Introduction
This chapter describes the configuration, basic structure, and features of RCA.
1. Overview
RCA (Raw Client Agent) uses a TCP/IP socket to enable communication between a Tmax client and an existing communication program unable to use the Tmax client library.
RCA is a multithreaded program and each thread corresponds to a Tmax client. The number of threads to be started must be specified according to the Tmax server license. RCA runs POSIX threads, which are scheduled by the kernel. Hence, RCA can process client requests more efficiently compared to a multi-CPU environment.
RCA is divided into a local mode and a remote mode according to the location of the RCA.
-
Local Mode
Located within the Tmax system to process server and client operations.
-
Remote Mode
Located outside the Tmax system to process server and client operations.
For more information about each mode, refer to System Usage. For more information about the system structure, refer to System Structure.
2. Configuration
The following describes how to configure an RCA.
-
RCAL
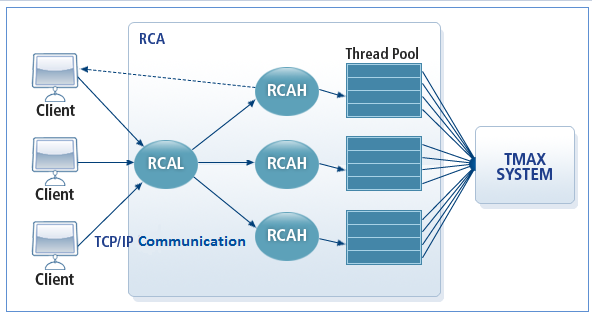
RCAL corresponds to a server process in a TCP/IP structure. The role of an RCAL is to listen for a connection request from other communication programs and send the connection information to RCAH. RCAL does not initiate a connection to other programs.
Configure RCAL in the following directory to control user access.
$TMAXDIR/bin/rcal
-
RCAH
RCAH is created with user logic.
RCAH is an executable file created by combining the Tmax client thread library ($TAMXDIR/lib/librcah.so) and a user defined client program. It is created with user logic. RCAH is a multithreaded program, which means a single client program (RCAH) can make connections to the Tmax system based on the number of threads.
RCAL can run up to 500 RCAHs simultaneously, and each RCAH contains up to 60 threads. A single RCA module supports up to 30,000 (500 * 60) clients. In this multithreaded process, global variables and static variables must be used carefully. For an example of an RCAH program, refer to RCAH Example.
-
Management Tool
RCA uses rcastat to monitor RCA and rcakill to terminate RCA.
Management Tool Description rcastat
Monitors RCA configuration information and the number of clients that access RCA. For more information about rcastat, refer to Monitoring.
rcakill
Removes the resources that an RCA uses to terminate the RCA.
3. System Structure
The system is divided into server mode and client mode according to the handling of the request.
3.1. Server Mode
In server mode, RCAL waits for a connection from a client to process the request.
The following is the flow of RCAL and RCAH processes in server mode.
3.2. Client Mode
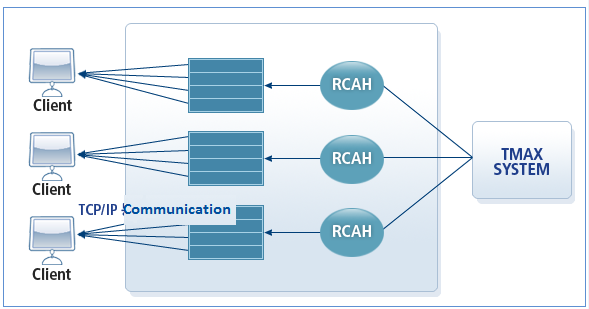
In client mode, a client connects to an RCA to send a request. A remote socket program listens for a connection request and each RCAH thread sends the connection request to the Tmax system.
When connected to the remote socket program, the RCA operates the same in both server and client mode. However in client mode, RCAL does not wait for a connection request from a remote node.
The following is the flow of an RCAH process in client mode.
4. Feature
RCA supports a multiport configuration. Up to 32 ports can be configured to support various types of clients. Different logic can be configured for each port to support the development of flexible business processes.
The following is an example of specifying multiple ports. The default port is 8899.
RCA_PORT="9000, 9001, 9002, 9003"
While programming, the values passed as arguments of thrinit(), thrmain(), and thrdone() are pointers to the RCAINFO struct ($TMAXDIR/usrinc/rca.h in the following example), and a developer can use the port number indicated in this struct to configure a logic for the port.
/* ------ type definition ------ */
typedef struct {
int fd;
int portno;
int count;
int status1;
int status2;
void *user_data;
void *system_data;
} *RCAINFO;
The following describes each struct field.
| Struct Field | Description |
|---|---|
fd |
TCP/IP socket created when a client accessed. |
portno |
Port number. In this example, it is 9000, 9001, 9002, or 9003. |
count |
Number of times a thread was called. |
|
The fields not mentioned in this guide are used internally in RCA, and they must not be manipulated by a user. |