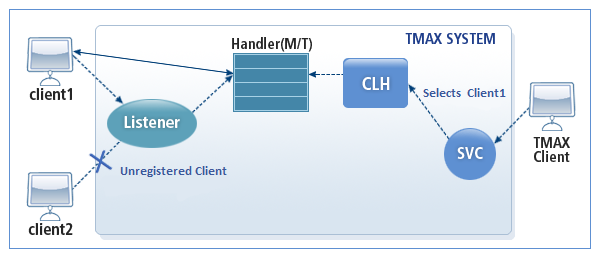
A listener process is required when running in the server mode. When the listener process receives a connection request from a non-Tmax client, it checks if the client is registered in the gateway environment file and then sends it to the handler process to allocate a thread to it. If the client is not registered in the gateway environment file, then it displays a warning message and rejects the connection request. If the client information cannot be found in the shared memory, then it can be dynamically registered since the gateway environment file search will be re-executed internally.
To distinguish clients in the Tmax service, only one connection is allowed for each IP. If the same client requests for an additional connection when the client is already connected to a thread, the existing connection will be disconnected and the additional request will also be cancelled.
When a Tmax service calls a gateway service, it must use the client ID registered in the gateway configuration file and the request is sent using a thread that is internally connected to the gateway. The total number of threads that can be allocated to the handler processes equals the number of clients configured in the gateway environment file plus 50 additional threads for dynamic accesses. Also, the number of handler processes must be adjusted to make sure that the number of threads per handler process does not exceed 50.
The following is the operating structure of TCPGWTHR when the client is accessed using the dedicated method in the server mode.
The following is a sample configuration in the Tmax environment file for connecting a client using the dedicated method in the server mode.
*SERVER
tcpgwlsn SVGNAME = svg1, MIN = 1, MAX = 1,
SVRTYPE = CUSTOM_GATEWAY, RESTART = N,
CLOPT = "-- -P 1029 -N 3 -k 98765 -F tcpgwlsn.dat"
tcpgwhdr1 SVNAME = svg1, MIN = 3, MAX = 3, SCHEDULE = RR,
SVRTYPE = CUSTOM_GATEWAY, CPC = 10, TARGET = tcpgwhdr,
CLOPT = "-- -P 1029 -s –L tcpgwlsn"
*SERVICE
svcgw SVRNAME = tcpgwhdr1
The following is a sample configuration in the gateway environment file for connecting a client using the dedicated method in the server mode.
# Client IP Server Port Client ID 61.33.32.123 1029 CLI1 61.33.32.124 1029 CLI2 61.33.32.125 1029 CLI3 61.33.32.126 1029 CLI4
2.2. Client Mode
There are two types of client modes according to the number of servers to connect.
-
Single server connection
-
Multi server connection
Single Server Connection
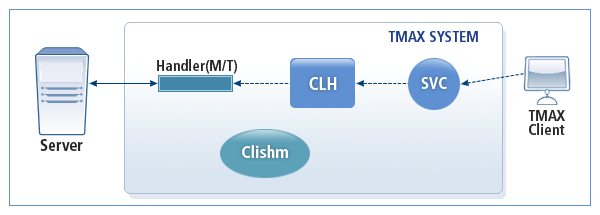
A Clishm process, instead of a listener process, is required when running in the client mode. The port and server IP to access the Tmax environment file must be registered to access a non-Tmax server.
The following is the operating structure of TCPGWTHR when connecting to a single server in the client mode.
The following is a sample configuration in the Tmax environment file for connecting a client through the single server connection method in the client mode.
*SERVER
clihdrshm SVGNAME = svg1, MIN = 1, MAX = 1,
SVRTYPE = CUSTOM_GATEWAY,
CLOPT = "-- -N 1 -k 91000"
tcpgwhdr1 SVNAME = svg1, MIN = 1, MAX = 1,
SVRTYPE = CUSTOM_GATEWAY,
CPC = 9, SCHEDULE = RR, TARGET = tcpgwhdr,
CLOPT = "-- -k 91000 -P 3777 –r 100.100.100.1 -N 1 –L clihdrshm"
*SERVICE
svcgw SVRNAME = tcpgwhdr1
Multi-server Connection
A Clishm process, instead of a listener process, is required when running in the client mode. To access multiple non-Tmax servers, information about each server must be registered in the gateway environment file.
When a Tmax service calls the gateway service, it checks for an allocated thread. If no thread has been allocated, an empty thread is allocated to access a non-Tmax server.
The following is the operating structure of TCPGWTHR when accessing multiple servers in the client mode.
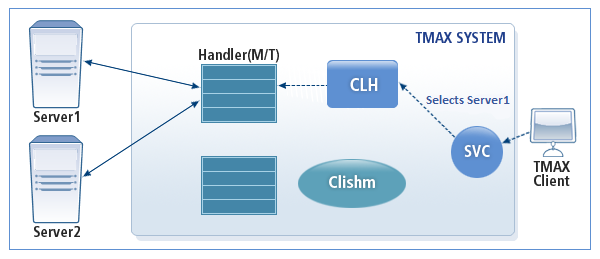
The following is a sample configuration in the Tmax environment file for connecting a client using the multi-server method in the client mode.
*SERVER
clihdrshm SVGNAME = svg1, MIN = 1, MAX = 1,
SVRTYPE = CUSTOM_GATEWAY,
CLOPT = "-- -N 10 -k 91000 -F tcpgwhdr.dat"
tcpgwhdr1 SVGNAME svg1, MIN = 10, MAX = 10, SVRTYPE = CUSTOM_GATEWAY,
CPC = 9, SCHEDULE = RR, TARGET = tcpgwhdr,
CLOPT = "-- -k 91029 -F tcpgwhdr.dat –L clihdrshm"
*SERVICE
svcgw SVRNAME = tcpgwhdr1
The following is a sample configuration in the gateway environment file for connecting a client using the multi-server connection method in the client mode.
# Server IP Server Port Server ID 61.33.32.123 9000 SERVER1 61.33.32.124 9100 SERVER2