Introduction to Domain
This chapter describes the concepts and architecture of a domain.
1. Basic Concepts
A domain is the basic unit of management. It consists of multiple servers and clusters that are divided according to tasks.
Services, server locations, and security policies can be different for each domain. Each domain has a separate configuration file and does not share settings with other domains. Domains should be created with the knowledge that the security configuration, applications, and resources are shared within each domain.
Consider the following when creating a domain.
-
Roles of servers in the domain
Configure servers with similar roles in the same domain.
-
Physical location of servers in the domain
The physical location of the servers is important for providing stable services.
-
Load on servers in the domain
Use an appropriate number of servers based on the required workload.
2. Relationship between JEUS and Domain
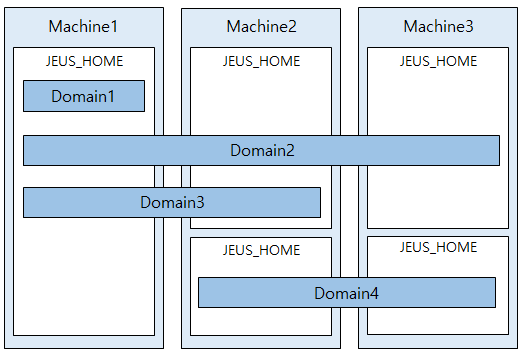
Each machine requires an instance of JEUS (installed in JEUS_HOME), which can contain one or more domains. A domain can be created in one instance or across multiple instances of JEUS.
|
Usually, a single JEUS instance is installed on each server. However, it is possible for a machine to have multiple instances of JEUS installed. |
For instance, a domain for personnel management and another for order management can be installed on three servers according to the applications' requirements. In the following example, Domain1 for personnel management service is installed on a single machine, Machine1. The domain for order management is installed on all three machines so that its services are still available if one of the servers fails.
The following diagram shows the relationship between JEUS and domains.
3. Components
A domain consists of Master Server (MASTER), Managed Servers (MS), and clusters.
-
Master Server (MASTER)
A domain must have a special server called Master Server (MASTER). MASTER configures servers, centrally manages all the applications and resources in the domain, and communicates with the administrator tool (jeusadmin) that are used to control and monitor servers.
-
Managed Server (MS)
A domain consists of one or more Managed Servers (MSs), which are responsible for providing services. A domain can contain a cluster with multiple MSs that provide the same or different services.
-
Cluster
A domain can contain zero or more clusters and other servers that do not belong to a cluster.
A cluster, which is a group of servers that provide the same services, are used to support scalability and reliability. Servers that are in the same cluster use the same resources and run the same applications. Refer to JEUS Clustering for detailed information about a cluster.
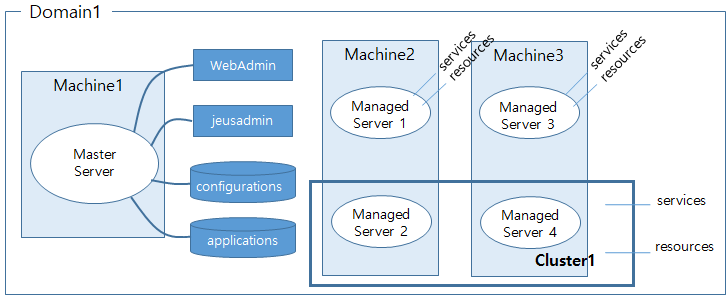
MASTER is located on Machine1. MASTER communicates with the administrator tool to receive and process user commands.
Machine 2 and Machine 3 each contain two MSs. Managed Server 2 and Managed Server 4 in Cluster 1 share applications and resources and provide the same services, but Managed Server 1 and Managed Server 3, which are not in Cluster 1, do not.
|
A basic domain must contain one server that acts as both MASTER and MS. This domain configuration should only be used for development and testing. In the production environment, separate servers should be used for management and services and MASTER should only be used to manage MSs. |
3.1. Master Server (MASTER)
Master Server must exist in every domain. It centrally manages and monitors MSs.
The following are the major functions of MASTER.
-
Managing domain configuration
-
Even if each MS in the domain is on a different server, they can use the same configuration.
MASTER must start first in order for MS to get the configuration from MASTER to start. If MS starts while MASTER is not running, its configuration will be synchronized when MASTER starts.
-
Configuration changes are applied to all MSs in the domain.
MASTER verifies any configuration changes and synchronizes them by applying the changes to other servers.
Refer to Changing Domain Settings for detailed information about managing the configuration for MASTER.
-
-
Managing all applications in the domain
-
Manages the status of all the applications in the domain.
MASTER manages and synchronizes the status of all the applications in the domain, ensuring applications in MSes are maintained in the same states as those in MASTER.
-
Manages all the application files in the domain.
MASTER synchronizes the files when an MS runs and when applications are deployed to the MS. If application files are not synchronized because MASTER was not running, they are synchronized when MASTER starts.
-
Controls the deployment of application services to servers or clusters in the domain.
To run applications in the domain, applications should be installed on MASTER or exist in an application store (repository).
To run applications on an MS, transfer the service objects to MASTER and deploy the applications. All commands associated with application queries and controls as well as deployment commands are performed by MASTER. If MASTER is not running, domain commands cannot be executed.
If an MS is in a cluster, applications can only be deployed to the target cluster. If a server is added to the cluster, MASTER guarantees that applications can also be serviced from the added server.
Refer to Application Managment in JEUS Applications & Deployment Guide for detailed information about application management performed by MASTER.
-
-
Monitoring and controlling the entire domain
The administrator tool jeusadmin can be used to monitor and control all servers, services, applications, and resources.
3.2. Managed Server(MS)
Managed Servers contain the necessary resources and deployed applications.
MS operation is managed by MASTER in the following ways.
-
Configuration and application synchronization
MASTER manages configurations and applications of the entire domain. Hence, any configurations or applications that are deployed to an MS should be deployed using MASTER. Configurations and application files received from MASTER are stored in the local cache as read-only. Upon connecting with MASTER, only the modified files in MASTER are synchronized with those in the cache. Any modifications to individual MS are not applied. All modifications are applied through MASTER.
-
Configuration synchronization
Configuration synchronization occurs when MS starts, when MS reconnects to MASTER, or when the domain configuration is modified.
-
Application synchronization
The status of an application is also synchronized with the application status in MASTER. Application synchronization is performed whenever MS starts or reconnects to MASTER. Refer to Application Synchronization in JEUS Deployment Guide for detailed information about application synchronization.
-
-
Cluster composition
To balance the load and handle errors, a cluster can be created with multiple MSs. It is recommended that all servers in the cluster contain the same resources and applications. For detailed information about clusters, refer to JEUS Clustering.
4. Production and Development Modes
The domain operation mode can be set to either of the following modes. The mode must be manually set in the configuration file (domain.xml).
-
Production mode
This mode is suitable for the actual production environment. The auto-reload or hot-swap functions of web applications are not provided. Set the production-mode to true in the domain.xml file.
-
Development mode
If the production-mode is set to false in the domain.xml file, the domain runs in the development mode.
|
5. Domain Restrictions
Consider the following when creating a domain.
-
Each domain must have one MASTER.
-
Configurations and resources cannot be shared between domains.
-
All servers in the domain must use the same version.
-
The name of each server and cluster in the domain must be unique.
-
The name of each domain on a JEUS instance must be unique.