Introduction
This chapter describes the overview and service types of X25 gateway.
1. Overview
X25 gateway (hereafter X25GW) is a Tmax gateway that serves as an interface between a Tmax server and a Non-Tmax server (hereafter remote node). X25GW is a type of Tmax server and works as a gateway between servers (UNIX, Windows, etc.) connected through X25. When X25GW receives a message from the remote node and makes a tpacall to the applicable service and the service result is sent to the remote node server. Reversely, if a Tmax service makes a request through tpcall or other methods, then X25GW sends the request message to the remote node and when it receives a reply, it makes a tpreturn to the initiator service.
Since X25 gateway handles the complex tasks required for connecting to other systems such as attaching, detaching, sending and receiving messages, a developer only needs to implement the business logic.
The X25GW operates in two methods. One is for transmitting data from Tmax to a remote node, and the other is for transmitting data from remote node to Tmax.
The following diagram shows X25GW operation.
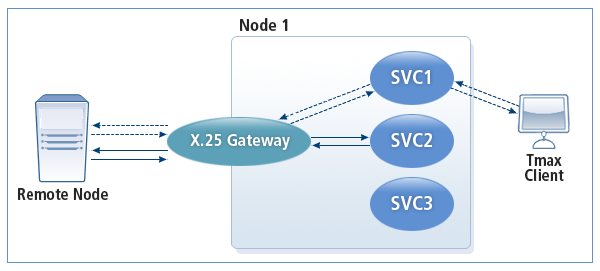
-
Service request initiated by Tmax
The service flow for this mode is represented by the dotted lines in X25GW Operation. A Tmax client makes a service request to the remote node. This is called an inbound service INBOUND Service.
-
Service request initiated by remote node
The service flow for this mode is represented by the solid lines in X25GW Operation. X25 gateway receives a service request from a remote node. This is called an OUTBOUND Service.
In an OUTBOUND service communication, a remote node calls a Tmax service using the service name.
The following is how X25GW operates when a service is requested in the synchronous/asynchronous mode.
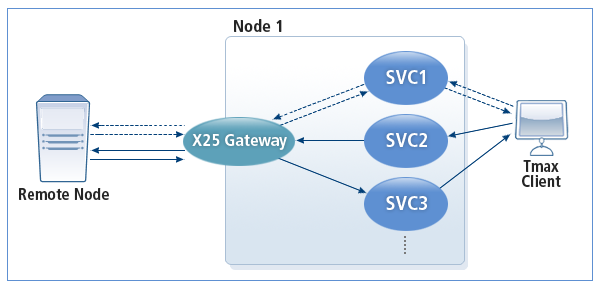
-
Synchronous Call
This method is represented by the dotted lines in X25GW Operation in Synchronous/Asynchronous Mode. A Tmax service waits until it receives a response from the remote node.
-
Asynchronous Call
This method is represented by the solid lines in X25GW Operation in Synchronous/Asynchronous Mode. When the Tmax client calls a Tmax service, control is passed from that service to X25GW and the service can receive other service requests. When X25GW receives a reply from the remote node, the request is passed to the service that processes responses.
X25GW installed on Tmax is a type of Tmax server, and it must be configured as a server in the Tmax environment file. While general servers are created using a TCS or UCS server library, but X25GW creates a server by linking external communication libraries (libx25gw.a, libx25gw.so) with a user-created program (custom.c). For detailed information about the Tmax environment configuration and how to create programs (custom.c, custom.h), refer to Environment Configuration and User Programs and Functions.
2. Service Types
X25GW is created by linking the libraries (libx25gw.a, libx25gw.so) with user created programs such as custom.c and custom.h. X25GW created in this way communicates with remote node and works as an intermediary in sending Tmax client requests to the remote node and enabling Tmax service to process requests from a remote node.
Depending on its operation mode, X25GW operates as either a synchronous X25GW or asynchronous X25GW.
2.1. Synchronous X25GW
The synchronous method is where a Tmax client or server requests a service and receives a response. In the opposite case, when the remote node requests a service, X25GW forwards the request to a Tmax service and returns the result to the remote node.
In the former case, X25GW operation depends on whether the Tmax service that sent the request to the remote node is blocking or non-blocking. If non-blocking, the result from the remote node is immediately returned to the requested channel.
When a Tmax client or server sends a request to the remote node in the synchronous mode, X25GW and the remote node must share the UID (unique ID).
Blocking Service
In a blocking service, a Tmax server or client requests a service to X25GW and waits for a response. If the service that received the client request makes a tpcall to the X25GW service, then the Tmax service (SVC1 in the diagram) blocks until it receives the result from the remote node.
When X25GW executes, the service called by the client calls X25GW and blocks until it receives a reply. Even when tpacall is called, tpgetrply blocks until it receives a reply. In order to accommodate a large number of requests, many servers are required to make up for the blocking time period.
A blocking service is suitable for external communication since many servers are needed to prepare for external system failures (machines, network).
The following diagram shows the operating structure of X25GW when calling a service in a blocking synchronous mode.
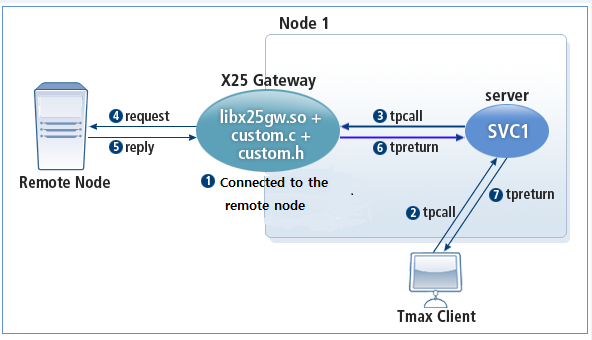
-
X25GW and the remote node are in the connected state.
-
A Tmax client sends a tpcall to the Tmax service.
-
The Tmax service receives the client request, and sends a tpcall to X25GW.
-
X25GW sends the request to the connected remote node.
-
When the remote node sends a reply, X25GW checks for any errors.
-
X25GW sends a reply (tpreturn) to the initiator service.
-
The service returns the reply (tpreturn) to the Tmax client.
Non-Blocking Service
A non-blocking service cannot be used when a Tmax client directly requests services to X25GW. It requires an intermediary server between the client and X25GW to send/receive the request/reply to/from X25GW and return the reply to the client. The sending and receiving services are placed in front of X25GW. The Tmax client calls the sending service, and the sending service terminates after forwarding the request to X25GW.
X25GW requests a service to the remote node, receives a reply, and sends it to the receiving service. The receiving service returns the reply to the client. In other words, the client requests a service and receives a reply (synchronous), but the server forwards the request and then terminates (asynchronous).
A non-blocking service can process more requests with fewer servers than a blocking service. Since a blocking service calls X25GW and then blocks, it requires more server processes to handle multiple requests simultaneously. However, since a non-blocking service is terminated after performing its tasks, it can process more requests with a small number of server processes.
A non-blocking service is more efficient for communication with external institutions.
The following diagram shows the operation of X25GW in a non-blocking service.
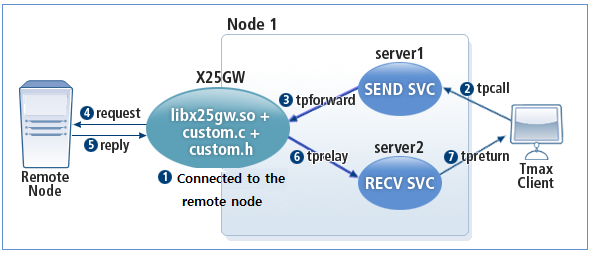
-
X25GW and the remote node are in the connected state.
-
A Tmax client sends a tpcall to the Tmax service.
-
The Tmax service receives the client request, and forwards (tpforward) it to X25GW.
-
X25GW sends the request to the connected remote node.
-
When the remote node sends a reply, X25GW checks for any errors.
-
X25GW sends the reply (tprelay) to the service that will process the return.
-
The service returns the reply (tpreturn) to the Tmax client.
Remote Synchronous Call
A remote node initiates a service request to X25GW. X25GW calls the requested service and receives a reply and sends it to the channel that requested the service. The remote node cannot make more than MAXSACALL number of concurrent calls to X25GW as defined in the Tmax environment file.
The remote synchronous call method is the most universal way of calling a Tmax service from a remote node. X25GW stores the remote node’s channel information and uses it to find the channel to send the reply. Other requests can be made as needed before the reply is returned to the channel. Since X25GW does not block the channel from the remote node and continues to receive other requests, requests are processed according to the X25GW operation method.
The following diagram shows the operation of X25GW when a service is called in the remote synchronous method.
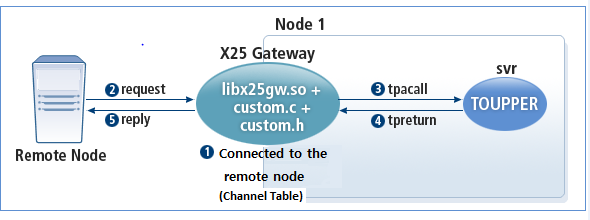
-
X25GW and the remote node are in the connected state.
-
The remote node sends a request to the channel connected with X25GW.
-
X25GW calls a Tmax service via tpacall().
-
X25GW receives a reply and finds the channel where the request originated from.
-
If the channel is normally connected, then the result is returned to the remote node.
2.2. Asynchronous X25GW
The asynchronous method is where a Tmax client, server, or remote node requests a service and does not receive a reply, or the request is processed in another program. A Tmax service requests the service to X25GW and another service receives a reply.
A client request is processed asynchronously via tpacall without receiving a reply. Reversely, a service can be initiated from the remote node and may not receive a reply or receive the reply through another channel. This is called the asynchronous method.
Requesting a Service from Tmax
A Tmax service makes a request via tpacall with TPNOREPLY to X25GW and then the service terminates. X25GW sends a request to the remote node and when it receives a reply it makes a tpacall to another service.
The following diagram shows the X25GW operation in an asynchronous service request.
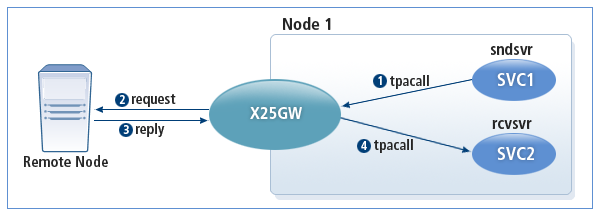
-
A Tmax service sends a request to X25GW via tpacall with TPNOREPLY.
-
X25GW sends the request to the remote node.
-
X25GW receives a reply from the remote node.
-
X25GW calls another Tmax service via tpacall with TPNOREPLY.
Requesting a Service from the Remote Node
When a remote node requests a service to X25GW, X25GW calls the Tmax service via tpacall. After processing, the Tmax service sends a reply to X25GW, and X25GW uses any available channel to return the reply to the remote node.
The following diagram shows the operation of X25GW when a service is requested from the remote node asynchronously.
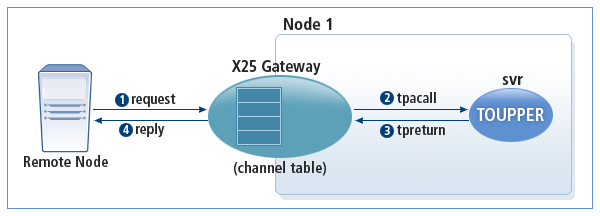
-
A remote node sends a request to X25GW.
-
X25GW sends the request to the Tmax service via tpacall.
-
The Tmax service sends a reply to X25GW.
-
X25GW finds the channel connected to the remote node in the channel table and sends the reply via the channel.
3. Other Gateway Functions
This section describes other functions of the X25 gateway.
3.1. Gateway Header
The gateway header is used when calling X25GW from the Tmax client or server. Other X25GW libraries must be used to use the gateway header. The libx25gw.a, and libx25gw.so libraries are normally used, but the libx25gw.gwh.a, or libx25gw.gwh.so library must be used when using the gateway header. The gateway header must be placed in the very first offset position in all data buffers. When using the user header, it must be placed after the gateway header in the buffer.
The gateway header is used for various purposes, but only the svc item can be used in X25GW. This item is used to specify the service name to process the reply data when using the non-blocking mode or the asynchronous method. The gateway header is usually used when a service request is processed in message units without using a user header.
3.2. Service Name Search Order
A non-blocking or asynchronous X25GW requires a Tmax service that will process a request or reply sent from the remote node. Since X25GW does not have service name information, the user must specify the service name. X25GW uses the following 3 methods to discover the service name.
The service name mentioned here must be registered in the Tmax configuration file.
-
When a Tmax client or service calls X25GW by specifying the service name in the gateway header, X25GW uses this name first. This only applies when the gateway header is used.
-
Find the service name in the user header. When a Tmax client or service calls X25GW, the user name can be specified in the user header and the user function get_service_name can be used to get the name.
-
The service name is specified in the [-S] of option of CLOPT. In this case, the same service is used for all messages.
|
When a service is requested for the first time from a remote node, these methods are not used. Instead, the user must specify the service name when calling the get_msg_info function. |
3.3. User Specified Channel
When X25GW is configured completely in asynchronous mode, the user can specify the channel to the remote node in the [-a] option of the CLOPT section. In a completely asynchronous mode, no replies are exchanged between the two sides. The reply data must also be sent as a service request.
For example, if tpacall with TPNOREPLY is sent from a Tmax client or service to X25GW, X25GW sends data to the remote node and terminates the service without storing the UID or any other data related to the service request. When X25GW receives a reply from the remote node, it processes the reply as another service request. The same applies to the reverse case when the remote node imitates a request.
In the previous case, the remote node channel can be specified in the [-u] option in the CLOPT section. The channel can be set in the following two ways.
-
When Tmax sends a service request to a remote node, X25GW calls the get_channel_num function and the channel is defined by the user by analyzing the transmitted data.
-
When the remote node initiates the request, the get_msg_info function saves its channel information and calls the Tmax service. To send the result to the remote node, the Tmax service calls tpacall with TPNOREPLY to X25GW. The user can call the get_channel_num function which uses the saved channel information to send the reply to the remote node. In this mode, the channel between X25GW and the Tmax engine is not blocked and the reply can be sent to the channel that initiated the service.
3.4. RESET Processing
X25GW can exchange a reset operation with the remote node. Excessive number of reset exchanges may occur due to system failure, program bugs, or invalid remote configuration. If too many resets occur, the gateway can fall into a loop and not be able to process the application properly. To prevent such a problem, X25 gateway automatically closes the session of the channel and reconnects when reset count exceeds the specified limit (100).