Introduction
This chapter describes the concepts and the structure of Host-link.
1. Overview
Host-link is a gateway that allows clients in an open environment to access the application services provided by legacy systems such as an IBM host.
The resources of the legacy system can be used without modifying application code. In addition, legacy systems can be optimally connected using standard communication protocols such as SNA or TCP/IP. Also, clients can use various web resources of the open environment.
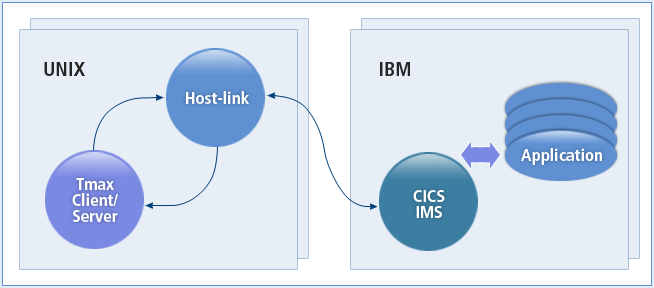
Host-link consists of two types: SNA (System Network Architecture) and TCP/IP. The type of Host-link used depends on the communication protocol to be used between a legacy system and an open environment system.
-
SNA
-
Provides DPL (Distributed Program Link) and DTP (Distributed Transaction Processing) of CICS, and APPC and CIP-C interfaces of IMS. The SNA type supports request/response communication and interactive communication modes.
-
To use the SNA type of Host-link, the following SNA gateway must be installed according to the server type.
Protocol Description Solaris
SunLinkTM
-
HP-UX: SNAPlus2
-
AIX: IBM Communications Server
-
-
There are two types of SNA, LU 0 and LU 6.2. LU is an acronym for logical unit, which is the type of package used in IBM SNA.
-
SNA LU 0
A single process handles various tasks.
-
SNA LU 6.2
Each process internally creates threads to execute services. These are kernel-level threads and up to 50 threads can be created. Each thread is responsible for a single LU session. To connect 50 or more sessions, additional processes must be started.
A service request from an open system to the host is called an INBOUND service, and a service request from the host to an open system is called an OUTBOUND service.
SNA LU 6.2 executes services in the following two modes.
Service Description DPL Mode
Delivers services through a mirror provided by the host. This mode is only supported in INBOUND services.
DTP Mode
Directly connects to the host service. This mode is supported in both INBOUND and OUTBOUND services. Depending on the setting specified in the Host-link environment configuration file, this mode can also be supported in either the INBOUND or OUTBOUND service.
-
-
-
TCP/IP
Connects to CICS and IMS, the TP-monitor for OS/390. The TCP/IP type supports the request/response communication mode and the interactive communication mode.
Host-link automatically starts and terminates together with the Tmax system, due to its custom gateway characteristics. Therefore, additional processes are not required to start and terminate the Host-link.
2. Host-link Structure
The structure of a Host-link can be described internally, and system-wide.
Host-link within an Entire System
Host-link is managed as a custom gateway within the Tmax system. To run a Host-link, it must be registered as a custom gateway in the Tmax configuration file. Host-link connects to the SNA gateway that resides in an open environment system to send requests from the open system to the host.
The following describes the advantages of a custom gateway.
-
Multiple channels
Host-link can simultaneously execute multiple tasks by connecting to Tmax through multiple channels. This becomes possible by creating multiple sessions between a Host-link and an SNA gateway in an open system.
-
Control of session count
When the number of requested services is greater than the number of sessions created between a Host-link and an SNA gateway, the excessive number of services will be stored in a queue of the sending process. When there are available sessions, the services are requested in the FIFO mode.
-
Managing a Host-link as a typical server process
A typical server process can be started and terminated for each process. A Host-link can also be started and terminated by using the tmdown and tmboot commands. In addition, the processing count and average response time can be checked by using tmadmin, a system management tool.
-
Calling a Host-link as a service
Host-link is defined as a single service in the Tmax configuration file. To use Host-link in an open environment system, Host-link is called as a service in the Tmax system.
Internal Structure
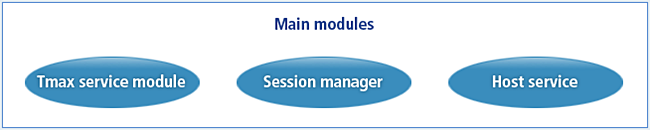
Host-link consists of the Tmax service module, the session manager module, and the host service module.
-
Tmax Service Module
The Tmax service module creates sessions between Tmax and a host system, and monitors the sessions. In addition, it delivers services requested from Tmax to the host service module, or sends service requests from the host service module to Tmax.
-
Session Manager Module
The session manager module connects Tmax and a host system in the SNA LU 0 or SNA LU 6.2 mode. It also monitors the connection to flexibly execute services between the two systems.
-
Host Service Module
The host service module sends the service request of a host process to the Tmax service module, and also delivers the service request of Tmax to the host system.