Examples
This chapter describes examples of X25GW service types.
1. OUTBOUND X25GW
In this example, the remote node sends a request and X25GW calls the user-specified service. When the service completes processing the request and sends the result to X25GW, X25GW sends the result back to the remote node. Configure X25GW by modifying custom.c according to the remote node environment.
The following diagram shows how X25GW operates in OUTBOUND mode.
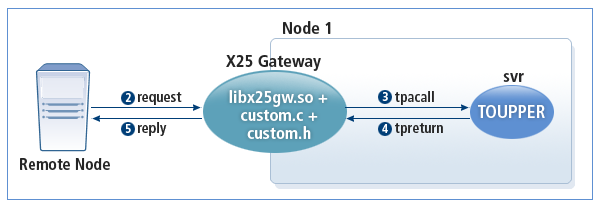
The program is composed of the following files.
| Type | File Name |
|---|---|
Configuration File |
x25gw.m, x25gw.cfg |
X25GW |
custom.c, custom.h |
Server |
svr.c |
1.1. Environment File
<x25gw.m>
*DOMAIN
res SHMKEY=88000,
MINCLH=1,
MAXCLH=1,
TPORTNO=8888
*NODE
node1 TMAXDIR=”/home/tmax”,
APPDIR=”/home/tmax/appbin”
*SVRGROUP
svg1 NODENAME=node1
*SERVER
x25gw SVGNAME=svg1,
MIN=1,
MAX=1,
CPC=5,
SVRTYPE=CUSTOM_GATEWAY,
CLOPT=”-- -F /home/tmax/config/x25gw.cfg”
svr SVGNAME=svg1,
MIN=1, MAX=1
*SERVICE
TOUPPER SVRNAME=svr
<x25gw.cfg>
# gwno | link_no | start_LCN_no | num_LCN | dir | reply_dedicated| dev_path # 0 1 1 4 any no /dev/x25pkt
1.2. X25GW
<custom.h>
#ifndef _CUSTOM_H_
#define _CUSTOM_H_
/* ---------------------------------------------------------- */
/* Fixed structures and macros */
#define MSG_MAGIC “Tmax”
#define REMOTE_REQUEST 0
#define REMOTE_REPLY 1
#define SVC_NAME_LENGTH 20
#define SYSID_LENGTH 20
/* msg_info_t struct must not be not redefined. */
typedef struct msg_info {
char svc[SVC_NAME_LENGTH];
int err;
int len;
int uid;
int flags;
int msgtype;
int channel_id;
char sys_id[SYSID_LENGTH];
} msg_info_t;
typedef struct msg_body {
char name[16];
char data[100];
} msg_body_t;
#endif
<custom.c>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/timeb.h>
#include “custom.h”
/* If the following functions are not required, the internal logic does not need to be implemented. */
/* However, they must be defined since they are used in the X25GW library. */
int init_remote_info(char *myname, int mynumber, int num_channel, int key)
{
return 1;
}
int remote_connected(int index, int linkno, int lcnno, int type)
{
return 1;
}
int get_msg_info(char *data, msg_info_t *info)
{
msg_body_t *body;
if ((info == NULL) || (data == NULL))
return -1;
body = (msg_body_t *)data;
info->err = 0;
info->flags = 0;
memset(info->svc, 0x00, SVC_NAME_LENGTH);
strncpy(info->svc, body->name, 8);
/* Return REMOTE_REQUEST to indicate that the request is from the remote node. */
return REMOTE_REQUEST;
}
int get_service_name(char *header, int err, char *svc)
{
return -1;
}
int put_msg_info(char *data, msg_info_t *info)
{
msg_body_t *body;
if ((info == NULL) || (data == NULL))
return -1;
body = (msg_body_t *)data;
/* Send the error status in body->name */
if (info->err) /* error */
strcpy(body->name, “Fail”);
else
strcpy(body->name, “Success”);
/* Returns the data length to send the results to the remote node. */
return info->len;
}
int get_channel_num(char *data)
{
return -1;
}
int remote_closed(int index, int type)
{
return 1;
}
int prepare_shutdown(int code)
{
return 1;
}
int outmsg_recovery(char *data, msg_info_t *info)
{
return -1;
}
int inmsg_recovery(char *data, msg_info_t *info)
{
return -1;
}
<Makefile>
# This Makefile is for ibm 32bit.
#TARGET must be the same as the SERVER name defined in the Tmax environment file.
TARGET = x25gw
APOBJS = $(TARGET).o
#To create X25GW,libX25GW.a or libX25GW.so must be linked.
LIBS = -lx25gw -ltmaxgw
OBJS = custom.o register.o
CFLAGS = -q32 -O -I$(TMAXDIR) -D_DBG
LDFLAGS = -brtl
APPDIR = $(TMAXDIR)/appbin
LIBDIR = $(TMAXDIR)/lib
.SUFFIXES : .c
.c.o:
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) -c $<
$(TARGET): $(OBJS)
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) -L$(LIBDIR) -o $(TARGET) $(OBJS) $(LIBS)
mv $(TARGET) $(APPDIR)/.
rm -f $(OBJS)
$(APOBJS): $(TARGET).c
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) -c $(TARGET).c
1.3. Server
<svr.c>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <usrinc/atmi.h>
TOUPPER(TPSVCINFO *msg)
{
int i;
printf("TOUPPER service is started!\n");
printf("INPUT : len=%d, data='%s'\n", msg->len, msg->data);
for (i = 0; i < msg->len; i++)
msg->data[i] = toupper(msg->data[i]);
printf("OUTPUT: len=%d, data='%s'\n",
strlen(msg->data), msg->data);
tpreturn(TPSUCCESS,0,(char *)msg->data, msg->len, 0);
}
2. Synchronous INBOUND X25GW
When a Tmax client (or a Tmax service) initiates a tpcall to X25GW, X25GW sends data to the remote node, and returns the result to the client/service when the remote node sends a reply.
It is important to specify the UID when a service is requested from the Tmax client to the remote node. Save the UID value (info→uid) specified in the X25GW library in the message using the put_msg_info function, or save the user generated UID in the message and then set the UID value to the uid attribute. The message containing the UID is sent to the remote node, and the remote node must return the UID without modifying it. When X25GW receives the reply, it calls the get_msg_info function to get the UID value and returns the reply back the client/service that requested the service.
The following is how X25GW operates in synchronous inbound mode.
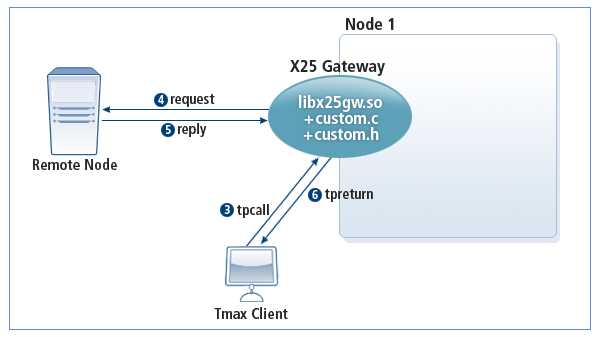
The program is composed of the following files.
| Category | File Name |
|---|---|
Configuration File |
x25gw.m, x25gw.cfg |
X25GW |
custom.c, custom.h |
Client |
cli_x25gw.c |
2.1. Environment File
<x25gw.m>
*DOMAIN
res SHMKEY=88000,
MINCLH=1,
MAXCLH=1,
TPORTNO=8888
*NODE
node1 TMAXDIR=”/home/tmax”,
APPDIR=”/home/tmax/appbin”
*SVRGROUP
svg1 NODENAME=node1
*SERVER
x25gw SVGNAME=svg1,
MIN=1,
MAX=1,
CPC=5,
SVRTYPE=CUSTOM_GATEWAY,
CLOPT=”-- -F /home/tmax/config/x25gw.cfg”
*SERVICE
X25GW SVRNAME=x25gw
<x25gw.cfg>
# gwno | link_no | start_LCN_no | num_LCN | dir | reply_dedicated| dev_path # 0 1 1 4 any no /dev/x25pkt
2.2. X25GW
<custom.h>
#ifndef _CUSTOM_H_
#define _CUSTOM_H_
/* ---------------------------------------------------------- */
/* Fixed structures and macros */
#define MSG_MAGIC “Tmax”
#define REMOTE_REQUEST 0
#define REMOTE_REPLY 1
#define SVC_NAME_LENGTH 20
#define SYSID_LENGTH 20
/* msg_info_t struct cannot be redefined. */
typedef struct msg_info {
char svc[SVC_NAME_LENGTH];
int err;
int len;
int uid;
int flags;
int msgtype;
int channel_id;
char sys_id[SYSID_LENGTH];
} msg_info_t;
/* ---------------------------------------------------------- */
/* Modifiable structures and macros */
/* msg_header_t and msg_body_t structs can be redefined. */
#define UID_FIELD 98
#define SVC_NAME_FIELD 92
#define UID_LENGTH 4
#define SVC_LENGTH 6
typedef struct msg_body {
char data[92];
char name[6];
char uid[4];
} msg_body_t;
#endif /* _CUSTOM_H_ */
<custom.c>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/timeb.h>
#include “custom.h”
/* If the following functions are not required, the internal logic does not need to be implemented. */
/* However, they must be defined since they are used in the X25GW library. */
int get_channel_num(char *data)
{
return -1;
}
int put_msg_complete(char *hp, char *data, msg_info_t *info)
{
return 1;
}
int get_service_name(char *header, int err, char *svc)
{
return -1;
}
int init_remote_info(char *myname, int mynumber, int num_channel, int key)
{
return 1;
}
int remote_connected(int index, int addr, int type, int fd)
{
return 1;
}
int get_msg_info(char *data, msg_info_t *info)
{
info->flags = 0;
if ((info == NULL) || (data == NULL))
return -1;
info->err = 0;
info->flags = 0;
/* Set info->uid. */
memcpy((char *)&(info->uid), (char *)&data[UID_FIELD], UID_LENGTH);
strncpy(info->svc, (char *)&data[SVC_NAME_FIELD], SVC_LENGTH);
info->svc[SVC_LENGTH] = 0;
if (info->uid == 0) {
return REMOTE_REQUEST;
}
else {
return REMOTE_REPLY;
}
}
int put_msg_info(char *data, msg_info_t *info)
{
int nSize = 0;
if ((info == NULL) || (data == NULL))
return -1;
if (info->err) {
printf(“info->err = %d\n”, info->err);
return -1;
}
else
/* When making a request to the remote node, this uid */
/* must be set to the value configured in the library.*/
memcpy((char *)&data[UID_FIELD], (char *)&(info->uid),
UID_LENGTH);
memcpy((char *)&data[SVC_NAME_FIELD], info->svc, SVC_LENGTH);
return info->len;
}
int remote_closed(int index, int type)
{
return 1;
}
int prepare_shutdown(int code)
{
return 1;
}
int outmsg_recovery(char *data, msg_info_t *info)
{
return -1;
}
int inmsg_recovery(char *data, msg_info_t *info)
{
return -1;
}
<Makefile>
# This Makefile is for ibm 32bit.
#TARGET must be the same as the SERVER name defined in the Tmax environment file.
TARGET = x25gw
APOBJS = $(TARGET).o
#To create X25GW, #libX25GW.a or libX25GW.so must be linked.
LIBS = -lx25gw -ltmaxgw
OBJS = custom.o register.o
CFLAGS = -q32 -O -I$(TMAXDIR) -D_DBG
LDFLAGS = -brtl
APPDIR = $(TMAXDIR)/appbin
LIBDIR = $(TMAXDIR)/lib
.SUFFIXES : .c
.c.o:
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) -c $<
$(TARGET): $(OBJS)
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) -L$(LIBDIR) -o $(TARGET) $(OBJS) $(LIBS)
mv $(TARGET) $(APPDIR)/.
rm -f $(OBJS)
$(APOBJS): $(TARGET).c
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) -c $(TARGET).c
2.3. Client
<cli_x25gw.c>
/* This program makes service request to X25GW.
This program is implemented after a connection is established between
X25GW and the remote node. */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <usrinc/atmi.h>
#include "custom.h"
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int ret;
msg_body_t *body;
char *buf;
long rlen;
ret = tmaxreadenv("tmax.env", "TMAX");
if (ret < 0) {
printf("tmaxreadenv fail...[%s]\n", tpstrerror(tperrno));
}
ret = tpstart((TPSTART_T *)NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("tpstart fail...[%s]\n", tpstrerror(tperrno));
return -1;
}
buf = tpalloc("STRING", 0, 0);
if (buf == NULL){
printf("buf tpalloc fail..[%s]\n", tpstrerror(tperrno));
tpend();
return -1;
}
body = (msg_body_t *)buf;
memcpy(body->data, argv[1], strlen(argv[1]));
body->data[51] = 0;
/* Call X25GW service. */
ret = tpcall("X25GW", buf, sizeof(msg_body_t), &buf, &rlen, 0);
if (ret < 0){
printf("tpcall fail...[%s]\n", tpstrerror(tperrno));
tpfree((char *)buf);
tpend();
return -1;
}
body = (msg_body_t *)buf;
printf("return value = %s\n", body->data);
tpfree((char *)buf);
tpend();
}
3. Non-blocking X25GW
The non-blocking X25GW method is often used when communicating with external institutions. This is because even with a small number of processes, it incurs less load on the system and can process more tasks. A blocking method calls X25GW directly from a Tmax client or service and receives a reply, but a non-blocking method uses separate sending and receiving processes to send a request to and process the reply from X25GW.
All processes that want to call X25GW must first call the sending process, and then the sending process pre-processes the request before calling X25GW via tpforward. Before processing the request, X25GW unblocks the channel connected to the Tmax engine and passes the request to the remote node. When X25GW receives a reply from the remote node, it finds and forwards the reply to the receiving service to process the reply in order. After the receiving process processes the reply, it sends the result to the initiating service requester.
Since the service that directly calls X25GW or the service that receives tprelay runs asynchronously, it incurs almost no overhead. However, the process that initially calls the sending service is blocked until it receives a reply.
The following diagram shows how a connection made between the remote node (server) and X25GW (client).
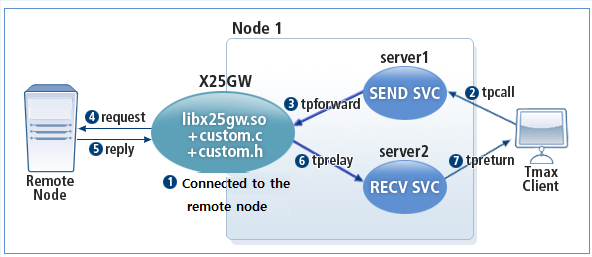
The program is composed of the following files.
| Type | File Name |
|---|---|
Configuration File |
x25gw.m, x25gw.cfg |
X25GW |
custom.c, custom.h |
Server |
sndsvr.c, rcvsvr.c |
Client |
cli_x25gw.c, custom.h |
3.1. Environment File
<x25gw.m >
*DOMAIN
res SHMKEY=88000,
MINCLH=1,
MAXCLH=1,
TPORTNO=8888
*NODE
node1 TMAXDIR=”/home/tmax”,
APPDIR=”/home/tmax/appbin”
*SVRGROUP
svg1 NODENAME=node1
*SERVER
x25gw SVGNAME=svg1,
MIN=1,
MAX=1,
CPC=5,
SVRTYPE=CUSTOM_GATEWAY,
CLOPT=”-- -F /home/tmax/config/x25gw.cfg –S RECVSVC –H 9”
sndsvr SVGNAME=svg1,
MIN=1,
MAX=1
rcvsvr SVGNAME=svg1,
MIN=1,
MAX=1
*SERVICE
X25GW SVRNAME=x25gw
SENDSVC SVRNAME=sndsvr
RECVSVC SVRNAME=rcvsvr
<x25gw.cfg>
# gwno | link_no | start_LCN_no | num_LCN | dir | reply_dedicated| dev_path # 0 1 1 4 any no /dev/x25pkt
3.2. X25GW
<custom.h>
/* ---------------------- custom.h -------------------------- */
#ifndef _CUSTOM_H_
#define _CUSTOM_H_
/* ---------------------------------------------------------- */
/* Fixed structures and macros */
/* Common of Agent Define */
#define MSG_MAGIC “Tmax”
#define REMOTE_REQUEST 0
#define REMOTE_REPLY 1
#define SVC_NAME_LENGTH 20
#define SYSID_LENGTH 20
/* msg_info_t struct cannot be redefined. */
typedef struct msg_info {
char svc[SVC_NAME_LENGTH];
int err;
int len;
int uid;
int flags;
int msgtype;
int channel_id;
char sys_id[SYSID_LENGTH];
} msg_info_t;
/* ---------------------------------------------------------- */
/* Modifiable structures and macros */
#define UID_FIELD 58
#define SVC_NAME_FIELD 52
#define UID_LENGTH 4
#define SVC_LENGTH 6
#define MSG_KEEP_SVC_SIZE 9
typedef struct msg_body {
char retsvcname[9]; /* The field that stores the data whose size is specified with the -H option */
char data[52];
char name[6];
char uid[4];
} msg_body_t;
/* The struct that excludes retsvcname, the internal header of the body,
when communicating with the remote node. */
typedef struct remote_body{
char data[52];
char name[6];
char uid[4];
}remote_body_t;
#endif
<custom.c>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/timeb.h>
#include “custom.h”
/* If the following functions are not required, the internal logic does not need to be implemented. */
/* However, they must be defined since they are used in the X25GW library. */
int get_channel_num(char *data)
{
return -1;
}
/* Set the service name to tprelay to. */
int get_service_name(char *header, int err, char *svc)
{
/*strcpy the internal user header (retsvcname).*/
strcpy(svc, header);
svc[8] = 0;
return 1;
}
int init_remote_info(char *myname, int mynumber, int num_channel, int key)
{
return 1;
}
int remote_connected(int index, int linkno, int lcnno, int type)
{
return 1;
}
/* get_msg_info and put_msg_info must be implemented same as the
synchronous client X25GW. */
int get_msg_info(char *data, msg_info_t *info)
{
info->flags = 0;
if ((info == NULL) || (data == NULL))
return -1;
info->err = 0;
info->flags = 0;
/* Set info->uid. */
memcpy((char *)&(info->uid), (char *)&data[UID_FIELD], UID_LENGTH);
strncpy(info->svc, (char *)&data[SVC_NAME_FIELD], SVC_LENGTH);
info->svc[8] = 0;
if (info->uid == 0) {
return REMOTE_REQUEST;
}
else {
return REMOTE_REPLY;
}
}
int put_msg_info(char *data, msg_info_t *info)
{
int nSize = 0;
if ((info == NULL) || (data == NULL))
return -1;
if (info->err) {
printf(“info->err = %d\n”, info->err);
return -1;
}
else
/* When a request is made to the remote node, this uid must be configured */
/* set to the value configured in the library.*/
memcpy((char *)&data[UID_FIELD], (char *)&(info->uid), 4);
memcpy((char *)&data[SVC_NAME_FIELD], info->svc, 6);
return info->len;
}
int remote_closed(int index, int type)
{
return 1;
}
int prepare_shutdown(int code)
{
return 1;
}
int outmsg_recovery(char *data, msg_info_t *info)
{
return -1;
}
int inmsg_recovery(char *data, msg_info_t *info)
{
return -1;
}
<Makefile>
Refer to the makefile example in Synchronous INBOUND X25GW.
3.3. Server
<sndsvr.c>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <usrinc/atmi.h>
SENDSVC(TPSVCINFO *msg)
{
char *sndbuf;
long len;
printf("[%s] Service Started!\n", msg->name);
len = (msg->len);
printf("len is [%d]\n", len);
if ((sndbuf=(char *)tpalloc("CARRAY", NULL, len)) == NULL) {
printf("sndbuf alloc failed !\n");
tpreturn(TPFAIL, -1, NULL, 0, 0);
}
memcpy(sndbuf, msg->data, msg->len);
/* Call X25GW service via tpforward. */
tpforward("X25GW", (char *)sndbuf, len, TPNOREPLY);
}
<rcvsvr.c>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <usrinc/atmi.h>
/* X25GW dynamically calls tprelay to this service. */
RECVSVC(TPSVCINFO *msg)
{
char *rcvbuf;
long len;
printf("[%s] Service Started!\n", msg->name);
len = msg->len;
rcvbuf = msg->data;
if(tpurcode != 0) {
printf( "tpurcode is [%d] tperrmsg is [%s]\n", tpurcode,
tpstrerror(tpurcode) );
tpreturn( TPFAIL, -1,(char *)rcvbuf, len, 0 );
}
tpreturn( TPSUCCESS, 0,(char *)rcvbuf, len, TPNOFLAGS );
}
3.4. Client
<cli_x25gw.c>
/* The following example program uses a Tmax client to call SENDSVC.
Before calling SENDSVC, configure the service to which X25GW
will tprelay to in the message header. */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <usrinc/atmi.h>
#include "../server/custom.h"
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int ret;
msg_body_t *body;
char *buf;
long rlen;
ret = tmaxreadenv("tmax.env", "TMAX");
if (ret < 0) {
printf("tmaxreadenv fail...[%s]\n", tpstrerror(tperrno));
}
ret = tpstart((TPSTART_T *)NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("tpstart fail...[%s]\n", tpstrerror(tperrno));
return 0;
}
buf = tpalloc("STRING", 0, 0);
if (buf == NULL){
printf("buf tpalloc fail..[%s]\n", tpstrerror(tperrno));
tpend();
return 0;
}
body = (msg_body_t *)buf;
memcpy(body->data, argv[1], strlen(argv[1]));
body->data[51] = 0;
memcpy(body->retsvcname, "RECVSVC", 9);
body->retsvcname[8] = 0;
memcpy(buf, (char *)body, sizeof(msg_body_t));
/* Call the service that will call X25GW. */
ret=tpcall("SENDSVC",buf,sizeof(msg_body_t), &buf, &rlen, 0);
if (ret < 0){
printf("tpcall fail...[%s]\n", tpstrerror(tperrno));
tpfree((char *)buf);
tpend();
return 0;
}
body = (msg_body_t *)buf;
printf("return value = %s\n", body->data);
tpfree((char *)buf);
tpend();
}