Introduction
This chapter describes the overview and service types of the system.
1. Overview
The TCP/IP service gateway (hereafter SVCGW) is a gateway provided in Tmax, which plays the role of an interface between a Tmax server and a Non-Tmax server (hereafter remote node).
SVCGW is divided into two modules. One transmits data between Tmax and the remote node through TCP/IP. The other is the TCP/IP communication library (hereafter COM library) that is responsible for the communication from remote node to Tmax’s SVCGW. The TCP/IP service gateway is a module that allows the Tmax system to communicate with non-Tmax systems through TCP/IP by using these 2 modules.
The COM library enables the use of TCP/IP communications between Tmax and SVCGW, without having to newly develop a program designed for TCP/IP communication. A user can use this library to receive or request a service from/to SVCGW. SVCGW receives messages from the remote node and sends a tpacall to the requested service, and the service result is returned to the remote node. If a request originates from a Tmax service to SVCGW using tpcall or another method, SVCGW sends the request to the remote node. When it receives the result from the remote node, it returns (tpreturn) the result back to the initiator service. Since complex tasks required for connecting to other systems through TCP/IP such as opening the socket and sending/receiving messages are all handled by the TCP/IP service gateway and the COM library, a developer can simply create the application logic.
SVCGW operations can be divided into two modes: one for when a Tmax service or client requests a service to the remote node and the other for when a remote node calls a Tmax service.
The following is the operating structure of SVCGW.
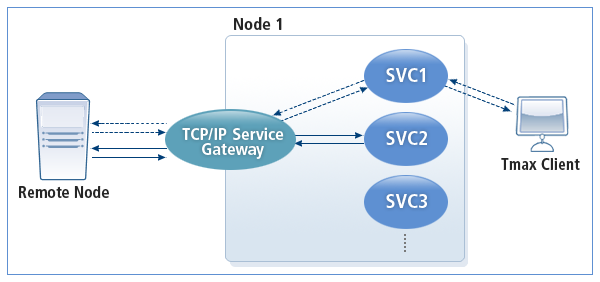
-
Service request initiated by Tmax
SVCGW receives a service request from a Tmax client or service and delivers the request to the remote node (represented by the dotted line in SVCGW Operation). This is called an INBOUND service. In an inbound service, when Tmax client makes a service request to the remote node, it uses the name of the service registered in SVCGW.
SVCGW asynchronously processes the service requests, which are sent from Tmax to the remote node. That is, when a service or client sends a tpcall to the remote node, SVCGW sends the service request to the remote node and immediately returns a normal response to the service or client. Since the remote node regards the response as a new service request, all services requested by Tmax are processed asynchronously.
-
Service request initiated by the remote node
SVCGW receives a service request from a remote node and then processes it (represented by the solid line in SVCGW Operation). When Tmax client receives a service request from the remote node, it uses the service name of Tmax. This is called an OUTBOUND service.
In an asynchronous communication, if the flags is set to COMMNOREPLY when a service is requested to SVCGW using the COM library, SVCGW only sends the service request to Tmax and does not receive a response.
In a synchronous communication, if the flags is not set to COMMNOREPLY when a service is requested to SVCGW using the COM library, SVCGW sends the service request to Tmax and sends back the reply to the remote node.
Deferred processing is supported when a remote node requests a service to Tmax. When the flags is set to COMMDELAY, SVCGW saves the request data in RQ to allow a user to batch process the data at a later time. Deferred processing is always performed in an asynchronous way.
SVCGW installed on Tmax is a type of Tmax server, and it must be configured as a server in the Tmax environment file. While general servers are created using a TCS or UCS server library, SVCGW is provided as an executable file so that the user can simply add SVCGW as a server in the Tmax environment file. For detailed information on the Tmax environment configuration, refer to Environment Configuration.
2. Service Types
SVCGW communicates with the remote node through TCP/IP, and acts as an intermediary between a Tmax client and a remote node for request processing.
The COM library modules used by a remote node are described in COM Library. Only the parts installed on Tmax are described in this section.
SVCGW operates in two ways: one when a Tmax service or client requests a service from the remote node and the other when a remote node calls a Tmax service. SVCGW always runs in the server mode and the remote node must always operate in the client mode. If a connection is made with the remote node, then services can be requested from any side.
2.1. Service Requests Initiated by Tmax
The service requests initiated by Tmax can be processed in two ways, NOREPLY service call and REPLY service call. A NOREPLY service call sends a service request to the remote node and does not receive a response. A REPLY service call sends a service request and regards the response as a new service request.
Since SVCGW can only request a service to a designated remote server, the user must know which remote node the request will be sent to. To do this, a service name must be configured in the Tmax environment file, and the service name must be set in the remote node information of the SVCGW environment file. When SVCGW receives a service request, it sends the data to the remote node using the registered service name.
NOREPLY Service Call
In the NOREPLY service call method, a Tmax service or client initiates a request to SVCGW through tpcall and the request is processed regardless of the result.
When the service, which has received a service request from a Tmax client, sends a tpcall to SVCGW, SVCGW sends the service request to the remote node and returns immediately without waiting for a response. When SVCGW is operates in this way, the Tmax service which the Tmax client has requested continues to receive other requests without waiting for a response from SVCGW.
The following is how SVCGW operates in the NOREPLY mode.
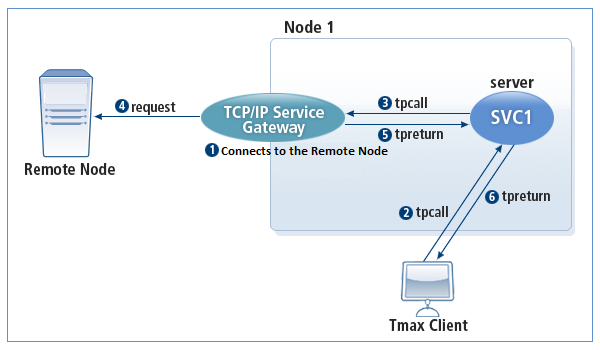
-
SVCGW and the remote node are in the connected state.
-
A Tmax client sends a tpcall to the Tmax service.
-
A Tmax service receives a client request and sends a tpcall to SVCGW.
Since there are many services registered with SVCGW, the user request must specify the target service name that is connected to the remote node.
-
SVCGW makes a request to the remote node connected to the user-specified service.
-
SVCGW sends a reply (tpreturn) to the initiator service.
-
SVCGW sends the reply (tpreturn) to the Tmax client that requested the service.
REPLY Service Call
In the REPLY service call method, a Tmax service or client initiates a request to SVCGW through tpcall and the request is processed regardless of result. The remote node processes the request and sends the result to another service on Tmax.
If the service that received a request from the Tmax client sends the request (tpcall) to SVCGW, then SVCGW forwards it to the remote node and returns immediately without waiting for the result. With the processing result, the remote node calls a new service on Tmax. When a new service is called, the service processing result may be returned or not depending on the flags setting of the ComSend function. This option is used to separate the initiator service from the one that processes the result.
The following is how SVCGW operates in the REPLY mode.
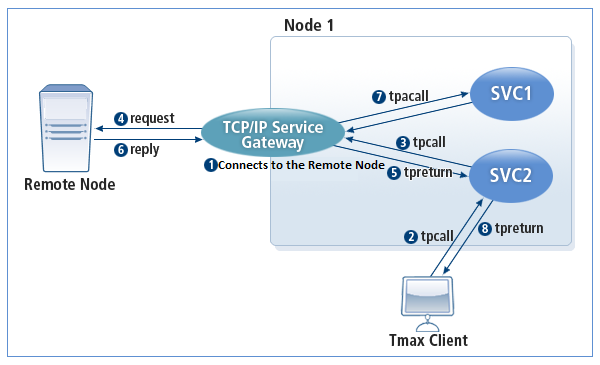
-
SVCGW and the remote node are in the connected state.
-
A Tmax client sends a tpcall to the Tmax service.
-
The Tmax service receives the client request and sends a tpcall to SVCGW.
Since there are many services registered with SVCGW, the user request must specify the target service name that is connected to the remote node.
-
SVCGW makes a request to the remote node connected to the user-specified service.
-
SVCGW sends a reply (tpreturn) to the initiator service.
-
SVCGW receives a result service call from the remote node.
-
SVCGW calls the user-specified service.
-
Tmax service sends the reply (tpreturn) to the Tmax client that requested the service.
2.2. Service Requests Initiated by Remote Node
Service requests initiated by a remote node can be processed either synchronously or asynchronously. In the synchronous mode, SVCGW initiates a service call and waits for the response. In the asynchronous mode, SVCGW initiates a service call but does not wait for the response. In the synchronous mode, another service call that comes in during a service request before receiving the response must be handled properly.
Synchronous Mode
In the synchronous mode, a service call is initiated from a remote node and SVCGW receives the result to send it to the channel that has requested the service. .
The number of calls which the remote node can simultaneously initiate cannot exceed the MAXSACALL setting in the Tmax environment file. A user initiates a call from the remote node to SVCGW and receives a response using the COM library. The flags of the ComSend must not be specified.
The remote synchronous call is the most universal method of calling a Tmax service from the remote node. SVCGW stores the remote node’s channel information and it finds the applicable channel among the channels it has and sends the result when it receives results from the service. Since the remote node’s channel is not blocked, SVCGW must handle other requests that come into the channel before the results are returned to the channel.
The following is how SVCGW operates in the synchronous mode.
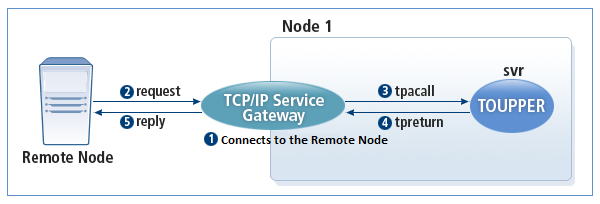
-
SVCGW and the remote node are in the connected state.
-
A remote node sends a message to the channel that is connected to the SVCGW.
-
SVCGW calls the Tmax service through tpacall().
-
SVCGW receives the service processing result and then looks for the channel of the initiator service.
-
If the channel is properly connected to the remote node, then SVCGW sends the result.
Asynchronous Mode
In the asynchronous mode, a service call is initiated from a remote node and SVCGW does not wait for a response from the service that processed the request.
To use the asynchronous mode, the flags of the ComSend must be set to COMMNOREPLY on the remote node. When COMMNOREPLY is specified, SVCGW initiates a call to the Tmax service but does not receive a response.
The following is how SVCGW operates in the asynchronous mode
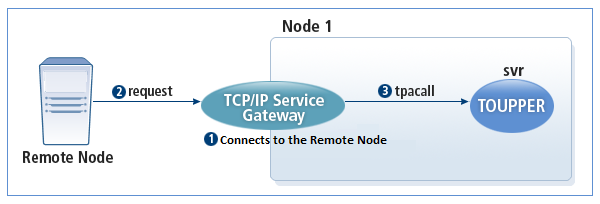
-
SVCGW and the remote node are in the connected state.
-
Remote node sends a message to the channel that is connected to the SVCGW.
-
SVCGW calls the Tmax service through tpacall().