Introduction
This chapter describes the concepts, types, and constraints of Tmax RPC (Remote Procedure Call).
1. Concepts
Tmax uses APIs, such as tpcall and tpacall, to call a service in a server.
Before developing a service, the application developer must consult with other developers to decide on input and output parameters of the service. Alternatively, the developer can define the interface of the functions called from the server and then use a utility in the interface. If the latter method is used, the server creates skeleton source files and the client automatically generates the stub source files. The files are then distributed to developers to enable them to implement server and client applications.
Tmax RPC is an additional component that defines the interfaces (mentioned in the previous paragraph), so that Tmax can be used immediately. Tmax RPC uses SQL statements to extract function interfaces in order to define the interfaces. If a user writes an SQL statement, Tmax RPC can analyze the statement and define the function parameters.
The following shows how to write an SQL statement.
ins_test: INSERT INTO sample(no, name) VALUES ($empno, '$name');
The following function can be defined by the previous SQL statement. The function can be used immediately when implementing a client application.
int ins_test(char *empno, char *name)
2. Types
Tmax RPC is divided into three types according to the service method:
-
Data Access server (hereafter DA server)
-
TP server
-
Function server (hereafter FS server)
2.1. DA Server
The DA server is used for applications that consist of a single SQL query. The interface is defined using SQL.
|
The DA server only processes a single query, so the application server mode must be set to Non-XA. For more information about the configuration, refer to Transaction in Tmax Application Development Guide. |
The following process shows how Tmax works when using the DA server.
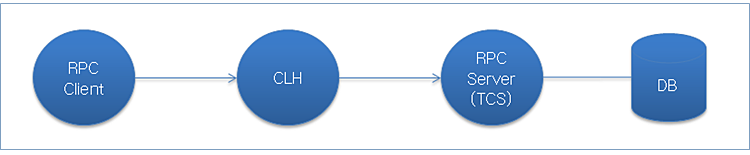
The following shows the server and client configuration for using the DA server.
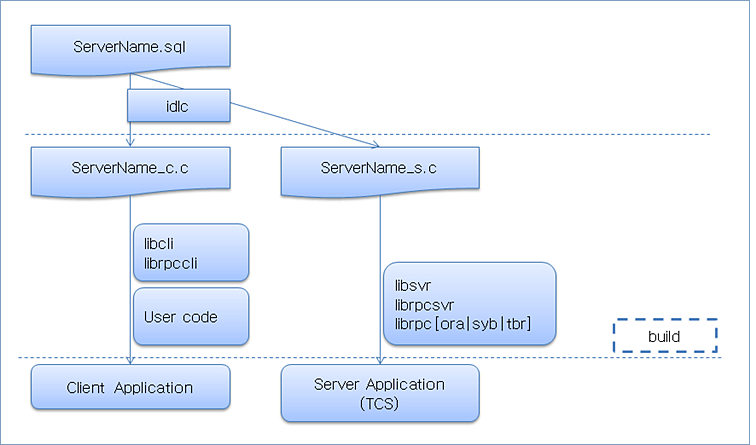
If the DA server is used, the developer is only required to configure the application server and to build an application. The application can then be executed without additional coding.
For example, when creating an insert application named ins_test, define the interface in the dstest.sql file. Tmax RPC sets the server name to match the interface file name, so define both the server and service names to dstest. (The concepts of server and service of Tmax must be reflected in the configuration.) The developer neither calls nor defines the dstest service directly, but if the ins_test function is requested by a client, the server creates a field buffer internally to tpcall dstest and the dstest server executes the corresponding query.
The following examples show the DA server environment configuration and SQL interface files.
-
DA server environment configuration
*SVRGROUP svg_rpc NODENAME =tmaxi4 *SERVER dstest SVGNAME = svg_rpc, CLOPT="-e $(SVR).out -o $(SVR).out -- -uscott -ptiger" *SERVICE dstest SVRNAME = dstest -
DA server SQL interface file
The SQL interface file of the DA server can differ depending on the idlc option. For more information about how to write the SQL interface definition file, refer to SQL Interface Definition File.
### dstest.sql ### #insert ins_test: INSERT INTO sample(no, name) VALUES ($empno, '$name'); #delete del_test: DELETE FROM sample WHERE no = $empno; #select all sel_all_test: SELECT [int] no, name FROM sample; #select name sel_test: SELECT name FROM sample WHERE no = $empno; #delete all del_all_test: DELETE FROM sample; #update update_test: UPDATE sample SET name='$name' WHERE no=$empno; #select binary b_sel_test: SELECT [binary] b_data FROM b_test_table; #insert binary b_ins_test: INSERT INTO b_test_table VALUES $b_data[binary] ;
2.2. TP Server
The TP server is used for applications that require multiple RPCs to be processed together using a transaction, not applications that consist of a single SQL query.
The following process shows how Tmax works when the TP server is used.
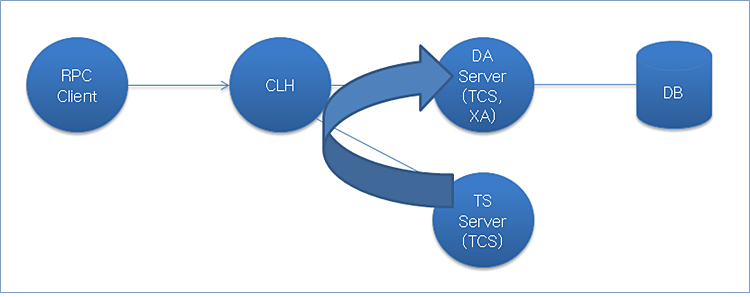
The following shows the server and client configuration for using the TP server.
Using multiple queries in an application is not suitable because the DA server works as Non-XA. If the TP server is placed in the middle and starts a transaction to call DA server functions, a single transaction containing multiple queries can be made.
To use the TP server, the interface file that enables clients to call the server and the interface SQL file used in the DA server are required. The client application calls the APIs of the TP server, and the APIs of the TP server call the APIs in the DA server. The DA server must be included in a single transaction so it must be set in xa svg.
The following shows examples of the TP server environment configuration and the interface file.
-
TP server environment configuration
*SVRGROUP svg_xarpc NODENAME = tmaxi4, OPENINFO = "Oracle_XA+Acc=P/scott/tiger+SesTm=60", DBNAME = ORACLE, TMSNAME = "tms_ora" *SERVER tstest SVGNAME = "svg_rpc" db1 SVGNAME = "svg_xarpc" *SERVICE TSTEST SVRNAME = tstest db1 SVRNAME = db1 -
TP server API interface file
For more information about how to write the API interface file, refer to API Definition File.
<*.def>
### tstest.def ### interface TSTEST { long trans_select ( [out] long sel_rows, [out] int empno[sel_rows], [out] char ename[][]); long trans_insert ( [in] int dummy); long trans_clear ( [in] int dummy); } -
DA server SQL interface file
For more DA server SQL interface file examples, refer to DA Server. For more information about how to write the file, refer to SQL Interface Definition File.
2.3. FS Server
The FS server is used to call user-defined functions unrelated to SQL. For example, a job reading a file requested by a client can be processed.
The process is similar to that of the TP server except that the DA server is not required.
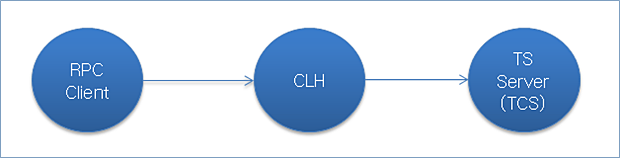
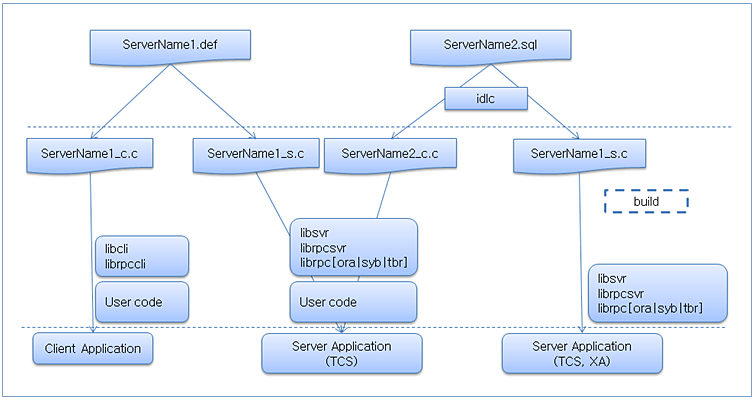
The following shows the server and client configuration for using the FS server.
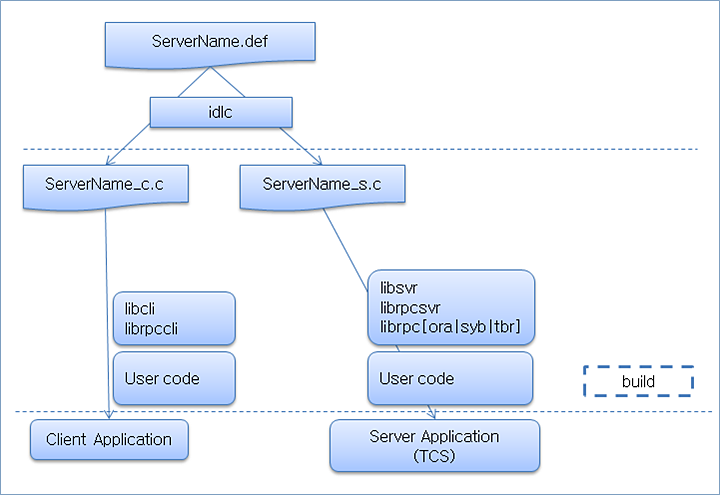
To use the FS server, API interface files must be created to write server code and client code.
The following shows the FS server environment configuration and the interface file.
-
FS server environment configuration
*SVRGROUP svg_rpc NODENAME =tmaxi4 *SERVER fstest SVGNAME = svg_rpc, CLOPT="-e $(SVR).out -o $(SVR).out -- -uscott -ptiger" *SERVICE fstest SVRNAME = fstest -
FS server API interface file
For more information about how to write the API interface file, refer to API Definition File.
<*.def>
interface FSTEST { long plus( [in] int a, [in] int b, [out] int c ); long savefile ( [in] char filename[], [in] char data[] ); long readfile ( [out] char filename[], [out] char data[] ); }
3. Environment Variables
The following describes Tmax RPC environment variables.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
TMAX_PRB_RPC_BLOB_NULL |
When RM is used, setting this to Y allows normal processing BLOB and LongRaw types with a length of 0 (null) when queried. By default, an error is returned under the same conditions. |
TMAX_PRB_RPC_NODATA_ERROR |
When RM is used, setting this to Y forces an error if the value of sqlca.sqlerrd[2] (number of rows) is 0 during UPDATE, DELETE, or INSERT operations. |
4. Constraints
The Tmax RPC server cannot be called by a regular server. Only the following operating systems and databases support Tmax RPC. (64-bit only)
The RPC Tibero library is built and deployed in Tibero 4.0 SP1. For other versions, the corresponding library is required.
| OS | Oracle 11 | Sybase 15.5 | Tibero 4.0 SP1 |
|---|---|---|---|
HP-IA 11.23 |
O |
O |
O |
HP-IA 11.31 |
O |
O |
O |
AIX 5.3 |
O |
O |
O |
AIX 6.1 |
X |
O |
O |
SUN5.10 sparc |
O |
O |
O |
Linux x86_64 |
O |
O |
O |