Service Flow Editor
This chapter describes the functions and uses of the Service Flow editor.
1. Overview
A Service Flow is a graphical representation of a sequence of steps in a business service. An AnyLink project must be created before creating a Service Flow Diagram (SFDL: Service Flow Definition Language) file. The incoming message events of the Service Flow are registered as internal services in AnyLink. Most of the services in AnyLink are message events of the Service Flow, and they call the Flow’s service activities according to the defined direction of the Service Flow after each step.
2. Creating a Service Flow
To create a Service Flow, select [New] > [Flow] from the context menu of the Project Navigator. Enter the required items in the Flow Diagram window, and then click [Finish].
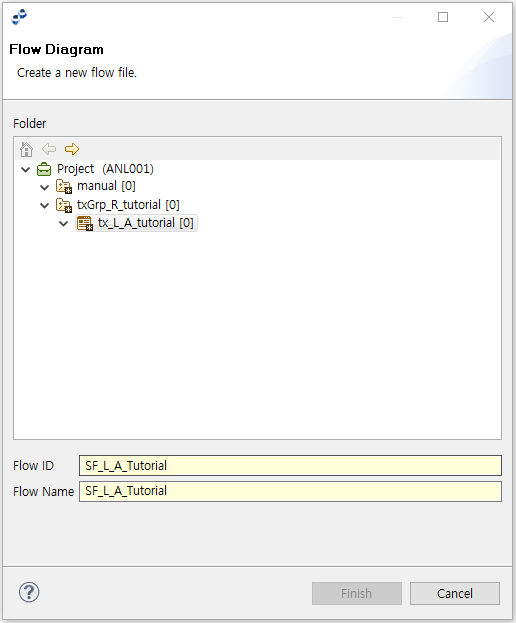
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
Flow ID |
Service Flow resource ID. Only alphanumeric and special (_) characters are allowed, and the first character must be an alphabet character. |
Flow Name |
Service Flow name. Only Korean, alphanumeric, and special (_) characters are allowed. Must follow the XML Naming Convention. |
3. Service Flow Diagram
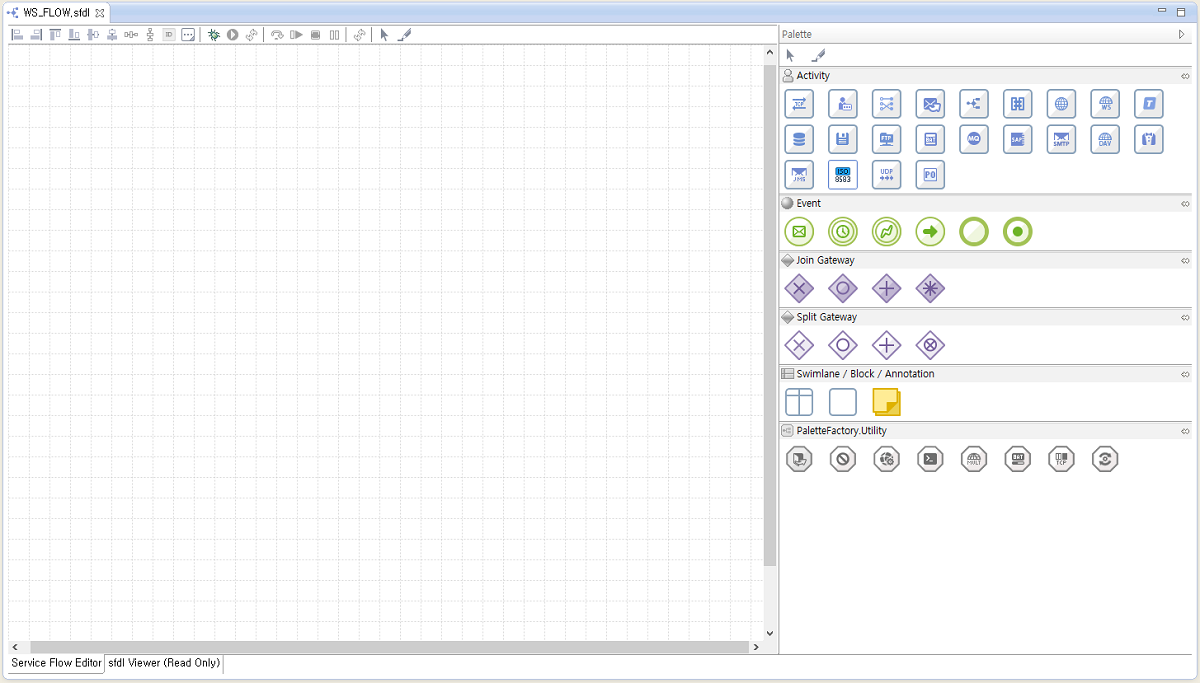
When a Service Flow is created, the following page is displayed with the editor on the left and the editor palette on the right.
-
[Toolbar]
The Toolbar consists of buttons for object alignment, display settings, and debugger functions.
 Service Flow Page - Toolbar
Service Flow Page - ToolbarButton Description 
Align objects to the left.
Align objects to the right.
Align objects to the top.
Align objects to the bottom.
Align objects to the center (horizontally).

Align objects to the center (vertically).

Distribute objects evenly (horizontally).

Distribute objects evenly (vertically).

Edit ID/Name label.

Toggle (show/hide) transition condition.

Run in debug mode. Opens the 'Select Server' window.

Open the 'Message Settings" dialog box for debugging.
 (13th icon)
(13th icon)Refresh debugger status.

Go to the next activity.

Go to the next break point.

Go to the end of the flow.

Pause debugger at the next activity if the debugger is running.
 (18th icon)
(18th icon)Show debugger status.

Change mouse pointer to 'Selection' mode.
Change mouse pointer to 'Transition' mode.
-
[Palette]
The palette consists of objects that can be used to create a Service Flow diagram.
A Service Flow, which is also called a process, consists of activities, events, and transitions. Click and move an object to the editor.
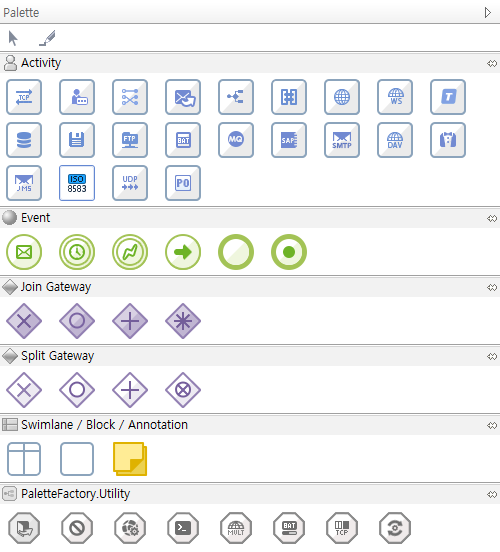 Service Flow - Palette
Service Flow - PaletteObject Type Description Selection, Transition
-
 (Select): Return to select mode.
(Select): Return to select mode. -
 (Transition): Arrow that represents the direction and order of flow between activities or events. Use this to connect the objects. A transition connects activities, events, and gateways to define a business process. A transition can also define a condition to determine the direction of the flow after a gateway.
(Transition): Arrow that represents the direction and order of flow between activities or events. Use this to connect the objects. A transition connects activities, events, and gateways to define a business process. A transition can also define a condition to determine the direction of the flow after a gateway.
Activity
Also called a task. Represents actions that must be performed in the current step of the Service Flow. This is mostly used to represent an Outbound Service. For more information, refer to Activity.
Event
Represents an event, such as a message, error, or timeout event. An event can be a Start Event without an incoming transition, an Intermediate Event with both incoming and outgoing transitions, or an End Event without an outgoing transition. For more information, refer to Event.
Gateway
Controls the convergence and divergence of a service flow.
A gateway can be a split gateway that splits a single transition into multiple transitions or a join gateway that joins multiple transitions into a single transition. For more information, refer to Gateway.
Swimlane/Block/Annotation
-
Swimlane: Dividing line between tasks in the Service Flow
-
Block: Used to group related Activities.
-
Annotation: Memo object.
For detailed information, refer to Swimlane/Block/Annotation.
Utility
Set of utilities used in the Service Flow. For detailed information, refer to Utility.
-
4. Activity
The following describes the Activity types.
| Menu | Description |
|---|---|
|
TCP outbound rule service call. |
|
User class activity. |
|
Source and target variable mapping. |
|
Service response message. Sends a normal or error response message to the request message of the message event. |
|
Service Flow process call. |
|
Multi-binding service call. |
|
HTTP outbound rule service call. |
|
Import a web service. |
|
Tmax (middleware) call. |
|
DB adapter service call. |
|
File adapter service call. |
|
FTP adapter service call. |
|
Batch outbound rule call. |
|
MQ outbound rule call. |
|
SAP outbound rule call. |
|
SMTP outbound rule call. |
|
WebDav outbound rule call. |
|
Tuxedo outbound rule call. |
|
JMS outbound rule call. |
|
ISO8583 outbound rule call. |
|
UDP outbound rule call. |
|
ProObject outbound rule call. |
An Activity has input and output parameters.
An Activity reads from the input parameter and writes to the output parameter. Both parameters are declared in the Block Activity that includes the Process or Activity.
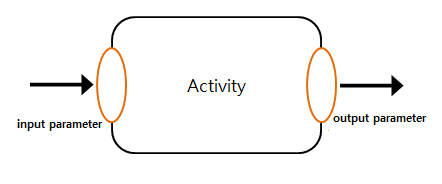
4.1. Configuring an Activity
Add an Activity to the editor, and then double-click on it or place the cursor on the Activity to show the Activity Preferences menu to configure the Activity.
| Menu | Description | Menu | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Basic Info |
|
Loop Properties |
|
Parameter Properties |
|
Copy |
|
Handler Properties |
|
Delete |
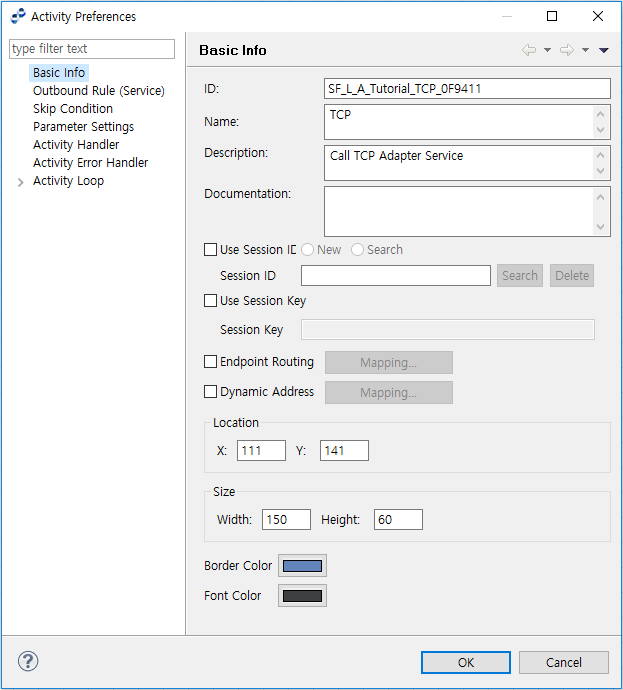
Basic Info
The following describes the Activity Preferences window.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
ID |
Activity ID. |
Name |
Activity name. |
Description |
Activity role. |
Documentation |
Activity description. |
Session ID |
Session ID of the Activity. This is used to connect with other Activities or Events with the same Session ID. |
Session Key |
Session key. This is used to connect to a session with the key. Only available for TCP activities. |
Endpoint Routing |
Routes to an endpoint or endpoint group with mapped VALUE. The endpoint group set in the outbound rule must be mapped to an endpoint group in the page displayed by selecting [System] > [Adapter] in WebAdmin. When setting VALUE of sub endpoint or endpoint group, a request message is sent to the endpoint. |
Dynamic Address Change |
Dynamically changes IP address and port number of a target to request to. Only available for TCP clients. |
Dynamic URL Change |
Dynamically changes IP address and port number of a target to request to. Only available for HTTP outbound. |
Location |
Activity position (x, y). Position can be set with this option, or more easily by using the mouse. |
Width |
Width (can also be adjusted with the mouse). |
Border Color |
Border color. |
Font Color |
Font color. |
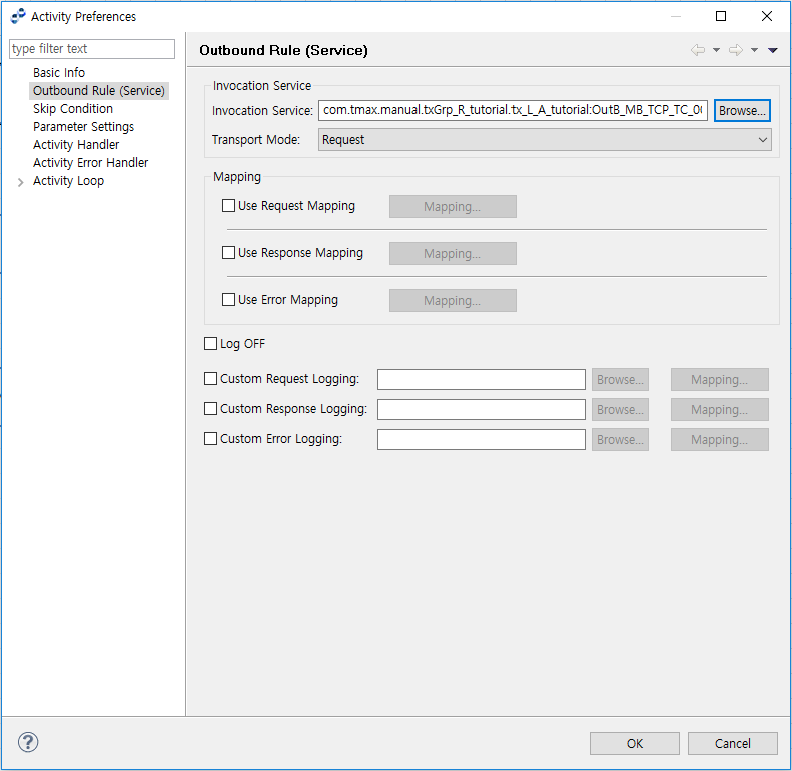
Outbound Rule (Service)
The following describes the Outbound Rule (Service) page of the Activity Preferences window.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
Invocation Service |
Select an existing Outbound Rule Service that can be used for the Activity. Click [Browse…] to search for the service. |
Transport Mode |
|
Mapping |
For information about mapping, refer to Mapping Dialog Boxes. |
Log OFF |
Execute log off on the Activity. |
Custom Request Logging |
Option to use custom request logging. Click [Browse…] to select a Custom Log Outbound Rule, and then click [Mapping…] to create a mapping. |
Custom Response Logging |
Option to use custom response logging. Click [Browse…] to select a Custom Log Outbound Rule, and then click [Mapping…] to create a mapping. |
Custom Error Logging |
Option to use custom error logging. Click [Browse…] to select a Custom Log Outbound Rule, and then click [Mapping…] to create a mapping. |
Skip Condition
The following describes the Skip Condition page of the Activity Preferences window.
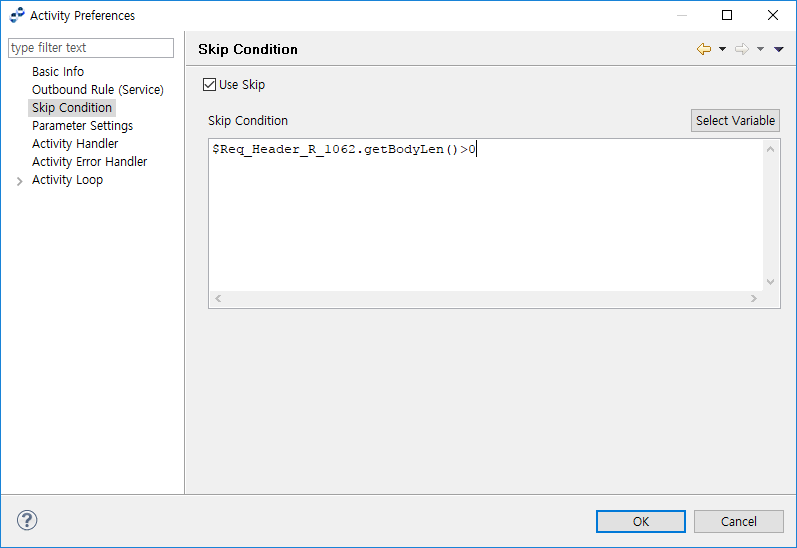
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
Use Skip |
Option to use skip condition for the process variable. |
Skip Condition |
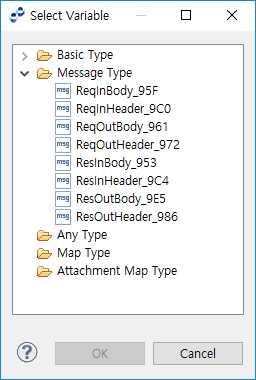
Condition for the selected variable. Click [Select Variable] to open the Select Variable dialog box (Activity Preferences - Select Variable) for selecting a process variable. |
Parameter Settings
The variable set in the parameter is used in the service call. If a mapping exists, the input parameter is used as the source of the input mapping, and the output parameter as the target of the output mapping.
The following describes the Parameter Settings page of the Activity Preferences window.
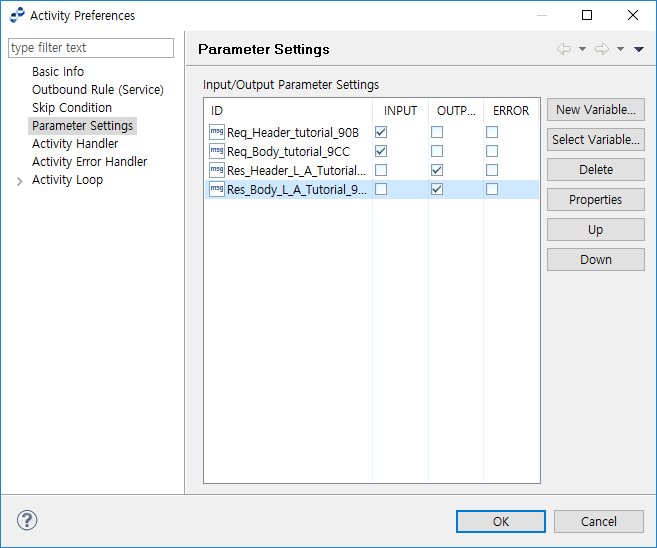
-
Input/Output Parameters
Item Description ID
Variable ID.
INPUT
Option to set the variable type to input.
OUTPUT
Option to set the variable type to output.
ERROR
Option to set the variable type to error.
-
Buttons
Button Description [New Variable]
Opens the Add New Process Variable dialog box to create a new variable (Activity Preferences - Add New Process Variable).
[Select Variable]
Opens the Select Variable dialog box to select an existing variable (Activity Preferences - Select Variable).
[Delete]
Deletes the selected variable.
[Properties]
Shows the selected variable information.
[Up]
Moves the selected variable one step up.
[Down]
Moves the selected variable one step down.
Click [New Variable] to open the Add New Process Variable window.
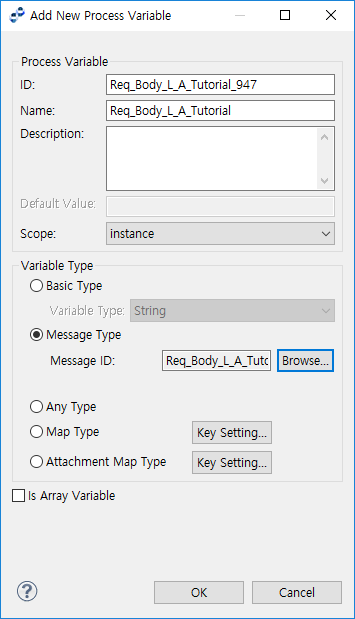 Activity Preferences - Add New Process Variable
Activity Preferences - Add New Process VariableItem Description ID
Variable ID.
Name
Variable Name.
Description
Variable description.
Default Value
If the Variable Type is 'Basic Type', enter a default value.
Scope
Preset to 'instance' (cannot be edited).
Variable Type
-
Basic Type: one of String, Float, Integer, DateTime, or Boolean type.
-
Message Type: a message is selected from DTO files that exist under the project’s service group through the 'Select Message' window.
-
Any Type: select this type when using a Java Class object as the Process Variable.
-
Map Type: specifies how to access key value, msg, and ctx information.
Click [Key Setting…] to open the 'Map Data Field Key Setting' window. A header variable for a service call must be a map type specified in the format, <String, String>.
-
Attachment Map Type: set an attachment file. This is normally used for a file adapter attachment.
Is Array Variable
Option to use an array variable.
-
Activity Handler
The following describes the Activity Handler page of the Activity Preferences window.
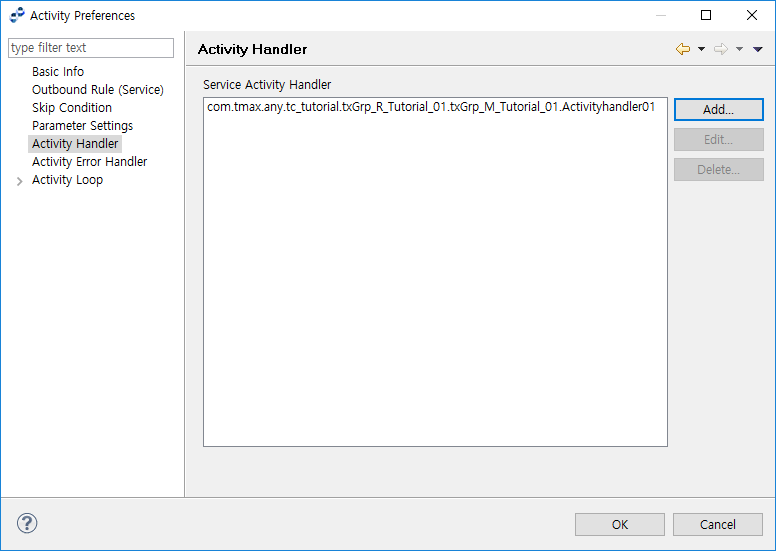
| Button | Description |
|---|---|
[Add…] |
Opens the Service List Dialog (Service List Dialog) to select a user-defined service as an Activity Handler. |
[Edit…] |
Opens a window to edit the selected handler. |
[Delete…] |
Deletes the selected handler. |
The following describes Service List Dialog where user-created activity handlers can be set.
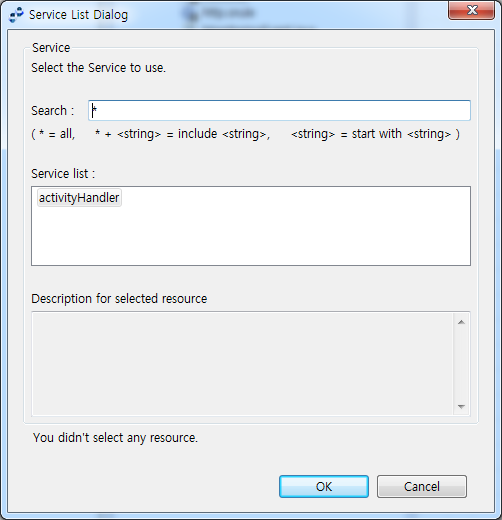
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
Search |
Searches for activity handlers. |
Service list |
Displays handlers. |
Activity Error Handler
The following describes the Activity Error Handler page of the Activity Preferences window. Buttons are same as those for the Activity Handler (Activity Preferences - Activity Handler) page.
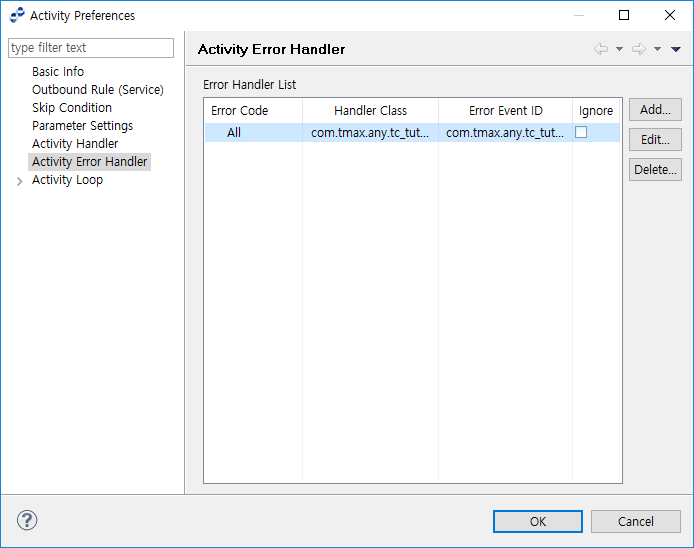
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
Error Code |
Error code for the handler to process. |
Handler Class |
User class for the handler. |
Error Event ID |
Error event ID. |
Ignore |
Option to ignore the error event in the Activity. |
Clicking [Add…] opens the following dialog box.
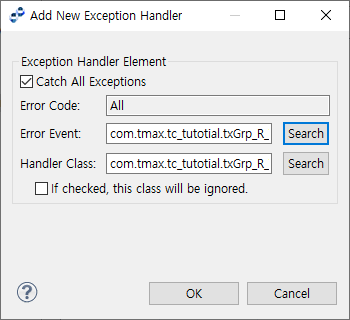
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
Catch All Exceptions |
Catches all exceptions. |
Error Code |
Error code to catch. If Catch All Exceptions is selected, the value is set to All automatically. |
Error Event |
Error event. You can search for an error event from Service List Dialog (Service List Dialog) by clicking [Search]. |
Handler Class |
Handler class. You can search for a handler class from Service List Dialog (Service List Dialog) by clicking [Search]. |
Activity Loop
The following describes the Activity Loop page of the Activity Preferences window.
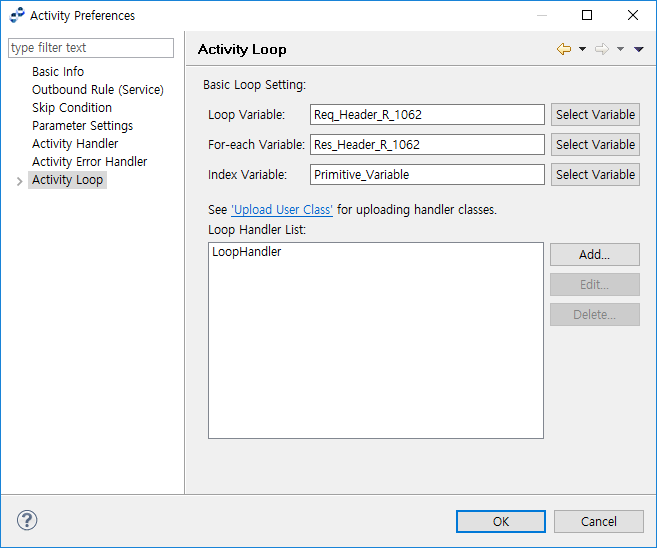
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
Loop Variable |
Variable that holds an array item. |
For-each Variable |
Variable that shares the type of the Loop Variable. Value is set in the order of the array items assigned to the Loop Variable. |
Index Variable |
An integer variable whose value is incremented after each pass. |
Loop Handler List |
List of loop handler classes. |
-
Standard Loop
Activity is repeated sequentially a specified number of times.
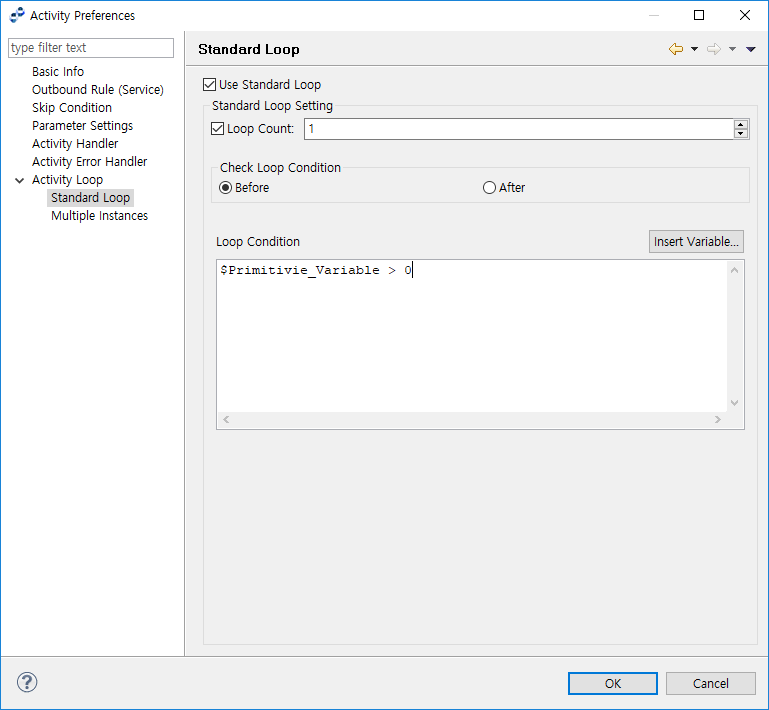 Activity Preferences - Standard Loop - Standard Loop
Activity Preferences - Standard Loop - Standard LoopItem Description Loop Count
Maximum number of iterations of the loop.
The loop may terminate before reaching this count if the 'Loop Condition' is not met. If the 'Loop Count' is set without a 'Loop Condition', the 'Loop Condition' is set to true by default.
When to Check
When to check the 'Loop Condition'.
-
Before: before executing the Activity (while loop).
-
After: after executing the Activity (until loop). The loop is executed at least once even if the 'Loop Condition' is not met.
Loop Condition
Loop condition.
The loop may terminate before reaching this count if the 'Loop Condition' is not met. If the 'Loop Count' is not set, the Activity repeats until the 'Loop Condition' fails.
If the 'Loop Count' is not set, the 'Loop Condition' must be set to an expression that does not always evaluate to true. Use <Ctrl>+Space as a shortcut to insert a variable.
-
-
Multiple Instances
Activity is executed sequentially or in parallel, and the loop count or loop condition may not be fixed.
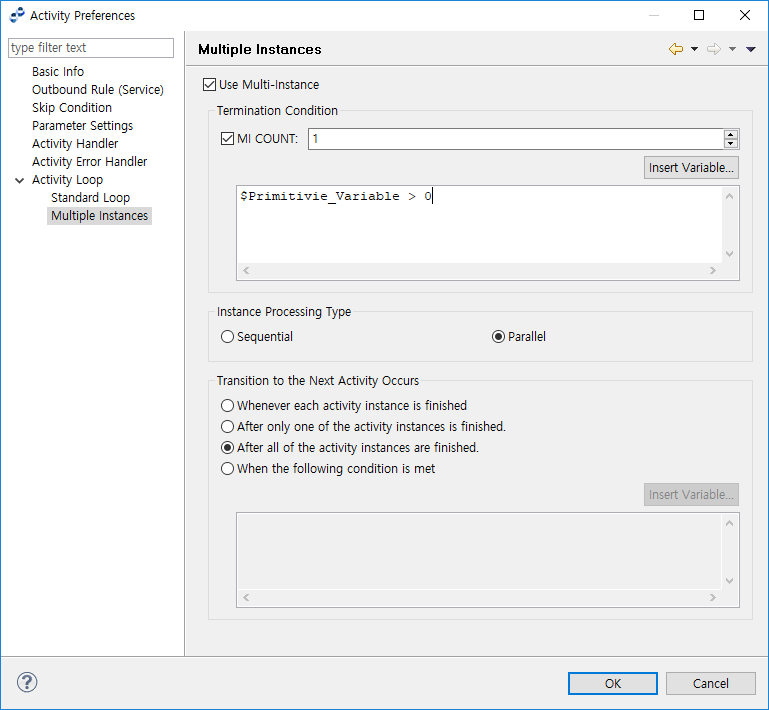 Activity Preferences - Activity Loop - Multiple Instances
Activity Preferences - Activity Loop - Multiple Instances-
Termination Condition
Termination condition for the Activity. Use 'MI Count' to set the maximum number of iterations and the ‘Loop Condition’ to set the loop termination condition.
-
Instance Processing Type
Item Description Sequential
Start instances sequentially.
Parallel
Start all instances in parallel.
-
Transition to the Next Activity Occurs
When to pass the Process Instance’s token to the next Activity after the current Activity is finished.
Item Description Whenever each activity instance is finished
Token is passed to the next Activity after each Activity Instance is finished. As many tokens as the number of finished instances are passed.
After only one of the activity instances is finished
Token is passed after one instance is finished.
Any preceding instance’s token is ignored.
After all of the activity instances are finished.
Token is passed after all Activity Instances are finished.
When the following condition is met
Token is passed when the specified condition is met.
If using Multiple Instances and 'Instance Processing Type' is set to 'Parallel', For-each Variable and Index Variable must be local variables since they may cause concurrency issues. If the 'Instance Processing Type' is set to 'Sequential' and 'Transition to the Next Activity Occurs' is set to 'After all of the activity instances are finished', the loop works like a Standard Loop.
-
4.2. Configuring a Specific Activity Type
The following describes how to configure a specific Activity type.
User Class Activity
A User Class Activity can be set by selecting an existing user class, which handles complex logic, from the Activity Preferences window.
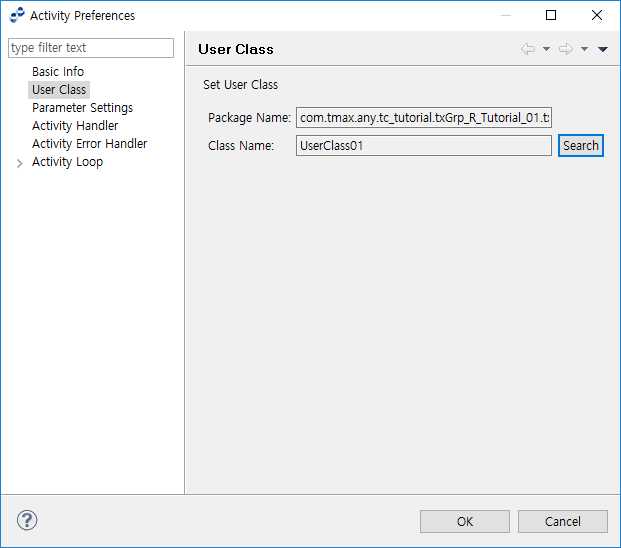
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
Package Name |
User class package name. |
Class Name |
User class name. |
Mapping Activity
Converts the variable values by using a pre-defined mapping. Mapping can be set from the Activity Preferences window.
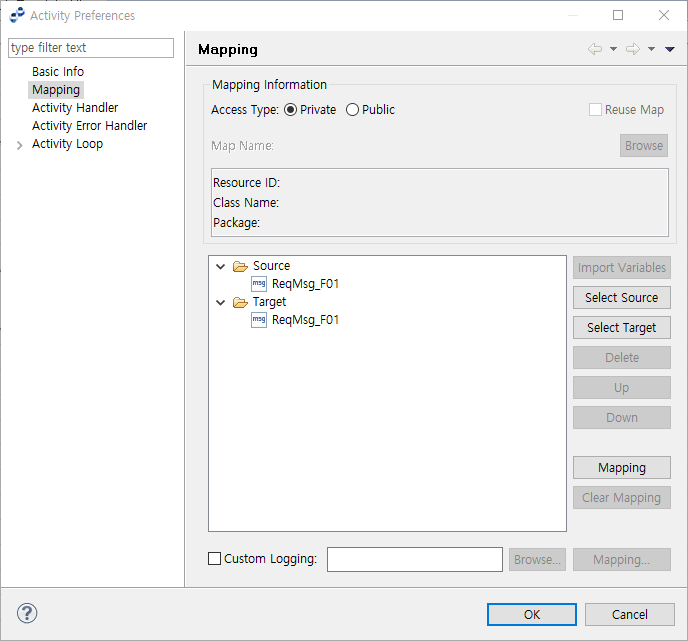
-
Mapping Information
Item Description Access Type
If Private is selected, mapping information is saved in the Activity instead of a separate map file to prevent access.
-
Buttons
Button Description [Import Variables]
Imports the message set in Public Mapping.
[Select Source]
Source process variable.
[Select Target]
Target process variable.
[Delete]
Deletes the selected variable.
[Up]
Moves the selected variable one step up.
[Down]
Moves the selected variable down step up.
[Mapping]
Opens the Mapping dialog box (Mapping Dialog Box) to map source and target process variables.
[Clear Mapping]
Clears the mapping information.
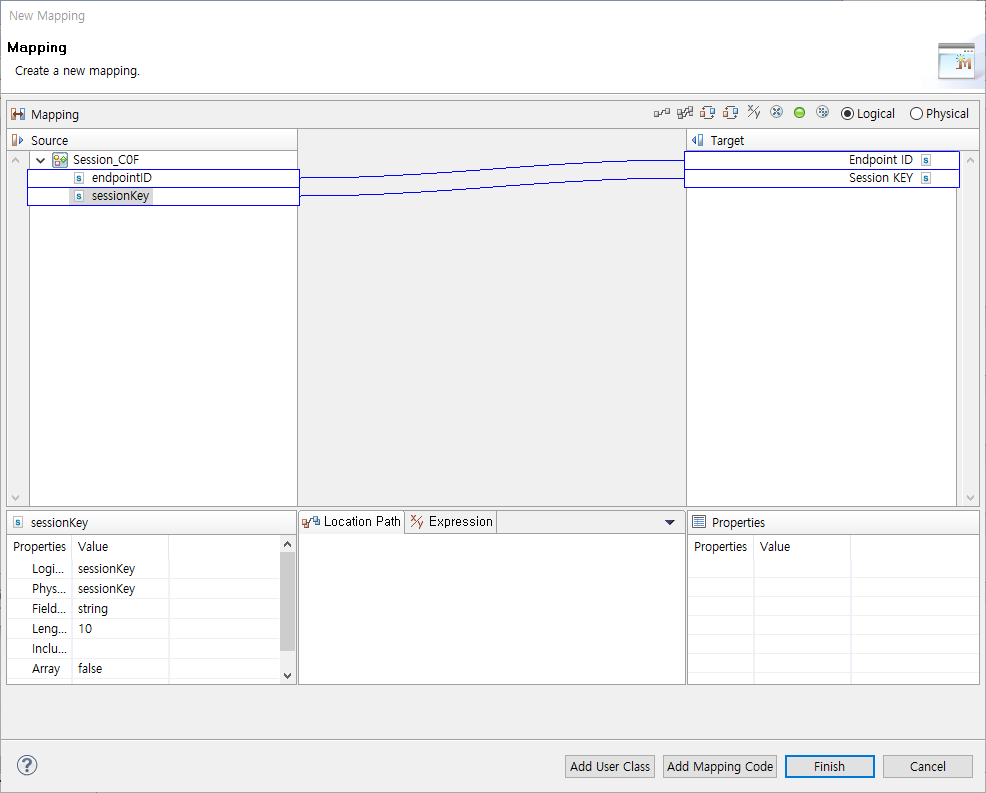
The following describes Mapping dialog box where source and target process variables can be mapped. To add a user mapping handler, click [Add User Class]. To enter Java code to be called during mapping, click [Add Mapping Code].
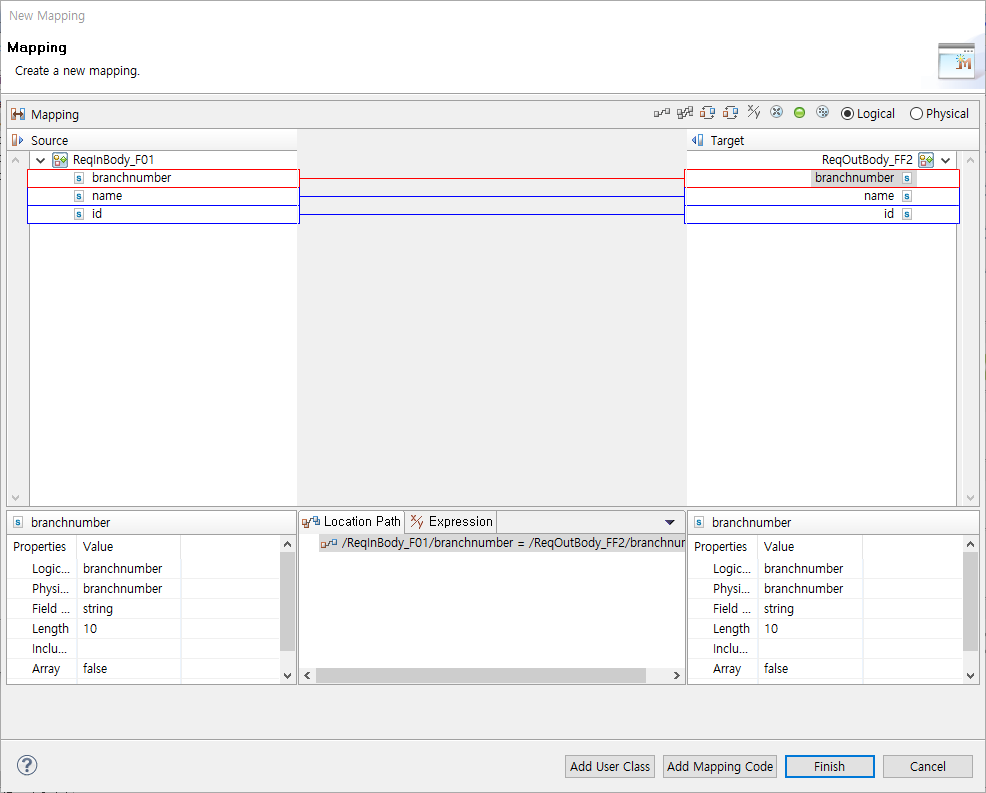
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
Source |
Variables to map. |
Target |
Variables for which a value is defined through mapping. |
Properties |
Searches variables or fields selected in Source or Target. The left Properties section is for Source, and the right Properties section is for Target. |
Location Path |
Connection information for the mapping. |
Expression |
Maps values. Strings are enclosed in double quotation marks (" "). |
Reply Message Activity
Sends a response to the message event of the inbound service. A Reply Message Activity can be set from the Activity Preferences window.
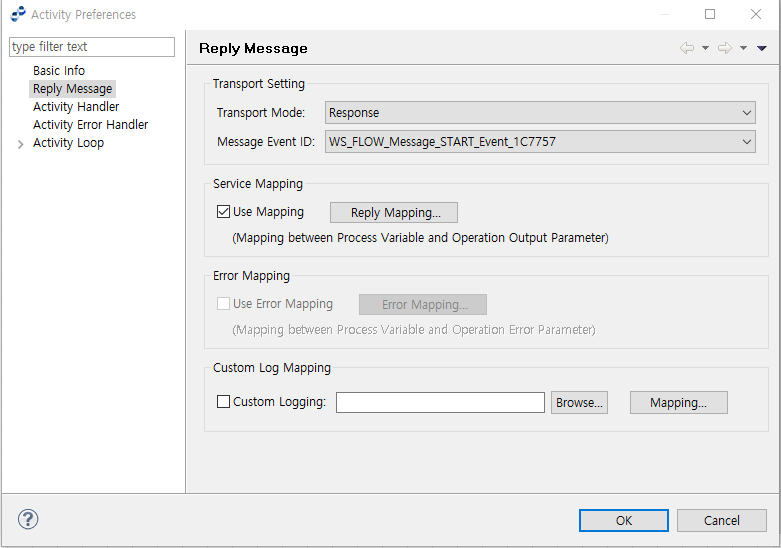
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
Trans Mode |
|
MessageEvent ID |
Message event of the Service Flow. |
Use Mapping |
Option to create mapping between process variable and output parameter from the Reply Mapping window. The 'Transport Mode' must be set to 'Mapping'. Click [Reply Mapping…] to open the Mapping window. |
Use Error Mapping |
Option to create mapping between process variable and error parameter from the Error Mapping window. The 'Transport Mode' must be set to 'Error'. Click [Error Mapping…] to open the Mapping window. |
Custom Log Mapping |
Option to create mapping between the Activity’s Custom Log and Activity variable.
|
Subflow Activity
A Response Message Activity can call another flow by configuring a subflow from the Activity Preferences window.
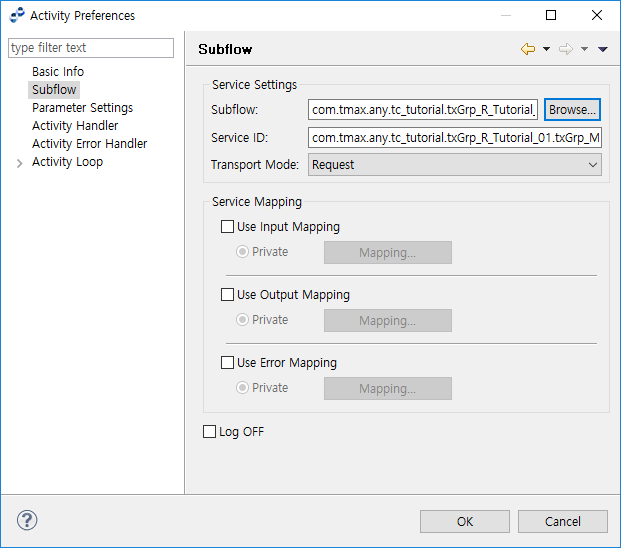
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
Subflow |
Service Flow. |
Service ID |
Service ID of the selected Subflow. |
Transport Mode |
|
Service Mapping |
Create an in/out mapping between Outbound Service’s variable and Activity parameter. Select 'private' to save the mapping in the Service Mapping section of the SFDL file so that other flows or Activities cannot access it. If not selected, a map file is created and made public so that it can be reused. |
Multi-Binding Activity
Calls multiple services that are configured in a single Activity.
5. Event
The following describes the Event types.
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
|
Message event for receiving a message. Can be either a Start or Intermediate event. |
|
Timer event that periodically starts a process by specifying the start and end times and the interval. Must be an Intermediate event. |
|
Error event. Can be a Start, Intermediate, or End event. |
|
Event for synchronization or process flow control. Can be a Start, Intermediate, or End event. |
|
An End event that has terminated successfully. |
|
An End event that has been forcibly terminated. This event is displayed as an abnormal termination in WebAdmin. |
5.1. Configuring an Event
Add an Event to the editor, and then double-click on it or place the cursor on the Event to show the Event Preferences menu to configure the Event.

The Copy and Delete buttons are same as those in Activity Preferences menu.
The following is the Basic Info page of the Event Preferences window. The description of the items that also appear in the Activity Preferences window has been omitted here.
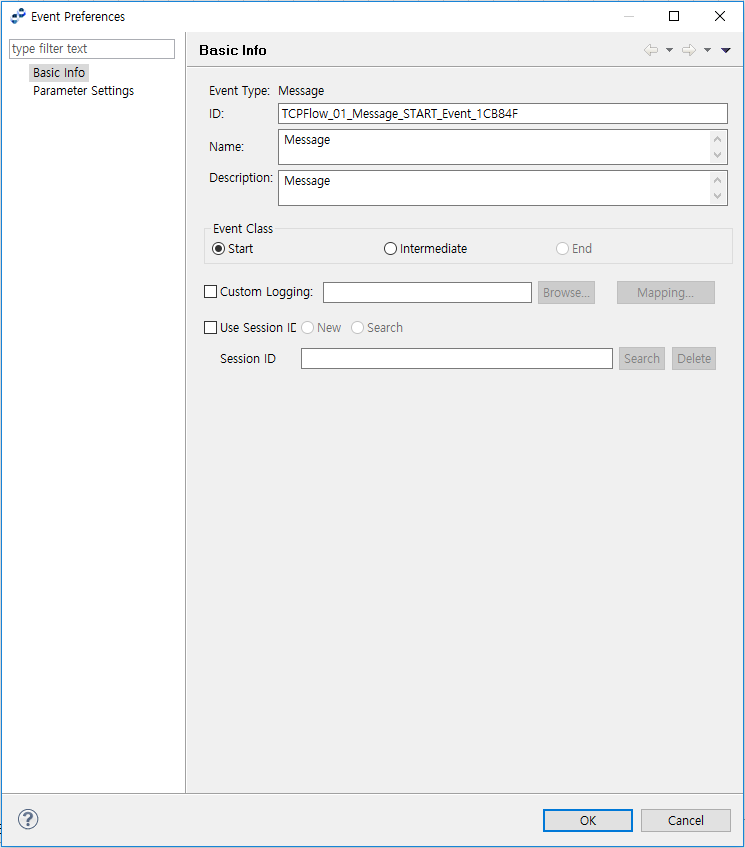
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
Event Class |
Select Start, Intermediate, or End type depending on the event’s role and position in the Service Flow. Some events may have additional constraints. |
Custom Logging |
Option to use custom logging.
|
Session ID |
Click [New] to enter a Session ID, or click [Search] to select an existing Session ID. |
5.2. Event Configuration by Type
-
Message Event
Message Event has the Parameter Settings section. For more information, refer to the description about the Activity Preferences window (Activity Preferences - Parameter Settings).
-
Timer Event
Timer Event has the Timer section with the start and end times and the interval for starting a process periodically.
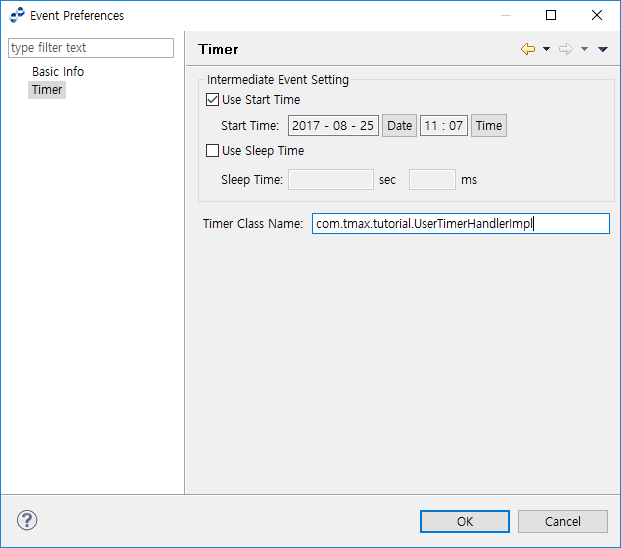 Event Preferences - Timer
Event Preferences - TimerItem Description Start Event Setting
-
If only 'Start Time' is set: executes once at the set time after server startup.
-
If only 'End Time' is set: executes once immediately after server startup (same as when no settings are entered).
-
If only 'Period' is set: executes at the set interval after server startup.
-
If 'Start Time', 'End Time', and 'Period' are set: executes at the set interval starting from the 'Start Time' until the 'End Time'.
Intermediate Event Setting
-
If only 'Start Time' is set: sleep until the set time, or sleep indefinitely if the set time has already passed.
-
If only 'Sleep Time' is set: sleep during the set period.
-
If 'Start Time' and 'Sleep Time' are set: sleep until the 'Start Time', and sleep for start time + n*sleep time if the 'Start Time' has already passed.
Timer Class Name
User class name.
-
-
Error Event
Error Event is set with Error Code information. An error code is required. Error codes defined in AnyLink can be checked by clicking the ? button at the right of the Error Code field.
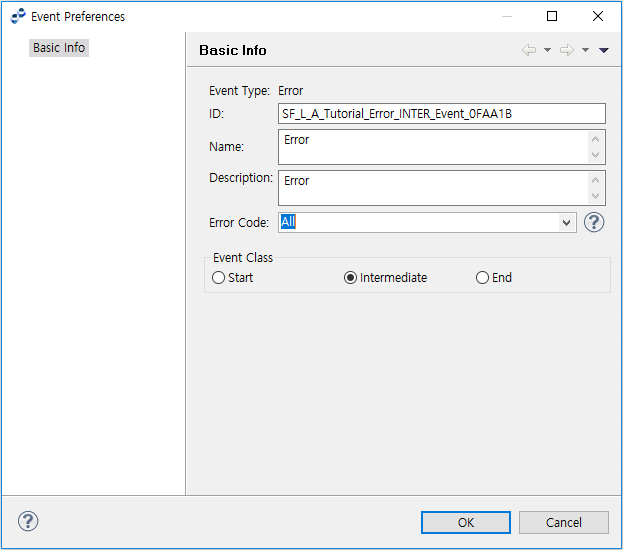 Error Preferences - Error Event
Error Preferences - Error Event -
Link Event
Link Event is set with Link ID information. Enter the target ID to connect to.
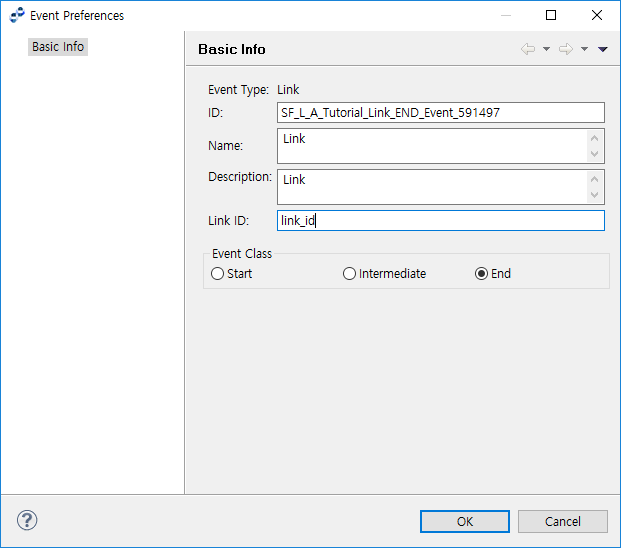 Event Preferences - Link Event
Event Preferences - Link Event
6. Gateway
The following describes gateway types.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
|
XOR Split is when a process instance is routed to one of many Transitions. A process that was split using an XOR Split can be rejoined using an XOR Join. A condition must be set for each transition of the XOR Split, and conditions are evaluated in the specified order until one evaluates to 'true'. If all conditions are evaluated as 'false', an exception occurs. Hence, it is recommended to specify an 'otherwise' condition for such case. |
|
XOR Event Split is similar to XOR Split, but routing is determined based on the occurrence of the next activity itself instead of on the activity transition (deferred choice pattern). XOR Event Split must be followed by a Timer Event, Message Event, or a block that starts with an Event. |
|
Or Split is when a process instance is routed to all Transitions whose condition evaluates to 'true'. Or Split must also be rejoined using Or Join. Transition’s conditions are similar to those for XOR Split, except that all Transitions that evaluate to 'true' are executed even if multiple Transitions have overlapping conditions. |
|
And Split is when a process instance is routed to all Transitions unconditionally. Since And Split splits to all Transitions, no conditions are required. And Join executes the next Activity only after receiving execution results from all split Transitions. |
|
Complex Join executes the next Activity after joining the specified number of Transitions. |
The following describes the Gateway Preferences window.
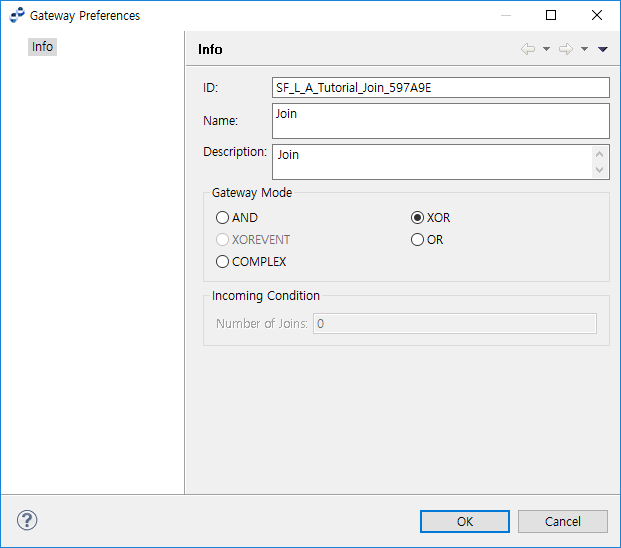
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
Gateway Mode |
Gateway type. |
Incoming Condition |
Number of transitions to join. Enabled only for a Complex Gateway. |
7. Swimlane/Block/Annotation
The following describes the Swimlane, Block, and Annotation objects.
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
|
Swimlane is a dividing line between tasks in the Service Flow. Swimlanes can be used to easily distinguish the sequence of tasks performed in parallel or actions. Double-click on the top label of the Swimlane to open the Swimlane Preferences window to edit the ID, Name, Size, and Border Color of the Swimlane. |
|
Block Activity can be set with process variables that can be used within the Block, and Message, Timer, and Error events. |
|
Memo used to enter object description for user convenience. |
7.1. Block Activity
A Block, similar to a Java function in concept, includes a group of Service Flow Activities and is created to handle events or exceptions that occur in the Block.
'Block Handler', 'Exception Handler', 'Activity Loop', and 'Block Variable' can be configured for a Block as for an Activity. Click [Block Variable] menu to define variables that can only be used in the Block.
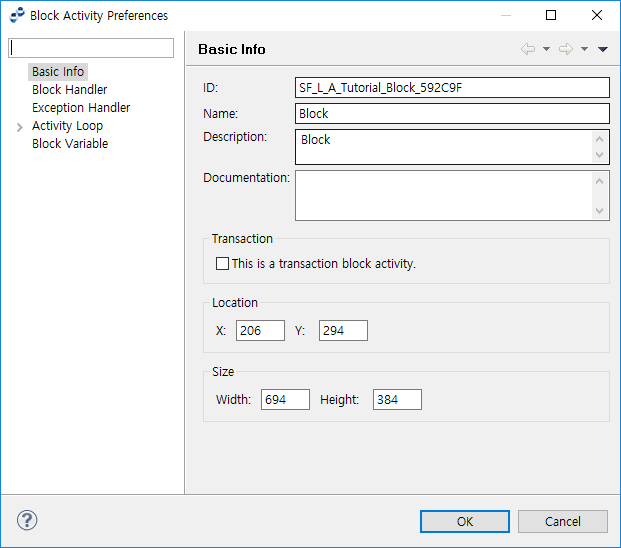
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
This is transaction block |
Option to allow the Block to support transactions. In a Transaction Block, Tx_Begin is automatically called when entering the Block, Tx_Commit is called when terminating the Block with 'None' event, and Tx_Rollback is called when terminating the Block abnormally or with 'Terminate' event. |
8. Utility
Utility provides a set of utilities used in a Service Flow.
The following describes utility objects.
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
|
Closes the session with the specified Session ID. |
|
Forcibly ends the session with the specified Session ID. |
|
Manages network status. |
|
Manages terminal login/logout and retrieves information about terminal users and administrators. |
|
Saves files received through HTTP multipart to a temporary path. The files are automatically deleted after the flow completes. |
|
Manages batch progress. |
|
The next Intermediate Event receives fragmented TCP messages. |
|
Forcibly ends a session with a specified endpoint ID or session key. |
8.1. SESSION CLOSE ACTIVITY
The following describes the Session Close Preference window for SESSION CLOSE ACTIVITY.
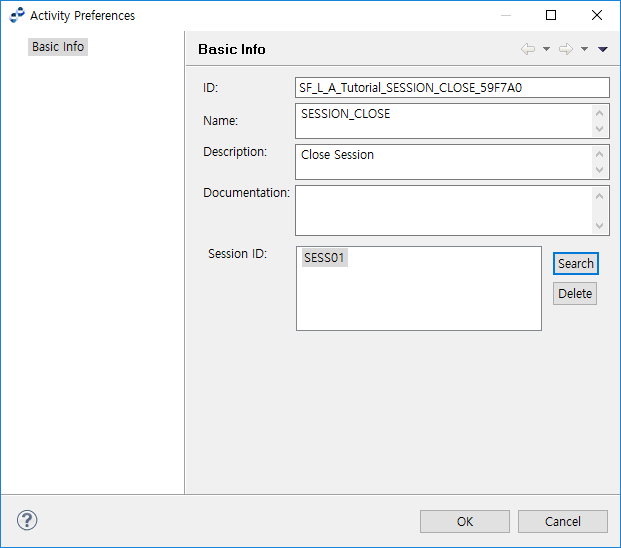
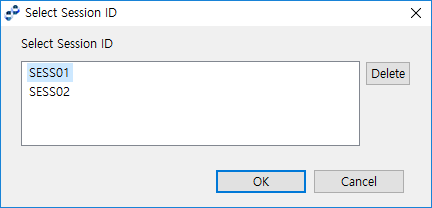
Select the 'Session ID' of the Service Flow. Click [Search] to open the Select Session ID dialog box.
8.2. SESSION ABORT ACTIVITY
The usage is the same as in the SESSION CLOSE ACTIVITY. Refer to SESSION CLOSE ACTIVITY.
8.3. NETWORK MANAGEMENT ACTIVITY
The following describes the Network Management Preference window for NETWORK MANAGEMENT ACTIVITY.
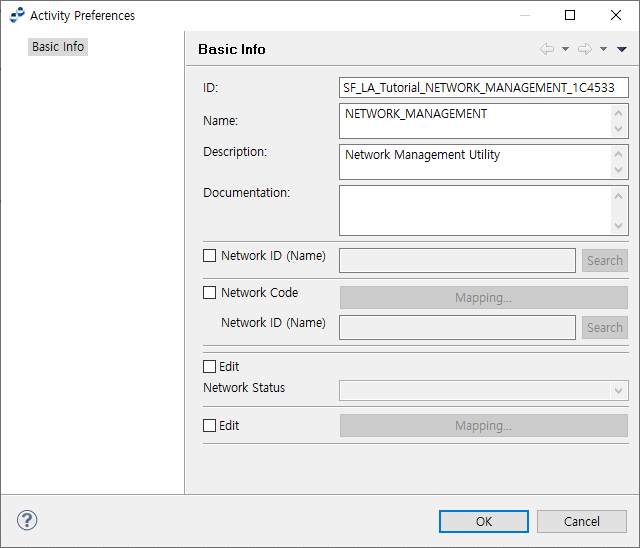
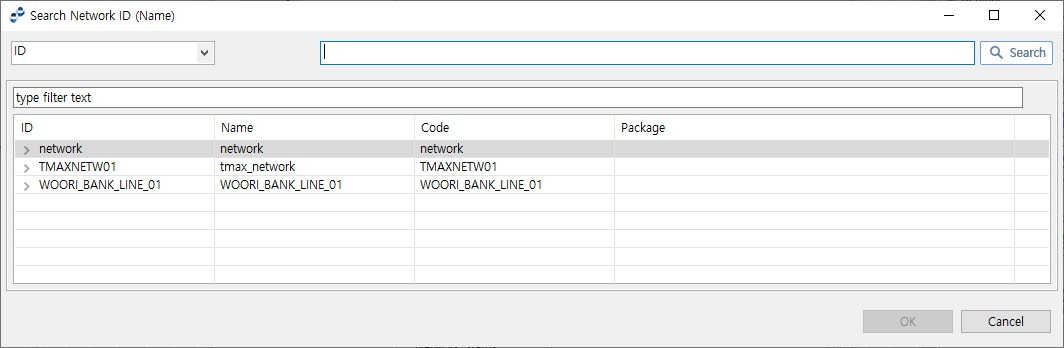
To select a fixed network, select 'Network ID (Name)' and click [Search]. This opens the Search Network ID (Name) dialog box where you can select a network ID added in WebAdmin.
If the flow variable has a code value, select 'Network Code' and click [Mapping…]. Map the code and then click [Search]. This opens the Search Network ID (Name) dialog box where you can select a network ID added in WebAdmin.
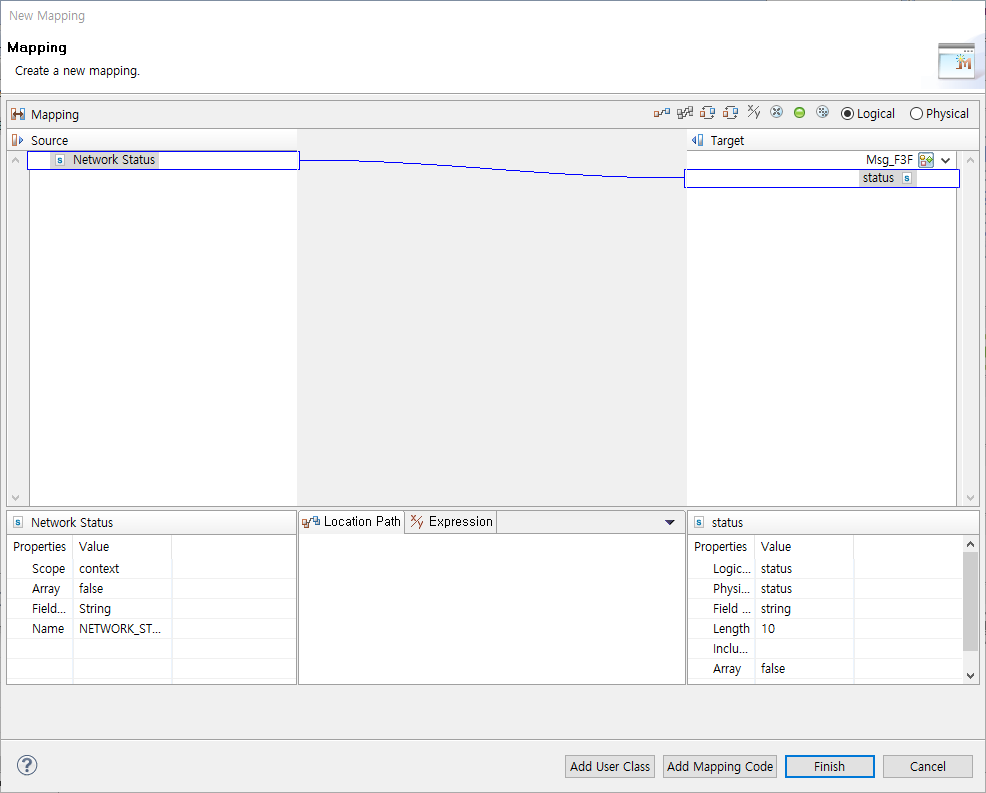
To change network status, select 'Edit'. To search network status, select 'Search' and click [Mapping…]. This opens network status Mapping where you can map network status to a flow variable.
8.4. MANAGER APPROVAL ACTIVITY
The following describes the Manager Approval Preference window for MANAGER APPROVAL ACTIVITY.
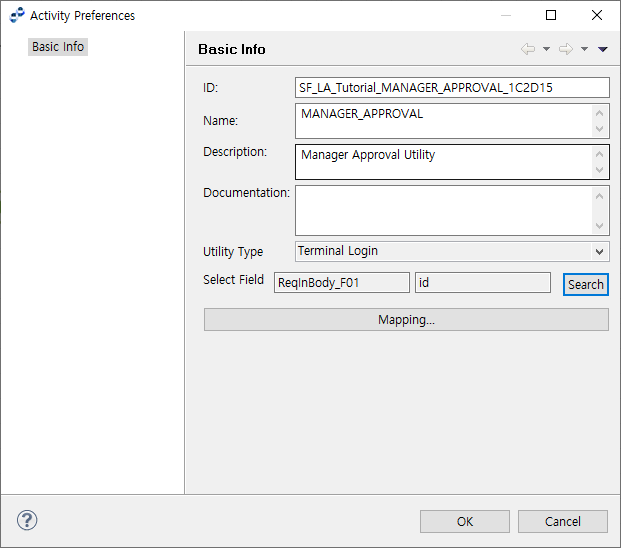
Select an action to take from Utility Type. User a terminal, or map User ID to search for from the Select Variable Field dialog box opened by clicking [Search] at the right of Select Field. The field value must be the same as User ID that can be searched for from WebAdmin by selecting [Configuration] > [Terminal] > [Users].
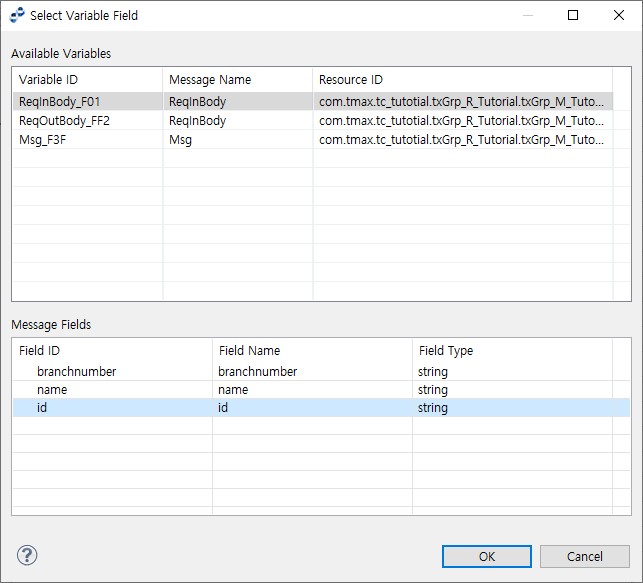
To map the results of taking an action for the utility type, click [Mapping…]. This opens the Terminal/User Information Mapping dialog box where you can map the results.
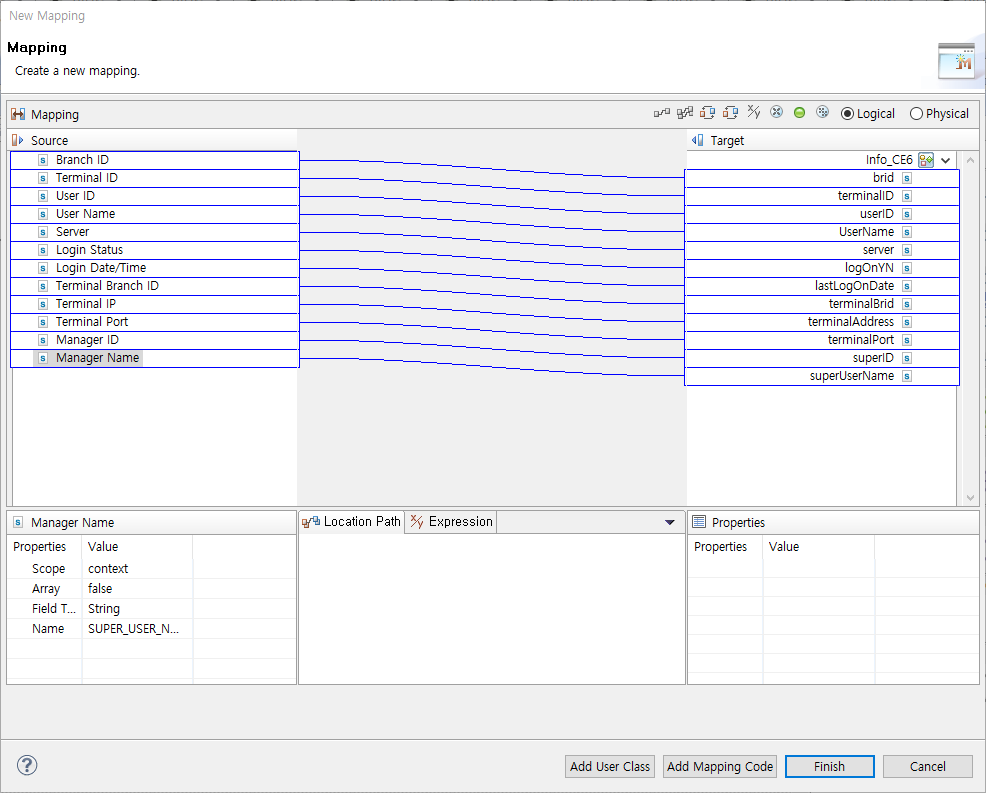
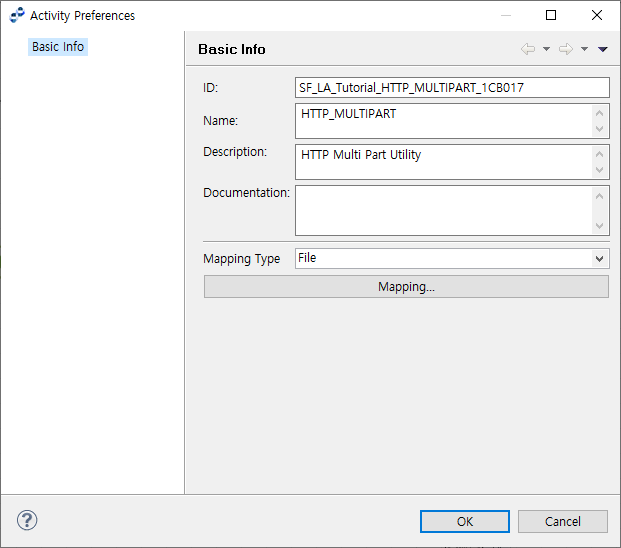
8.5. HTTP MULTIPART ACTIVITY
The following describes the HTTP Multipart Preference window for HTTP MULTIPART ACTIVITY.
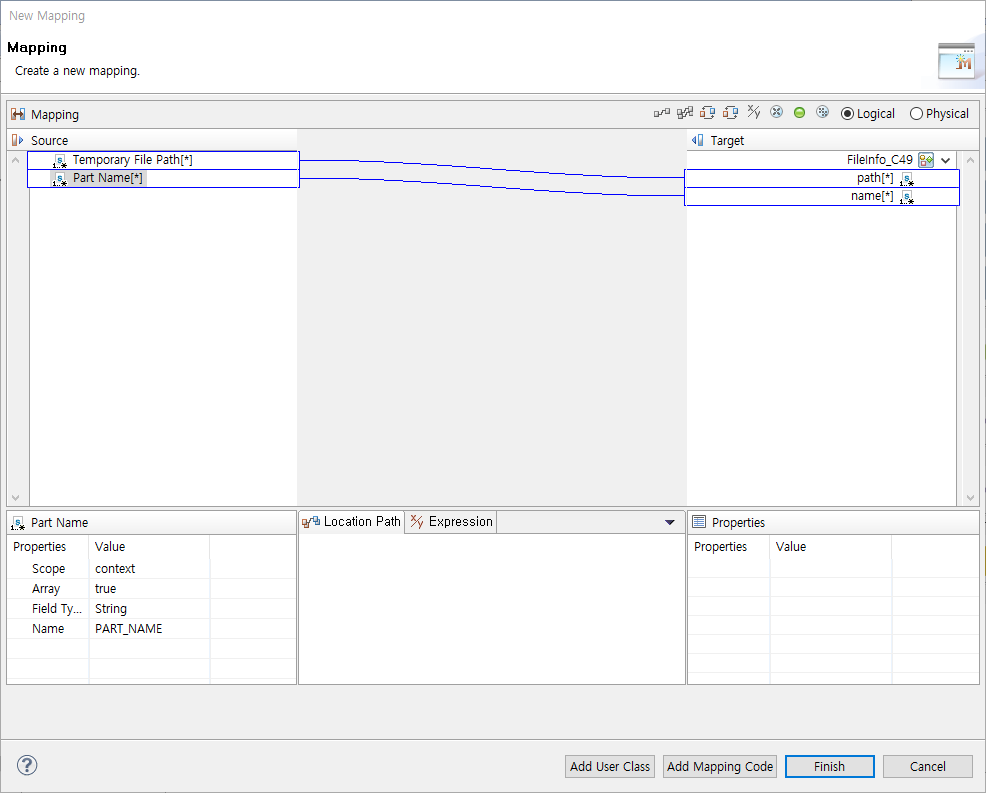
Select a type from Mapping Type. The File mapping can be created through file path and name, and the Byte mapping can be created through file contents and information.
To map multipart file information, click [Mapping…]. This opens the Multipart Mapping dialog box where you can map the information.
8.6. BATCH PROGRESS ACTIVITY
The following describes the Batch Progress Preference window for BATCH PROGRESS ACTIVITY.
To show batch progress, set Show Batch Progress to true when defining the batch outbound rule used by the flow.
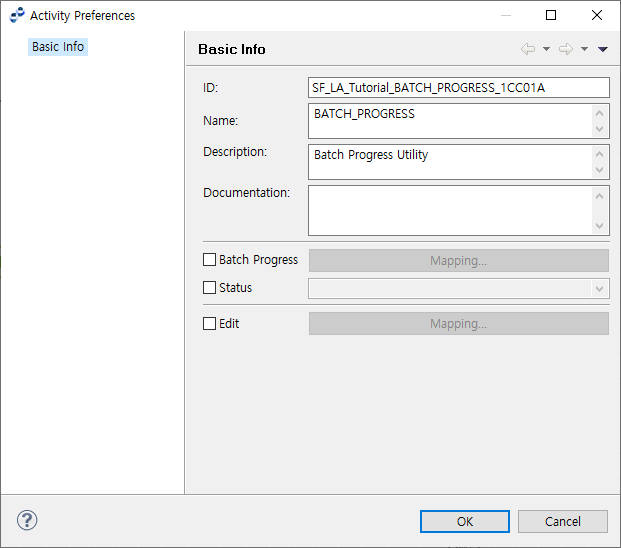
To change batch progress information, select 'Batch Progress' and click [Mapping…]. This opens the Batch Progress Mapping dialog box where you can map batch progress information.
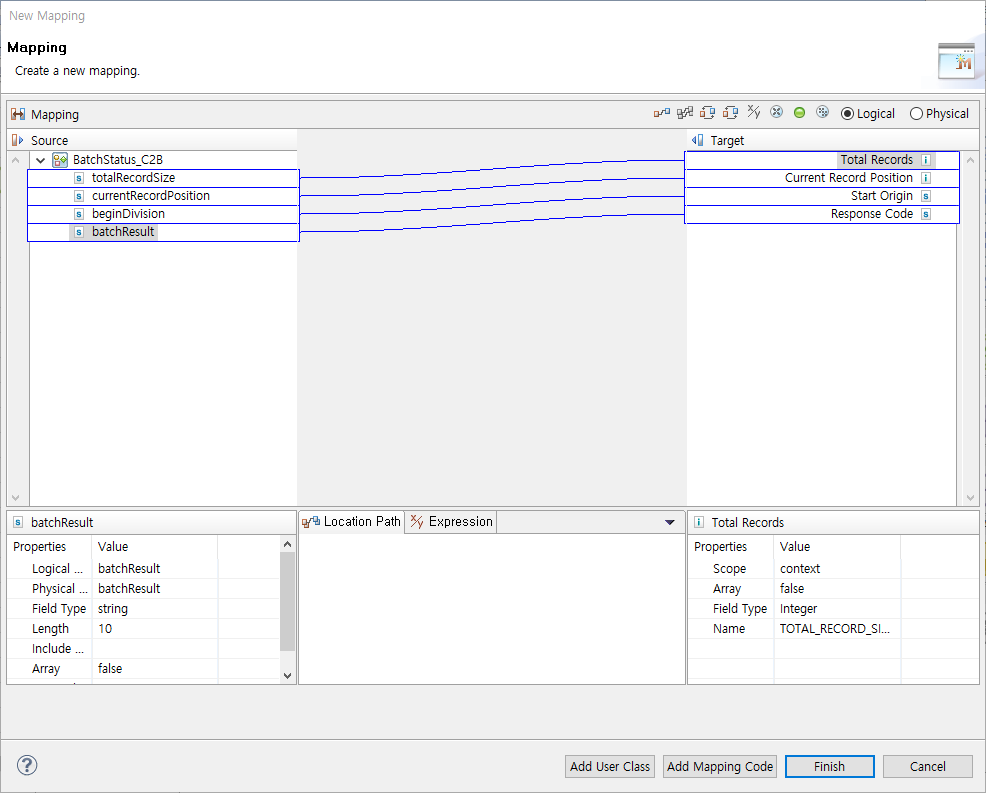
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
Batch Progress |
Changes batch progress information through mapping.
|
Status |
Changes batch process status (either Complete or Failed). |
Search |
Searches batch processing results through mapping. |
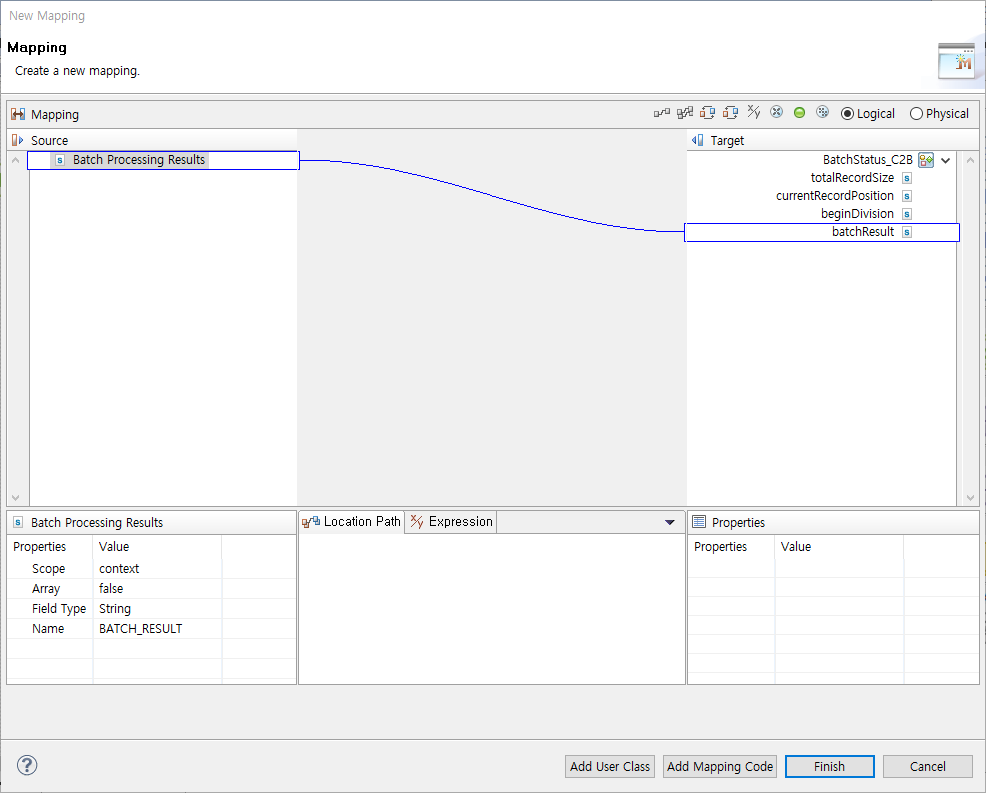
To change batch status, select 'Status' and select the status. To search batch process results, select 'Search' and click [Mapping…]. This opens the Batch Process Result Mapping dialog box where you can map batch process results.
8.7. TCP MESSAGE SPLIT ACTIVITY
The following describes the TCP Message Split Preference window for TCP MESSAGE SPLIT ACTIVITY. To use this function, select Use Message Fragmentation in the TCP Endpoint Details page shown by selecting [System] > [Adapter] in WebAdmin.
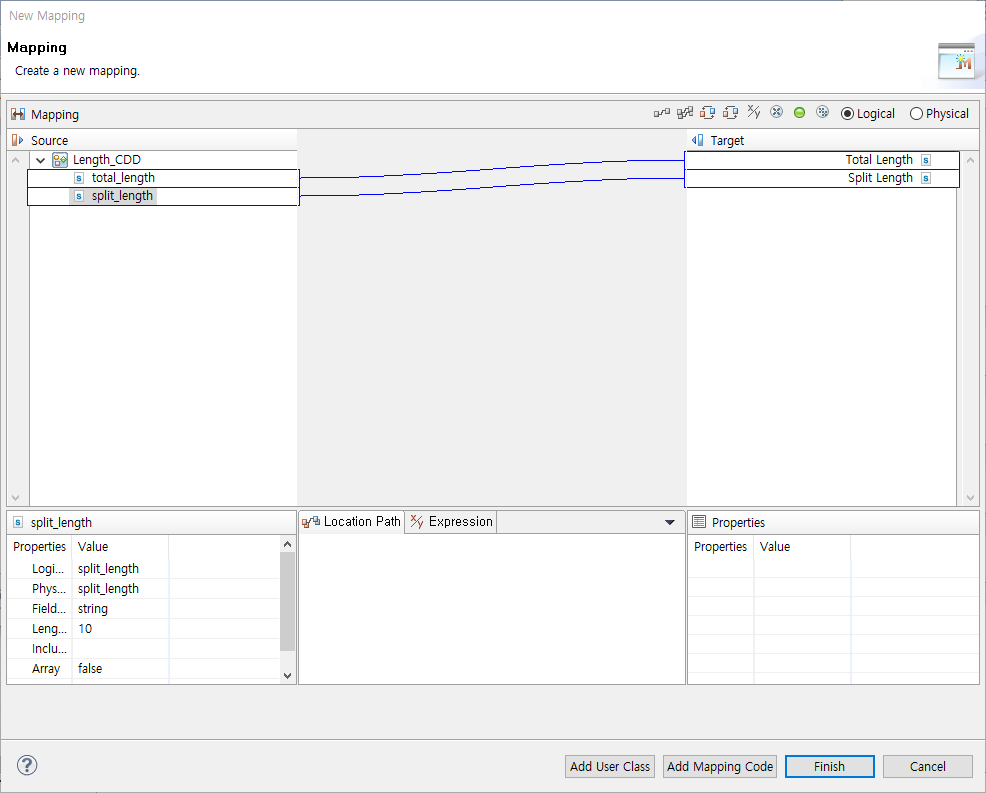
If TCP MESSAGE SPLIT ACTIVITY is set, Intermediate Event processed after the activity receives a message by using 'Total Length' and 'Split Length' set in TCP MESSAGE SPLIT ACTIVITY. 'Total Length' is the total length of a message, and 'Split Length' is the length of a message to read after splitting it.
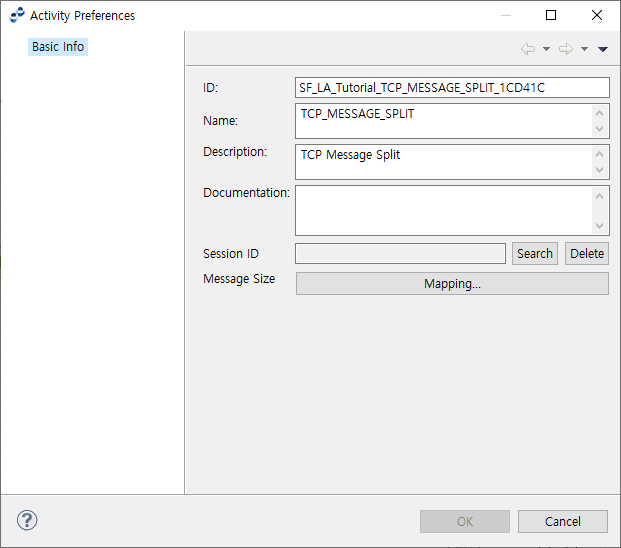
Select 'Session ID' added in the service flow. Clicking [Search] opens the Select Session ID dialog box.

To map the length of messages to receive, click [Mapping…]. This opens the Message Length Mapping dialog box where you can map the length. Intermediate Event processed after this mapping receives a message by using the total mapped length and split length.
8.8. CONTROL SESSION ACTIVITY
The following describes the Control Session Preference window for CONTROL SESSION ACTIVITY.
To map a session to end, click [Mapping…]. This opens the Session Information Mapping dialog box where you can map the session.