Introduction
This chapter introduces the WebService gateway and its operating structure.
1. Overview
A web service is a standardized technology that allows applications to communicate with each other, independent of platform and programming languages. It is also a software interface that implements network-accessible operations through standard XML messaging. Since a web service defines the messaging protocol, programming standards, and a convenient environment for finding the desired service, it is visible and can be used via the Internet by any user with the proper permissions.
1.1. Web Service
A web service is an application that can be accessed through the Internet Uniform Resource Identifier (URI). Web service interface and binding are defined, described, and can be discovered in XML documents. A web service can interoperate with other published web services on the Internet and with existing back-end applications.
Up to now, the application architecture has been classified into two categories, the unified system that runs on the mainframe and the client/server system that runs on the desktop.
Although both systems operate well, their programs can only run on the particular system architecture. Application programs in such closed architecture are not easily accessible to many users on the web. As a result, the software industry has moved towards the direction of Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA), and the applications on SOA can dynamically interoperate with each other over the web.
SOA applications allow smaller, modularized subsystems in place of the existing large-scale software system. Each subsystem can be implemented using different technologies, exist on a different machine, and be reused. Any user can easily access SOA applications over the internet using standard web protocols such as XML and HTTP.
These service-oriented technologies have already been implemented many years ago through various technologies, such as RMI, COM, and CORBA. While these technologies have the downside of being dependent on the vendor or implemented technology, web services are not.
Characteristics of a Web Service
A web service has the following characteristics.
-
A web service can be accessed via the Web.
-
A web service describes itself.
-
It describes its own roles, functions, and properties allowing a web service client to understand the service. The service is described in a file called WSDL(Web Service Description Language) and published for use by other applications.
-
It ensures reliability through recovery/rollback.
-
-
A web service communicates with a web service client through XML messages exchanged using standard internet protocols such as HTTP. A web service client can be an application or another web service.
-
A web service runs in the request-response or one-way method, and can be called through synchronous or asynchronous communication. Regardless of such operating and communication methods, a message is the fundamental unit of exchange between a web service and a web service client.
Advantages of a Web Service
A web service provides the following advantages.
-
A web service supports open internet standards.
A web service sets open standards such as SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol), WSDL, UDDI (Universal Description, Discovery, and Integration) for web service interoperability which also ensures the interoperability of application programs that support web services.
-
A web service is platform and language independent.
-
A web service uses web protocols like HTTP to allow easy access without issues such as a firewall.
2. WebService Gateway
WebService Gateway (WebService Gateway, hereafter WSGW) is a gateway server that allows a web service provider to call a Tmax service or Tmax to call an external web service provider.
WSGW performs the roles of the provider and consumer. When WSGW acts as the web service provider, a Tmax service can be used as a web service without modification. WSGW acts as a service provider that processes SOAP request messages exchanged using the HTTP protocol.
In order to run WSGW, it must be registered in the GATEWAY section of the Tmax environment file, and it also requires the configuration file and service information file.
2.1. Web Service Provider
When the SOAP request message is received from a web service consumer, WebService gateway analyzes the SOAP message and calls the applicable Tmax service. It wraps the results into a SOAP message and returns it to the consumer.
WSGW uses the tmmbfgen, untmmbfgen, and xwsdlgen utilities to function as a service provider. To run the service, the Tmax environment configuration, WebService gateway configuration, service information (service information binary file), and WSDL files must be configured.
The following is the operating structure of WSGW as a web service provider.
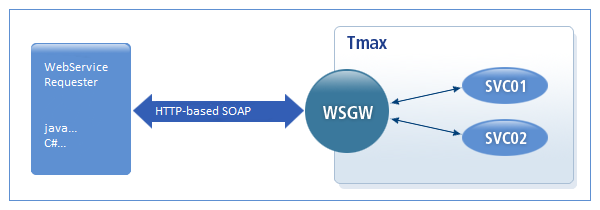
-
Create the service information file.
-
Create the service information binary file using tmmbfgen.
-
Create the WebService gateway configuration file.
-
Configure WebService gateway in the Tmax environment configuration file.
-
Start WebService gateway by executing the wsgwreload command in tmadmin or by restarting Tmax.
-
Create the wsdl document using xwsdlgen and provide it to the service consumer.
-
The service consumer creates the client application using the wsdl document.
2.2. Web Service Consumer
A web service consumer requests service from the provider in Tmax that provides external web services.
When a Tmax client or server calls a service allocated to WebService gateway, the request message is wrapped into a SOAP message and sent to the provider (such as WAS) through WebService gateway. WSGW connects to the provider upon a request and terminates the request after receiving the message.
WSGW uses the tmmbfgen, untmmbfgen, and xwsdlgen utilities to function as a service consumer. To run the service, the Tmax environment configuration, WebService gateway configuration, service information (service information binary file) files must be configured.
The following is the operating structure of WSGW as a consumer.
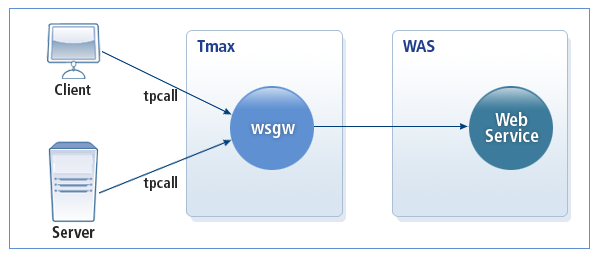
-
Create the service information file.
-
Create the service information binary file using tmmbfgen.
-
Create the WebService gateway configuration file.
-
Configure WebService gateway in the Tmax environment configuration file.
-
Start WebService gateway by executing the wsgwreload command in tmadmin or by restarting Tmax.
-
Call the web service from the Tmax client and server.