Environment Configuration
This chapter describes how to register a Host-link.
1. Tmax Configuration File
A Host-link can be used by adding it to the SERVICE section of the Tmax configuration file. However, to use the transaction function (2PC, Synclevel2), the GATEWAY section must be used instead of the SERVER section.
Currently, the transaction gateway is available only in LU 6.2 and is supported only when the gateway type is SNACICS.
|
For more information about the configuration items of each section, refer to Tmax Administration Guide. |
1.1. SERVER Section
The following shows the format of the SERVER section. For actual registration, refer to the usage example.
*SERVER
ServerName SVGNAME = server-group-name,
[SVRTYPE = CUSTOM_GATEWAY,]
[MIN = number,]
[MAX = number]
...
Required Parameters
-
ServerName = string
-
Name of the server that manages Host-link shared memory. This must be specified only once in the SERVER section.
-
A server can be registered with a user-specified name. After registration, the registered name of the Host-link program must be copied to the path specified in the APPDIR entry of the environment configuration file.
-
-
SVGNAME = string
-
Name of the server group.
-
Optional Parameters
-
SVRTYPE = CUSTOM_GATEWAY
-
Type of the server. Use CUSTOM_GATEWAY to specify Host-link.
-
-
MIN = numeric
-
Range: 1 to MAX_INT
-
Default Value: 1
-
Minimum number of Host-link processes.
-
-
MAX = numeric
-
Range: 1 to MAX_INT
-
Default Value: 1
-
Maximum number of Host-link processes.
-
Usage
The following is an example of a SERVER section configuration.
*SERVER
hkh SVGNAME = svg1,
SVRTYPE = CUSTOM_GATEWAY
snalugw SVGNAME = svg1,
SVRTYPE = CUSTOM_GATEWAY,
MIN = 2,
MAX = 2
...
1.2. GATEWAY Section
The following shows the format of the GATEWAY section. The GATEWAY section is optionally configured if necessary. For actual registration, refer to the usage example.
*GATEWAY
GatewayName NODENAME = node-name,
GWTYPE = SNACICS,
[CPC = channel-number]
...
Required Parameters
-
GatewayName = string
-
Name of the gateway. Specify the name of the Host-link executable file.
-
A gateway can be registered with a user-specified name. After registration, the registered name of the Host-link program must be copied to the path registered in APPDIR of the environment configuration file.
-
-
NODENAME=string
-
Name of the node.
-
-
GWTYPE=SNACICS
-
Type of the gateway. Set the currently supported SNACICS.
-
Optional Parameters
-
CPC = numeric
-
Range: 1 to 128
-
Default Value: 1
-
Number of CPCs. CPC is an acronym for CLH Per Channel, referring to the number of CLH process channels between the nodes of the Tmax system. CLH is the Tmax engine that connects servers with clients.
-
Usage
The following is an example of a GATEWAY section configuration.
*GATEWAY
snacics_s GWTYPE = SNACICS,
NODENAME = node1,
CPC = 10
snacics_r GWTYPE = SNACICS,
NODENAME = node1,
CPC = 10
1.3. SERVICE Section
The following shows the format of the SERVICE section. For actual registration, refer to the usage example.
*SERVICE ServiceName SVRNAME = server-process-name ...
Required Parameters
-
ServiceName = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters (8-character limit when using a Map in CONVERSION)
-
Name of the function (service routine name) within the server program. The name must be unique in the SERVICE section. It must be unique in a multi-domain environment as well.
-
-
SVRNAME = server-process-name
-
Name of the server that the service will belong to.
-
Usage
The following is an example of a SERVICE section configuration.
*SERVICE SNALUGW SVRNAME = snalugw ...
2. Host-link Configuration File
The Host-link configuration file is used to register various information required to run the Host-link system, including service information, data logging, data conversion, and session channel usage method. This file contains 8 sections. The HOSTLINK, SERVER, SERVICE, and LUINFO sections are required. All other sections are optional.
2.1. HOSTLINK Section
The following shows the format of the HOSTLINK section. It specifies the environment of the Host-link system.
*HOSTLINK
Host-link Name TMAX = Y|(N) ,
SHMKEY = shared memory segment key
Required Parameters
-
Host-link Name = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
Host-link name. The name must be unique in the HOSTLINK section.
-
-
TMAX = Y|N
-
The following table describes each configuration value. Only Y is currently supported.
Value Description Y
Operates Host-link by linking with Tmax.
N
Operates Host-link independently. This option is not currently supported.
-
-
SHMKEY = numeric
-
Range: 32768 to 262143
-
Host-link manages internal information by using shared memory. This value indicates the segment in the shared memory.
-
2.2. SERVER Section
The following shows the format of the SERVER section. It specifies the Host-link environment.
* SERVER
ServerName TMAXSVRNAME = tmaxserver name,
TMAXSVRNO = server index,
SVRTYPE = {LU0 | LU62S | LU62R | CTG | CICSTCPIP | IMSTCPIP },
[HLINKNAME = Host-Link name,]
[FUNCTION = DPL | DTP,]
[HOSTID = host id,]
[SESSION_TYPE = IMS_INITSELF|IMS_AUTO|CICS_INITSELF|CICS_AUTO,]
[MSGSIZE = 1 ~ MAX_INT,]
[TIMEWAIT = WAIT | NOWAIT,]
[LINKDOWN_TIMEOUT = 1 ~ MAX_INT,]
[SESSION_TIMEOUT = 1 ~ MAX_INT,]
[BUFFERING = Y | N,]
[INBOUNDLU = (POOL) | DEDICATE,]
[BIDLU = (POOL) | DEDICATE,]
[LINKNAME = linkname,]
[TRXID = transaction_xid,]
[HOSTADDR = Host IP Address or DNS,]
[HOSTPORT = Host Port,]
[LISTENPORT = listen port,]
[SESSION = 1 ~ MAX_INT,]
[MAXSVR = 1 ~ MAX_INT,]
[REPSEND = Y | N,]
[COMMSIZETYPE = INPUT_EQUAL|INPUT_1024|INPUT_2048|INPUT_4096|
MAPFILE|SPECIFY_SIZE,]
[DELOUTHSIZE = 1 ~ MAX_INT,]
[SVRLIST = Server List]
Required Parameters
-
ServerName = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
Server name is a logical name that represents a single Host-link process. It must be unique in the SERVER section.
-
If a Host-link is registered and the MIN and MAX parameters are set to 2 in the Tmax configuration file, two servers must be specified in the SERVER section.
-
-
TMAXSVRNAME = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
The name of this parameter must be the same as the server name specified in the SERVER section of the Tmax configuration file.
-
-
TMAXSVRNO = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
Indexes for the MIN and MAX parameters of the SERVER section in the Tmax configuration file.
-
If the MIN and MAX in the SERVER section are both set to 2, the indexes can be set to 00 and 01, starting from 00.
-
-
SVRTYPE = {LU0 | LU62S | LU62R | CTG | CICSTCPIP | IMSTCPIP}
-
Type of protocol used to communicate with the host.
-
Currently, only LU0, LU62S, LU62R, and CTG are supported.
-
Optional Parameters
-
HLINKNAME = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
This parameter must be the same as the Host-link name of the HOSTLINK section.
-
-
FUNCTION = DPL | DTP
-
Method for calling a function.
-
This parameter is applicable only when SVRTYPE is either LU62S or LU62R.
-
-
HOSTID = string
-
Size: Up to 4 characters
-
ID of the host with which the client wants to establish a session.
-
To create a session with the host, the Host-link sends the Initself data to the host. HOSTID is included in this Initself data.
-
This parameter is applicable only when SVRTYPE is set to LU0. This parameter is required when SVRTYPE is LU0.
-
-
SESSION_TYPE = IMS_INITSELF | IMS_AUTO | CICS_INITSELF | CICS_AUTO
-
Default Value: IMS_INITSELF
-
Method for processing Initself when creating a session to the host.
-
This parameter is applicable only when SVRTYPE is set to LU0.
-
-
MSGSIZE = numeric
-
Default Value: 1024
-
Range
Type Description LU 0
1 to MAX_INT
LU 6.2
1024 to MAX_INT (Set to 32,000 when using OpenFrame CICS.)
-
-
TIMEWAIT = WAIT | NOWAIT
-
Set the behavior when a timeout occurs on the Tmax client or server.
-
The following describes each configuration value.
Value Description WAIT
Maintains the current session.
NOWAIT
Terminates the current session and starts a new one.
-
-
LINKDOWN_TIMEOUT = numeric
-
Range: 1 to MAX_INIT
-
Time interval to check whether an idle link between the Host-link and the host is still active.
-
-
SESSION_TIMEOUT = numeric
-
Size: 1 to MAX_INIT
-
Time interval to check whether an idle session is still active.
-
-
BUFFERING = Y | N
-
This parameter must be specified to use sessions in the pool mode.
-
Set the behavior when no session is available for the Host-link process.
-
The following specifies each configuration value.
Value Description Y
Does not send a new request to another process, but stores it in a queue.
N
Sends a new request to another process.
-
-
INBOUNDLU = (POOL) | DEDICATE
-
Mode for operating sessions.
-
This parameter is applicable only when SVRTYPE is set to LU0.
-
-
BIDLU = (POOL) | DEDICATE
-
Mode for processing BID data. For more information about the pool and dedicate modes, refer to INBOUND.
-
This parameter is applicable only when SVRTYPE is set to LU0.
-
-
LINKNAME = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
Name of the link used to establish a physical connection to the host.
The name can be checked using the following command.
sna –d l
-
Host-link performs services only when the LINKNAME is activated. If the name is not activated, the Host-link process will be shown as NOT-READY in tmadmin.
-
This parameter is required when SVRTYPE is set to LU0, LU6.2S, or LU6.2R.
-
-
TRXID = string
-
Size: Up to 4 characters
-
Transaction ID. The specified information is used along with the program name to locate the host service.
-
-
HOSTADDR = literal
-
Size: Up to 255 characters
-
Host address. An IP address or DNS can be specified.
-
This parameter is applicable when SVRTYPE is set to CICSTCPIP or IMSTCPIP. This parameter is currently unused.
-
-
HOSTPORT = numeric
-
Range: 1 to Max_INT
-
Host port.
-
This parameter is applicable only when SVRTYPE is set to CICSTCPIP or IMSTCPIP. This parameter is currently unused.
-
-
LISTENPORT = numeric
-
Range: 1 to Max_INT
-
Listening port.
-
This parameter is applicable only when SVRTYPE is set to CICSTCPIP or IMSTCPIP. This parameter is currently unused.
-
-
SESSION = numeric
-
Range: 1 to Max_INT
-
Session value used for connecting to the host when SVRTYPE is set to CTG.
-
For LU0 or LU6.2, this parameter is automatically set to the total number of sessions of the server’s LU.
-
-
MAXSVR = numeric
-
Range: 1 to Max_INT
-
Set this parameter to the same value as MIN and MAX in the Tmax configuration file.
-
When Host-link processes start, the number of sessions specified in SESSION will be connected to the Host-link processes.
-
This parameter is applicable only when SVRTYPE is set to CTG.
-
-
REPSEND = Y | N
-
For tpacall (NOREPLY), this parameter applies to the response.
-
The following specifies each configuration value.
Value Description Y
Sends the response using sendtype = AP_SEND_DATA_DEALLOC_FLUSH.
N
Sends the response using sendtype = AP_SEND_DATA_DEALLOC_ABEND.
-
-
COMMSIZETYPE = INPUT_EQUAL | INPUT_1024 | INPUT_2048 | INPUT_4096 | MAPFILE | SPECIFY_SIZE
-
COMMAREA size.
-
This parameter is applicable only when SVRTYPE is set to LU62S.
-
The following describes each configuration value.
Value Description INPUT_EQUAL
Must be set to the same size as the input data.
INPUT_1024
Must be set to the nearest multiple of 1024 that is equal to or greater than the size of the input data.
INPUT_2048
Must be set to the nearest multiple of 2048 that is equal to or greater than the size of the input data.
INPUT_4096
Must be set to the nearest multiple of 4096 that is equal to or greater than the size of the input data.
MAPFILE
Must be set to the same value as 'COMMSIZE' in the map file.
SPECIFY_SIZE
Must be set to the same value as 'MSGSIZE'.
-
-
DELOUTHSIZE = numeric
-
Range: 1 to Max_INT
-
Size of data to be discarded when the host receives data. Data will be discarded from the beginning portion of the data.
-
This parameter is applicable only when SVRTYPE is set to LU0 or LU62S.
-
-
SVRLIST = string
-
Size: Up to 256 characters
-
This parameter is applicable only when SVRTYPE is set to CTG.
-
Usage
The following is an example of parameter settings for session operation.
-
SNA LU 0
If the INBOUNDLU parameter is set to POOL, Host-link requests services from the host in the round robin mode using a session. If the BIDLU parameter is set to DEDICATE, it will receive BID data using a specific session.
*SERVER snalugw00 ... INBOUNDLU = POOL, BIDLU = DEDICATE, ... -
SNA LU 6.2
If the FUNCTION parameter is set to DPL, sessions are used in DPL mode when the Tmax system requests services from the host.
*SERVER snalusgw00 ... FUNCTION = DPL, ...
2.3. SERVICE Section
The following is the format of the SERVICE section. It is used to configure BID, ROP, OUT, and TCL services of the SERVER section.
*SERVICE
ServerName [BIDSVCNAME = BID svc name,]
[BIDSVCPOS = 1 ~ MAX_INT,]
[BIDSVCSIZE = 1 ~ 16,]
[ROPSVCNAME = ROP svc name,]
[ROPSVCPOS = 1 ~ MAX_INT,]
[ROPSVCSIZE = 1 ~ 16,]
[OUTSVCNAME = outsvc name,]
[OUTSVCPOS = 1 ~ MAX_INT,]
[OUTSVCSIZE = 1 ~ 16,]
[RLYSVCNAME = relay svc name,]
[RLYSVCPOS = 1 ~ MAX_INT,]
[RLYSVCSIZE = 1 ~ 16,]
[TCLSVCNAME = tclsvc name,]
[TCLSVCPOS = 1 ~ MAX_INT,]
[TCLSVCSIZE = 1 ~ 16,]
[CANSVCNAME = cansvc name,]
[POSTOKSVCNAME = postoksvc name,]
[POSTFAILSVCNAME = postfailsvc name]
Required Parameters
-
ServerName = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
This parameter must be the same as the server name specified in the SERVER section.
-
Optional Parameters
-
BIDSVCNAME = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
Name of the Tmax service that will process BID data that was forcibly transmitted from the host.
-
The registered name must be specified in Tmax.
-
-
BIDSVCPOS = numeric
-
Range: 1 to Max_INT
-
Location of the service that will process BID data. The service to be specified exists in a specific location of the BID data.
-
The service name in the specified location must be registered in Tmax. If this is specified, then the service name defined in BIDSVCNAME will not be used.
-
-
BIDSVCSIZE = numeric
-
Range: 1 to 16
-
Length of the service name when retrieving the service to process BID data from a specific location within the BID data.
-
This parameter is required if BIDSVCPOS is specified.
-
-
ROPSVCNAME = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
Service in the Tmax system that will process data sent by the host to a printer that is connected to a specific terminal.
-
The specified service name must be registered in Tmax.
-
-
ROPSVCPOS = numeric
-
Range: 1 to Max_INT
-
Location within the ROP data from which the service to process the ROP data will be retrieved.
-
The service name in the specified location must be registered in Tmax. If this parameter is specified, the service name defined in ROPSVCPOS will not be used.
-
-
ROPSVCSIZE = numeric
-
Range: 1 to 16
-
Length of the service name when retrieving the service to process ROP data from a specific location within the ROP data.
-
-
OUTSVCNAME = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
Name of the Tmax service that will process data requested by the host.
-
If only this parameter is registered and OUTSVCPOS is not, all data requested by the host will be processed by the service specified in this parameter.
-
The specified service name must be registered in Tmax.
-
-
OUTSVCPOS = numeric
-
Range: 1 to Max_INT
-
Location within the OUTBOUND data from which the service to process host-requested data will be retrieved.
-
The service name at this location must be registered in the Tmax system. If set, the service name defined in the OUTSVCNAME parameter will not be used.
-
-
OUTSVCSIZE = numeric
-
Range: 1 to 16
-
Length of the service name when retrieving the service to process OUTBOUND data from a specific location within the OUTBOUND data.
-
-
RLYSVCNAME = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
If a Host-link is called through tpforward, the Host-link always forwards the processing results to the Relay service. Regardless of the TPNOREPLY setting in the flag, the Host-link requests services from the host and forwards the received data to the service defined in this parameter with tprelay.
-
This parameter is ignored if RLYSVCPOS and RLYSVCSIZE are specified. When a service to be relayed is also set in the user header, this parameter takes precedence.
-
The specified service name must be registered in Tmax.
-
-
RLYSVCPOS = numeric
-
Range: 1 to Max_INT
-
Location of the service name to be relayed using tprelay in the data received from the host when calling a Host-link service via tpforward.
-
If RLYSVCSIZE is also specified, this parameter takes precedence. If set, the service name defined in RLYSVCNAME will not be used.
-
-
RLYSVCSIZE = numeric
-
Range: 1 to 16
-
Length of the service name when locating the service name to be relayed via tprelay in the data received from the host.
-
-
TCLSVCNAME = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
When a Host-link is called through tpacall in which the flag is set to TPNOREPLY, the Host-link only requests services from the host but cannot process the reply. If this parameter is configured, the Host-link sends a tpacall to the specified service.
-
This parameter is ignored if TCLSVCPOS and TCLSVCSIZE are specified.
-
When a service to be relayed is also set in the user header, this parameter takes precedence.
-
The specified service name must be registered in Tmax.
-
-
TCLSVCPOS = numeric
-
Range: 1 to Max_INT
-
Location of the service name to be used in tpacall within the data received from the host when the Host-link is called with the flag set to TPNOREPLY.
-
If set, the service name defined in TCLSVCNAME will not be used.
-
If TCLSVCSIZE is also specified, this parameter takes precedence.
-
-
TCLSVCSIZE = numeric
-
Range: 1 to 16
-
Length of the service name when locating the service name to be called via tpacall in the data received from the host.
-
-
CANSVCNAME = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
If a response from the host is received after a timeout, the data is discarded. If this parameter is configured, the Host-link sends a tpacall to the specified service.
-
This parameter is applicable only when SVRTYPE is set to LU62S.
-
The specified service name must be registered in Tmax.
-
-
POSTOKSVCNAME = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
This parameter is applicable only when SVRTYPE is set to LU0 or LU62R.
-
If data is successfully sent to the host, a tpacall is sent to the service that defined the data.
-
The specified service name must be registered in Tmax.
-
-
POSTFAILSVCNAME = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
This parameter is applicable only when SVRTYPE is set to LU0 or LU62R.
-
If data transmission to the host fails, a tpacall is sent to the service that defined the data.
-
The specified service name must be registered in Tmax.
-
2.4. LOGGING Section
The LOGGING section specifies the file and service to store all data transmitted from a host.
* LOGGING
Log Server Name [LOGPATH = log path,]
[LOGTYPE = (HEX) | TEXT | E2A,]
[LOGSVC = log service name]
Required Parameters
-
Log Server Name = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
Server that will store logs. The name of the server must be the same as the name defined under the SERVER section.
-
The specified server stores logs as a file or calls the service specified in the LOGSVC parameter.
-
Optional Parameters
-
LOGPATH = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
Path and name of a log file
-
If an absolute path (beginning with '/') is specified, that path is used. If a relative path (not beginning with '/') is specified, the log file is stored in the subdirectory of the directory specified in ULOGDIR under the NODE section in the Tmax configuration file.
-
This parameter is ignored when LOGSVC is specified
-
Logging will not be performed if LOGTYPE is not specified along with this parameter.
-
-
LOGTYPE = (HEX) | TEXT | E2A
-
Type of data logging.
-
The following specifies each configuration value.
Value Description HEX
Displays output data as a hexadecimal value. (Default value)
TEXT
Displays text data as lines.
E2A
Displays HEX data after converting EBCDIC code to ASCII code.
-
Stores log files in the name of a server when LOGPATH is not specified.
-
-
LOGSVC = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
Service that will log transmitted data. This data will not be logged in the file provided by the Host-link system.
-
Host-link calls services in the same way it calls data by adding a specific header (LOGHEADER, userinc/hlinkapi.h)
-
The specified service name must be registered in Tmax.
-
Usage
The following is an example of data logging.
*LOGGING
snalu0gw00 LOGPATH = aaa,
LOGTYPE = HEX,
LOGSVC = LOGSVC
If ULOGDIR=/home/tmax/log/ulog is set in the NODE section of the Tmax configuration file, log files are stored in "/home/tmax/log/ulog/aaa_server index.current time."
Since the LOGTYPE item is set to HEX, data is stored in HEX format as shown in the following example. Because the LOGSVC parameter is specified, data is logged in the specified LOGSVC instead of the file provided by the Host-link system.
HOSTLINK → HOST Length[70] time[14:10:58.375] 00000000 e3f1c9d8 c3e5c840 40d3f0f5 f8f3f740 |.......@@......@| 00000010 40f9f1f0 4040f0f0 f0f04040 40404040 |@...@@....@@@@@@| 00000020 40e5c8e3 f5f0f040 d3404080 80808080 |@......@.@@.....| 00000030 a040f4f5 f9f9f5f0 f4f0f0f8 f0f8f3f9 |.@..............| 00000040 f0f91ed5 1e0d |...... | HOST → HOSTLINK Length[70] time[14:10:58.376] 00000000 e3f1c9d8 c3e5c840 40d3f0f5 f8f3f740 |.......@@......@| 00000010 40f9f1f0 4040f0f0 f0f04040 40404040 |@...@@....@@@@@@| 00000020 40e5c8e3 f5f0f040 d3404080 80808080 |@......@.@@.....| 00000030 a040f4f5 f9f9f5f0 f4f0f0f8 f0f8f3f9 |.@..............| 00000040 f0f91ed5 1e0d |...... |
2.5. CONVERSION Section
The format of the CONVERSION section is as follows. It is used to convert the data of the relevant server.
* CONVERSION
ServerName [INBOUND = Y|(N)]
[INBOUND_KOR = Y|(N),]
[INBOUND_SKIP = 1 ~ MAX_INT,]
[OUTBOUND = Y|(N),]
[OUTBOUND_KOR = Y|(N),]
[OUTBOUND_SKIP = 1 ~ MAX_INT,]
[MAPPATH = map path]
Required Parameters
-
ServerName = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
The name of the server must be the same as the name defined under the SERVER section.
-
Optional Parameters
-
INBOUND = Y|(N)
-
Default Value: N
-
If this parameter is set to Y, Host-link converts all data to be transmitted to the host from ASCII to EBCDIC and also from the complete code system of Korean to the combined code system of Korean. When converting Korean characters, ASCII recognizes a 2-byte sequence as Korean if the first bit of the first byte is set to 1. The host determines whether the character is Korean or EBCDIC code based on characters indicating the start and end of the string.
For example, '홍길동' is converted to '0x0e홍길동0x0f'. For '홍 길 동', it is converted to '0x0e홍0x0f + space + 0x0e길0x0f + space + 0x0e동0x0f'.
-
-
INBOUND_KOR = Y|(N)
-
Default Value: N
-
Specifies whether to include Korean characters when converting code.
-
The following specifies each configuration value.
Value Description Y
Converts ASCII to EBCDIC (including Korean).
N
Converts ASCII to EBCDIC (excluding Korean).
-
If INBOUND is set to N, the INBOUND_KOR=Y is ignored.
-
-
INBOUND_SKIP = numeric
-
Range: 1 to Max_INT
-
Number of bytes to exclude during code conversion. This parameter is used to ignore HEX data included in the data.
-
If INBOUND is set to N, the value specified in INBOUND_SKIP is ignored.
-
-
OUTBOUND = Y|(N)
-
Default Value: N
-
If this parameter is set to Y, Host-link converts all data to be transmitted to a host from EBCDIC to ASCII and also from the combined code system of Korean to the complete code system of Korean. he characters indicating the start and the end of a Korean string are converted to spaces and inserted at the end of that string.
For example, '0x0e홍길동0x0f' is converted to '홍길동+space+space'.
-
-
OUTBOUND_KOR = Y|(N)
-
Default Value: N
-
Specifies whether to include Korean characters when converting code.
-
The following specifies each configuration value.
Value Description Y
Converts ASCII to EBCDIC (including Korean).
N
Converts ASCII to EBCDIC (excluding Korean).
-
If OUTBOUND is set to N, the OUTBOUND_KOR=Y is ignored.
-
-
OUTBOUND_SKIP = numeric
-
Range: 1 to Max_INT
-
Number of bytes to exclude during code conversion.
-
This parameter is used to ignore HEX data included in the data.
-
If OUTBOUND is set to N, the value specified in OUTBOUND_SKIP is ignored.
-
-
MAPPATH = literal
-
Size: Up to 255 characters
-
For communication between Host-link and the host, data must be exchanged in the format handled by each service. This parameter specifies a directory containing the files that define each format.
-
The following describes the file names.
Type Description LU0
The first 8 bytes of the data (8 bytes following the user header if a user header exists).
LU62S
The pgmname of the TPGWINFO_T data structure.
LU62R
The Tmax service name. Since the map file name is 8 characters long, the Tmax service name must be within 8 characters.
-
Usage
The following is an example of data conversion.
*CONVERSION
snalugw00 INBOUND = Y,
INBOUND_KOR = N,
INBOUND_SKIP = 50,
OUTBOUND = N,
OUTBOUND_KOR = N,
OUTBOUND_SKIP = 55,
...
In this example, Host-link converts all data sent to the host from ASCII to EBCDIC and from the complete code system of Korean to the combined code system of Korean. Since the INBOUND_KOR is set to N, Korean characters are excluded from the conversion. The number of bytes specified in the INBOUND_SKIP field is excluded. Contrary to INBOUND, OUTBOUND is set to N, so no conversion from EBCDIC to ASCII is performed.
When the MAPPATH parameter is set in the CONVERSION section, a map file must be registered. The name of the map file must exist in the path defined in the MAPPATH and be registered as "file name.map" file. The file name must be defined within 8 characters.
The following shows an example of registering a map file and describes each item.
# As COMMSIZE must be used both in INPUT and OUTPUT, # the larger between the input and output data must be entered. *COMMSIZE 1024 *INPUT #--------------------------------------------------------------- # Item Name Item Lengh Data Type # Data Type: CHAR, NUMERIC(UNPACK), KOREAN, BINARY, USER-TYPE #--------------------------------------------------------------- a 10 CHAR b 10 KOREAN c 5 NUMERIC d 10 BINARY *OUTPUT a 10 CHAR b 10 KOREAN c 5 NUMERIC d 10 BINARY e 3 USER1 <USER1> e1 6 CHAR e2 10 KOREAN e3 8 BINARY </USER1>
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
COMMSIZE |
Length of the data transmitted between Host-link and a remote node. Set this to the length of the longest message. |
INPUT |
Format of the messages sent from the gateway to a remote node. This item also registers the format of the replies returned from the remote node to Tmax. |
OUTPUT |
Format of the replies sent from a remote node to the gateway. This item also registers the format of requests that are sent from the remote node to Tmax. |
The INPUT/OUTPUT section consists of the following items.
-
Item Name
This name is used only for user reference. The gateway recognizes this as an item name but does not use it internally.
-
Item Length
Actual length of each item in transmitted and received data. The gateway converts the length to an offset, which always begins with 0.
-
Data Type
Data type of each item in transmitted and received data.
Data Type Description CHAR
This type includes English characters, numbers, and Korean characters. When the CHAR type is used, the accurate size of the converted message must be specified.
When a Korean string is used with other characters (English letters, numbers, and special characters), the characters at the start and the end of the string are included. When converting to UNIX, the characters indicating the start and the end of the Korean string are changed to spaces and moved to the end of the string.
NUMERIC
This type is used when data are all numeric. Code conversion is performed in the same way as the CHAR type.
Note that NUMERIC does not indicate an integer.
KOREAN
This type is used when data are all Korean characters. Code is converted in 2-byte units.
SOSI
This type is similar to the KOREAN type. But this type includes the characters indicating the start and the end of a Korean string after the conversion. When the code is converted to UNIX, the characters indicating the start and the end of the Korean string will be changed to spaces and moved to the end of that string.
CHARSOSI
This type is similar to the SOSI type. However, it does not convert the characters indicating the start and the end of the Korean string when the code is converted to UNIX. This type only supports the conversion from the host system to a UNIX system.
BINARY
Data of this type are not converted. Specify this type for the data you do not want to convert.
USER-TYPE
This type is used for specifying array data type.
For example, code conversion becomes difficult in the following case:
When multiple items are displayed in a screen repeatedly, each item must be registered every time. In addition, it is difficult to find out the repeat count of each item when registering the repeat count as data. In this case, USER-TYPE is specified because array type data can be easily converted.
USER1 in the above map file is a user-defined type. A type name can be specified by the user.
[Note]
Note that the length of an item in user-defined type data indicates the size of the buffer that will store the repeat count of an array. That is, the number of array repeat count varies by each message. The repeat count is a numeric value and must be stored as a CHAR type. Then, <USER-TYPE> must be inserted before each item, and after each item, </USER-TYPE> must be inserted. In the above example, e1, e2, and e3 are treated as array items. In each message, 3 bytes (data length) are read from the start position of the 'e' item to retrieve the repeat count. Then the codes is repeated according to this repeat count and converted.
2.6. DUMMYDATA Section
This section specifies the data received from the host as dummy data if its size is 0 or if it contains a specific value. This section is applicable only when the server type (SVRTYPE) is LU0.
The following is the format of the DUMMYDATA section.
* DUMMYDATA
ServerName [ZEROSIZE = (Y)|N,]
[DUMMYPOS = dummy position,]
[DUMMYVAL = dummy value]
Required Parameters
-
ServerName = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
The name of the server must be the same as the name defined under the SERVER section.
-
Optional Parameters
-
ZEROSIZE = (Y)|N
-
Default Value: Y
-
This parameter is used when the length of the data received from the host is 0 byte.
-
The following specifies each configuration value.
Item Description Y
Treats 0 byte data received from the host as a reply. Sends the reply to the client who will call a service of Host-link.
N
Ignores 0 byte data when it is received.
-
-
DUMMYPOS = numeric
-
Range: 1 to Max_INT
-
Location of the data to be ignored when it is received from the host.
-
If not specified, all data received from the host will be sent to the client.
-
-
DUMMYVAL = string
-
Size: Up to 8 characters
-
Specifies the value to compare with the data at the specified location in the DUMMYPOS parameter. The specified value is converted to an EBCDIC code.
-
2.7. USERHEADER Section
The following is a format of the USERHEADER section. It specifies the user header between Host-link and an open environment system.
* USERHEADER
ServerName [HSIZE = 1 ~ 512,]
[SVCPOS = 1 ~ HSIZE - 1,]
[SVCSIZE = 1 ~ 16,]
[LUTYPEPOS = 1 ~ HSIZE - 1,]
[LUTYPESIZE = 1 ~ 8,]
[LUNAMEPOS = 1 ~ HSIZE - 1,]
[LUNAMESIZE = 1 ~ 8,]
[WSNAMEPOS = 1 ~ HSIZE - 1,]
[WSNAMESIZE = 1 ~ 8,]
[ERRCODEPOS = 1 ~ HSIZE - 1,]
[ERRCODESIZE = 1 ~ 4,]
[TIMEWAITPOS = 1 ~ HSIZE - 1]
Required Parameters
-
ServerName = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
The name of the server must be the same as the name defined under the SERVER section.
-
Optional Parameters
-
HSIZE = numeric
-
Range: 1 to 512
-
Length of the header.
-
Host-link stores the header data, and when receiving a response from the host, it adds the header data to the beginning of the response before sending it to an open environment system. When a service or BID data is requested from the host, this header is added to the beginning of the received data to call the specified service.
-
This header is required to operate sessions in the dedicate mode since the information for finding a session is retrieved from the header data.
-
-
SVCPOS = numeric
-
Range: 1 to HSIZE-1
-
Position of the service name within the user header data.
-
When Host-link is called through tpacall with the TPNOREPLY flag or via tpforward, and a response is received from the host, it invokes the service specified in this parameter.
-
-
SVCSIZE = numeric
-
Range: 1 to 16
-
Length of the service name within the user header data.
-
-
LUTYPEPOS = numeric
-
Range: 1 to HSIZE-1
-
Position of the desired session among the sessions allocated for each task when sending data to the host.
-
This parameter is applicable when using a number of sessions allocated for each task.
-
This parameter is applicable only when SVRTYPE is set to LU0.
-
-
LUTYPESIZE = numeric
-
Range: 1 to 8
-
Length of a specific session among the sessions allocated for each task when sending data to the host.
-
This parameter is applicable only when SVRTYPE is set to LU0.
-
-
LUNAMEPOS = numeric
-
Range: 1 to HSIZE-1
-
Position of the session used by the Host-link system when sending and receiving the service requested from the open environment system.
-
This parameter is applicable only when SVRTYPE is set to LU0.
-
-
LUNAMESIZE = numeric
-
Range: 1 to 8
-
Length of the session used by the Host-link system when sending and receiving the service requested from the open environment system.
-
This parameter is applicable only when SVRTYPE is set to LU0.
-
-
WSNAMEPOS = numeric
-
Range: 1 to HSIZE-1
-
Position of a specific session to be used for sending and receiving data. This parameter is applicable only when sessions are operated in the dedicate mode.
-
This parameter is applicable only when SVRTYPE is set to LU0.
-
-
WSNAMESIZE = numeric
-
Range: 1 to 8
-
Length of a session to be used for sending and receiving data.
-
This parameter is applicable only when sessions are operated in the dedicate mode and SVRTYPE is set to LU0.
-
-
ERRCODEPOS = numeric
-
Range: 1 to HSIZE-1
-
Position of the error code to be sent to an open environment system when Host-link has failed to receive a response from the host due to an error or a timeout.
-
Host-link converts the error code to characters using the length specified in ERRCODESIZE. Then, it places them at the position specified in this parameter and sends the response.
-
-
ERRCODESIZE = numeric
-
Range: 1 to 4
-
Length of the error code. This parameter is used along with ERRCODEPOS.
-
-
TIMEWAITPOS = numeric
-
Range: 1 to HSIZE-1
-
Position used to specify whether to start a new session (NOWAIT) or continue using the current session (WAIT) when a timeout occurs.
-
Gateway Header
When SVRTYPE is set to LU62S, a gateway header must precede the user header . The gateway header is defined in "usrinc/hlinkapi.h" as follows:
struct tpgwinfo {
char svc[XATMI_SERVICE_NAME_LENGTH];
char trxid[HOST_TRANS_LENGTH];
char pgmname[HOST_PROGRAM_LENGTH];
char userid[HOST_USERID_SIZE];
char passwd[HOST_PASSWD_SIZE];
char resvd[16];
};
typedef struct tpgwinfo TPGWINFO_T;
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
char svc[XATMI_SERVICE_NAME_LENGTH] |
Service that processes response data when Host-link is running in the non-blocking mode or asynchronous mode. |
char trxid[HOST_TRANS_LENGTH] |
TP name of the host to be called. This member is required when SVRTYPE is LU62S and the function is DPL. The size must not exceed 4 characters. |
char pgmname[HOST_PROGRAM_LENGTH] |
Program name of the host to be called. When SVRTYPE is set to LU62S, the MAP file is referenced using the name defined in this member. |
char userid[HOST_USERID_SIZE] |
User ID. |
char passwd[HOST_PASSWD_SIZE] |
Password. |
char resvd[16] |
Currently not used. |
Usage
The following is an example of a user header.
*USERHEADER
snalu0gw00 HSIZE = 41, # user total header size
SVCPOS = 1, # user defined svc name position
SVCSIZE = 15, # user defined svc name length
LUTYPEPOS = 16, # inbound lu type position
LUTYPESIZE = 7, # inbound lu type length
LUNAMEPOS = 23, # output only, lu name position
LUNAMESIZE = 7, # output only, lu name length
WSNAMEPOS = 30, # only INBOUNDLU is DEDICATE
WSNAMESIZE = 7, # only INBOUNDLU is DEDICATE
ERRCODEPOS = 37, # output only
ERRCODESIZE = 3, # output only
TIMEWAITPOS = 40 # time wait position
2.8. LUINFO Section
The following is a format of the LUINFO section. It specifies the session information between the host and the Host-link system.
*LUINFO
LU Name SVRNAME = servername
[HOSTID = Host ID,]
[WSNAME = ws name,]
[DIRECTION = INBOUND | OUTBOUND,]
[LUTYPE = LU type,]
[FQPLUNAME = partner-fully qualified LU name,]
[TPNAME = LU name used for connecting a session to the host,]
[MODENAME = session purpose,]
[SYNCMODE = NONE | CONFIRM | SYNCPT,]
[SESSION = 1 ~ 50,]
[NETNAME = LU network name]
Required Parameters
-
LU Name = string
-
Size: Up to 8 characters
-
LU session name.
-
-
SVRNAME = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
Name of the server where an LU session will connect.
-
Optional Parameters
-
HOSTID = string
-
Size: Up to 4 characters
-
Host ID to which the session belongs.
-
-
WSNAME = string
-
Size: Up to 16 characters
-
This parameter is used by Host-link to operate sessions in the dedicate mode.
-
Data can be sent and received through a session by storing the configured value in the user header and specifying its location in the WSNAMEPOS and WSNAMESIZE fields of the USERHEADER section.
-
Applicable when the server type is SNA LU 0.
-
-
DIRECTION = INBOUND | OUTBOUND
-
Specifies whether the session is INBOUND or OUTOUND.
-
Applicable when the server type is SNA LU 0.
-
-
LUTYPE = string
-
Size: Up to 8 characters
-
Used to categorize each session by its purpose.
-
Specifies the desired type for INBOUND sessions (DIRECTION = INBOUND). This type must be set at the position defined in the LUTYPEPOS and LUTYPESIZE fields in the USERHEADER section of the Host-link configuration file.
-
OUTBOUND (DIRECTION = OUTBOUND) sessions are classified into the following three types.
Type Description General Session
The host initiates a service routine
BID Session
The host forcibly sends a message.
ROP Session
Data is sent to a specific terminal’s printer.
-
Applicable when the server type is SNA LU 0.
-
-
FQPLUNAME = string
-
Size: Up to 17 characters
-
Fully qualified name of a counterpart LU. This is applicable when the server type is SNA LU 6.2.
-
-
TPNAME = string
-
Size: Up to 64 characters
-
Local TPNAME of the LU.
-
Applicable when the server type is SNA LU 6.2.
-
-
MODENAME = string
-
Size: Up to 8 characters
-
Mode name for the session. Contact the host administrator for the mode name to be used.
-
Applicable when the server type is SNA LU 6.2.
-
-
SYNCMODE = NONE | CONFIRM | SYNCPT
-
Default Value: NONE
-
Supports the host’s Syncpoint level.
-
Applicable when the server type is SNA LU 6.2.
-
-
SESSION = numeric
-
Range: 1 ~ 50
-
Number of sessions that can be configured in a single LU.
-
When the server type is SNA LU 0, this can be set to 1 because only one session can be created per LU.
-
-
NETNAME = string
-
Size: Up to 8 characters
-
Network name of the LU. A fully qualified LU name consists of 'LU network name.LU name'. For example, TESTNET is the LU network name for "TESTNET.TESTLU".
-
3. Service Configuration
This chapter describes each service and explains how to configure it.
3.1. INBOUND
INBOUND services include tpcall, tpacall, and tpforward.
tpcall
The tpcall services can be used in the same way as services provided by other service processes in the Tmax system. Unlike general server processes, Host-link can simultaneously process multiple services by using CPC. For example, if CPC is set to 5, Host-link can process five services simultaneously.
The service processing procedure is as follows:
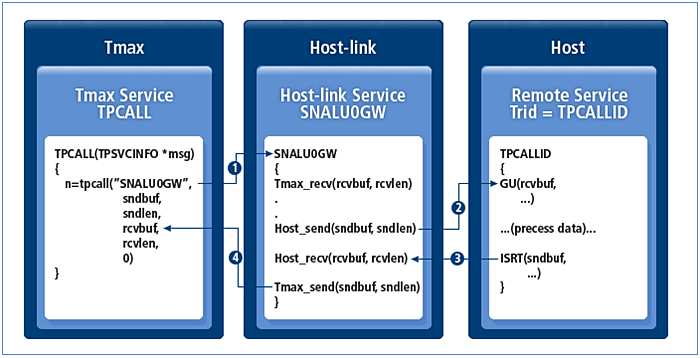
-
Tmax calls the Host-link service defined in the Tmax configuration file.
-
Host-link sends data to the program provided by the host.
-
The host processes the service and sends the result to Host-link.
-
Host-link sends the response data to Tmax that invoked the service.
tpacall
The tpacall service is divided into services that respond to Tmax after processing the requested service, and those that do not.
-
Responding service
A service that responds to the Tmax system is processed in the same way as the tpcall service.
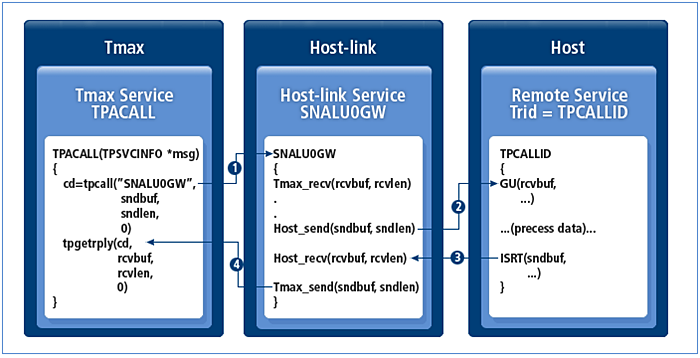 tpacall - Service that responds to Tmax
tpacall - Service that responds to Tmax-
Tmax calls the Host-link service defined in the Tmax configuration file.
-
Host-link sends data to the program provided by the host.
-
The host processes the service and sends the result to Host-link.
-
Host-link sends the response data to Tmax that invoked the service.
-
-
Non-responding service
The processing procedure for a service that does not respond to the Tmax System is as follows.
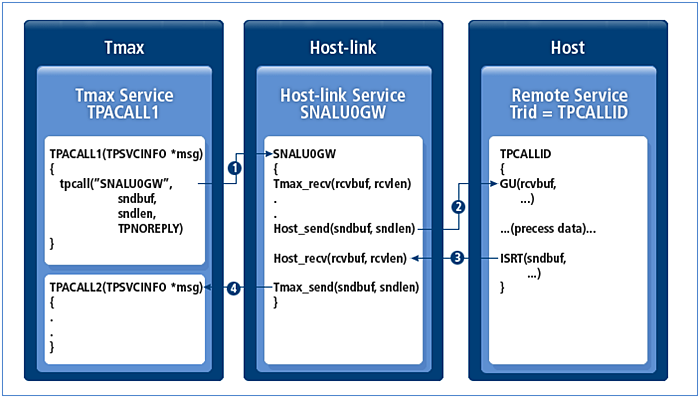 tpacall - Service that does not respond to Tmax
tpacall - Service that does not respond to Tmax-
Tmax calls the Host-link service defined in the Tmax configuration file.
-
Host-link sends data to the program provided by the host.
-
The host processes the service and sends the result to Host-link.
-
Host-link sends the response data to Tmax that invoked the service.
For services that do not respond to Tmax, Host-link can receive a reply from the host and relay it to another service. The relayed service is specified using the following configuration. If the following configuration is not specified in the configuration file, the response data received from the host will be ignored. Call a service via tpacall with the flag set to TPNOREPLY, and specify the service to which Host-link will relay the reply in the Host-link configuration file.
-
SECVICE Section
*SERVICE snalu0gw00 TCLSVCNAME = TPACALL_RECV, # defaule svc name TCLSVCPOS = 1, TCLSVCSIZE = 10, ...Host-link recognizes the first data through eleventh data received from the host as the service name and calls the corresponding services. If TCLSVCPOS and TCLSVCSIZE are not defined, Host-link calls the service specified in TCLSVCNAME.
-
USERHEADER Section
*USERHEADER snalu0gw00 HSIZE = 100, # user total header size SVCPOS = 1, # user defined svc name position SVCSIZE = 10, # user defined svc name size LUNAMEPOS = 11, # output only LUNAMESIZE = 10, # output only WSNAMEPOS = 21, # only INBOUNDLU is DEDICATE WSNAMESIZE = 10, # only INBOUNDLU is DEDICATE ERRCODEPOS = 31, # output only ERRCODESIZE = 4, # output only TIMEWAITPOS = 1 # WAIT or NOWAIT value positionService names are recognized using the SVCPOS and SVCSIZE parameters.
-
TPGWINFO_T
Recognizes the service name defined in the SVC member of TPGWINFO_T.
-
tpforward
The tpforward service is divided into services that call a Host-link service without the flag set to TPNOREPLY and services that call a Host-link service with the flag set to TPNOREPLY.
-
Without the TPNOREPLY flag set
This service can only be called by server programs. In Tmax version 3.5 and eariler, a request is processed as shown below. In Tmax 3.8 or higher, a request is always processed via tpforward with the TPNOREPLY flag regardless of the flag setting.
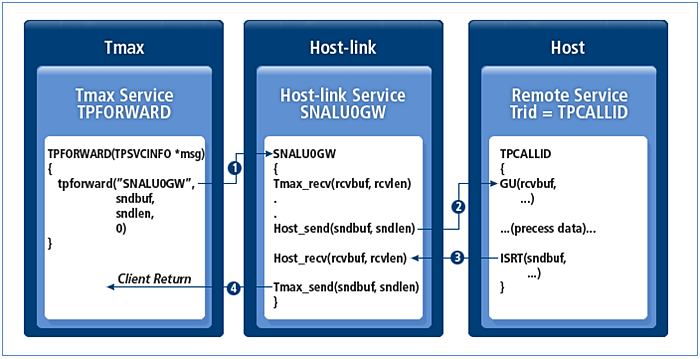 tpforward - with the TPNOREPLY Flag Set
tpforward - with the TPNOREPLY Flag Set-
Tmax calls the Host-link service defined in the Tmax configuration file.
-
Host-link sends data to the program provided by the host.
-
The host processes the service and sends the result to Host-link.
-
Host-link sends the response to the client that invoked the tpforward service.
-
-
With the TPNOREPLY flag set
A service is processed as follows:
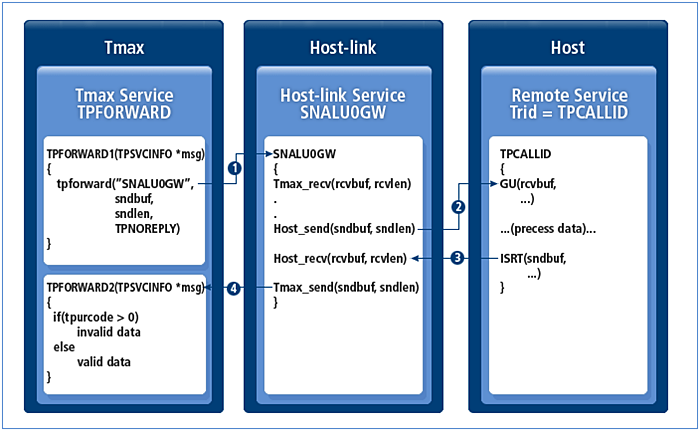 tpforward - without the TPNOREPLY Flag Set
tpforward - without the TPNOREPLY Flag Set-
Tmax calls the Host-link service defined in the Tmax configuration file.
-
Host-link sends data to the program provided by the host.
-
The host processes the service and sends the result to Host-link.
-
Host-link sends the response to the service defined in the configuration file.
When a server process calls a Host-link service via tpcall, the server process will be in a blocked state until a response is received. To overcome this limitation, the service is divided into sending services and receiving services.
The sending service calls a service via tpforward to Host-link and then terminates the service. When Host-link receives a response from the host, it invokes the receiving service to process the response. The receiving service name is recognized via the Host-link configuration file, in the same way as tpacall.
-
SERVICE Section
*SERVICE snalu0gw00 ... #RLYSVCNAME = TPACALL_RECV, # defaule svc name RLYSVCPOS = 1, # svcname position RLYSVCSIZE = 10, # max length 16 ...If an error occurs when Host-link requests a service from the host, Host-link sends the error to the service defined in the RLYSVCPOS and RLYSVCSIZE. The service defined in RLYSVCPOS and RLYSVCSIZE must determine whether the service data is valid or contains errors before starting the service. If tpurcode is greater than 0, data is treated as an error. Otherwise, it is treated as valid.
If RLYSVCPOS and RLYSVCSIZE are not specified, the error is sent to the service specified in RLYSVCNAME.
-
USERHEADER Section
*USERHEADER snalu0gw00 HSIZE = 100, # user total header size HSVCPOS = 1, # user defined svc name position HSVCSIZE = 10, # user defined svc name size ...Service names are recognized using the HSVCPOS and HSVCSIZE parameters.
-
TPGWINFO_T
Recognizes the service name defined in the SVC member of TPGWINFO_T.
-
3.2. OUTBOUND
An OUTBOUND service is used when the host calls a Tmax service. The processing procedure for OUTBOUND services is as follows.
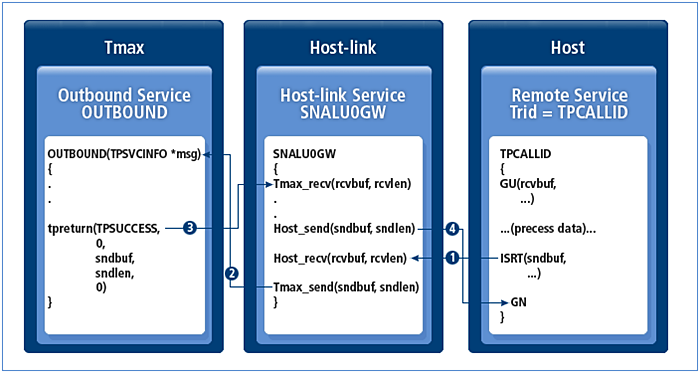
-
The host requests a service from Host-link.
-
Host-link calls the Tmax system service as defined in the configuration file.
-
Tmax processes the request and sends the result to Host-link.
-
Host-link sends the response data to the host.
The service name provided by the Tmax system is recognized in the following two methods.
-
SERVICE Section
*SERVICE snalu0gw00 ... #OUTSVCNAME = OUTBOUND, # defaule svc name OUTSVCPOS = 1, # outsvc position OUTSVCSIZE = 10, # max length 16 ...Host-link calls the service in the location specified in OUTSVCPOS and OUTSVCSIZE. If OUTSVCPOS and OUTSVCSIZE are not specified, all OUTBOUND data call the service specified in OUTSVCNAME.
-
USERHEADER Section
*USERHEADER snalu0gw00 ... ERRCODEPOS = 1, #reponse error position ERRCODESIZE = 4, # max length 4 ...ERRCODEPOS and ERRCODESIZE are used when sending an error if there is no service provided by Tmax or the Tmax system is abnormally shut down. Error data is defined from data received by the host at the position defined in ERRCODEPOS, with the size specified in ERRORCODESIZE. This error data is sent to the host.
3.3. BID and ROP
BID and ROP are the functions that allow the host to forcibly send a message to Host-link. When Host-link receives BID or ROP data, it calls the BID or ROP service specified in the SERVICE section of the Host-link configuration file.
While OUTBOUND services must send the processing results to the host, BID data is only received from the host and does not send a response.
The service processing procedure is as follows.
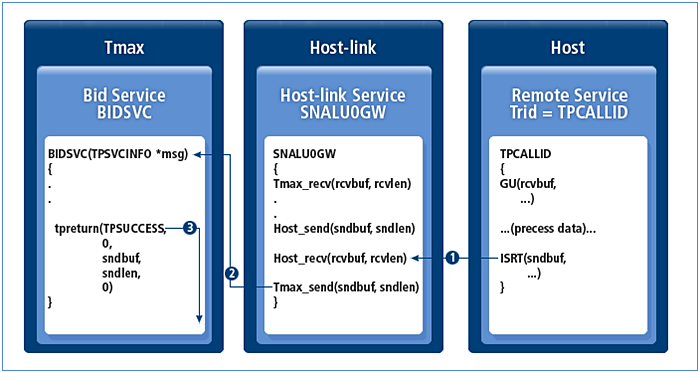
-
The host requests BID or ROP data.
-
The gateway calls the corresponding Tmax service specified in the configuration.
-
The service performs tpreturn after processing the request. Since the request is a BID or ROP, the response is not sent to the host.
The service name provided by the Tmax system is recognized through the SERVER section in the configuration file.
*SERVICE
snalu0gw00 ...
#BIDSVCNAME = BIDSVC, # defaule svc name
BIDSVCPOS = 1, # svcname position
BIDSVCSIZE = 10, # max length 16
#ROPSVCNAME = ROPSVC, #default svc name
ROPSVCPOS = 11, #svcname position
ROPSVCSIZE = 10, # max length 16
...
Host-link locates the service name defined in BIDSVCPOS and BIDSVCSIZE. (For ROP services, ROPSVCPOS and ROPSVCSIZE are used.)
If BIDSVCPOS and BIDSVCSIZE are not specified, all BID data call the service specified in BIDSVCNAME. (For ROP, ROPSVCNAME is used.)
4. Compiling the Configuration File
The hkcfl command is used to compile the configuration file.
hkcfl
hkcfl is a command that compiles a text-based Host-link configuration file into a binary Host-link configuration file (hlinkcfg). If an error occurs during compilation, the compilation stops. When the compilation completes successfully, a binary format configuration file is created.
Usage of the hkcfl command is as follows.
hkcfl [-h] [-p] [-o binary Host-link configuration filename] -i text-based Host-link configuration filename
-c comment character -d
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
[-h] |
Displays online help. |
[-p] |
Displays the compilation details of the Host-link configuration file. |
[-o binary Host-link coonfiguration filename] |
Specifies the name of the binary Host-link configuration file, which is the result of compilation. This can be specified with a path. If no path is specified, the compilation is created in $TMAXDIR/config. (Default value : 'hlinkcfg') |
-i text-based Host-link configuration filename |
Specifies the name of the text-based Host-link configuration file. This is a required option. If no directory is specified, $TMAXDIR/config is used. This can be specified with a path, and if the source file cannot be found, a warning message is displayed. |
-c command character |
Changes the comment character in the text-based configuration file. By default, '#' is used for comment. |
-d |
The HOSTADDR information defined in the configuration file and the information to be stored in the output file are displayed in the debug log. At this time, the HOSTADDR information of all SERVER sections is output regardless of whether it is an IP or DNS. |