Introduction
This chapter describes how to use JEUS Scheduler.
1. Overview
JEUS Scheduler is used to schedule a one-time or recurring task.
JEUS Scheduler is an extended feature of JEUS. Although JEUS Scheduler is similar to the timer service of EJB, they are different. While an EJB Timer Service can be used only in the EJB environment, JEUS Scheduler can be used in any environment including the EJB environment and in Java SE applications in general. For example, you can use JEUS Scheduler to periodically delete temporary files and monitor database connections for system management.
Because you cannot use Java SE Timer (java.util.Timer) directly in the Jakarta EE environment, you need to use EJB Timer Service or JEUS Scheduler instead. While EJB Timer Service can be used only in an EJB environment, JEUS Scheduler can be used in all Jakarta EE environments as well as general Java SE applications.
If you are familiar with Java SE Timer (java.util.Timer), you can easily learn how to use JEUS Scheduler because of their similarities. Note that JEUS Scheduler provides end time and max count settings that are not offered by Java SE Timer.
The following are supported conditions for using JEUS Scheduler and its features:
-
As a standalone scheduler in Java SE applications.
-
As a standalone scheduler in Jakarta EE application clients.
-
Connect to JEUS server scheduler service from remote environments.
-
Register jobs in the JEUS server configuration file for use in the JEUS server.
-
Use JEUS server scheduler service from Jakarta EE components such as servlet, JSP, and EJB.
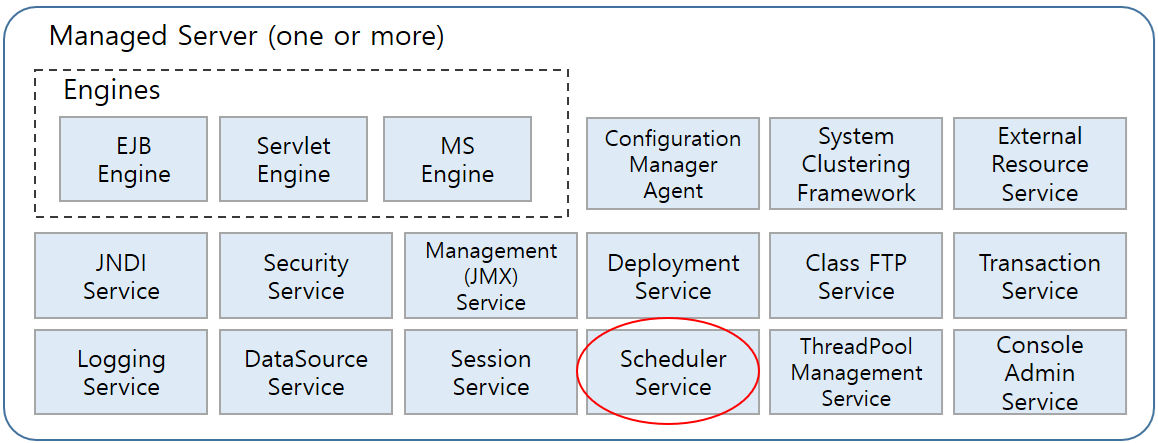
2. Scheduler Component Structure
JEUS Scheduler can be used both in user applications and on a JEUS server. A JEUS server can start the scheduler service and schedule tasks remotely using the configuration file.
The following figure shows JEUS Scheduler as a component of the JEUS server.
3. Scheduler Server
Scheduler’s service and execution method vary according to the server type.
The following figure shows the execution method by Scheduler Server.
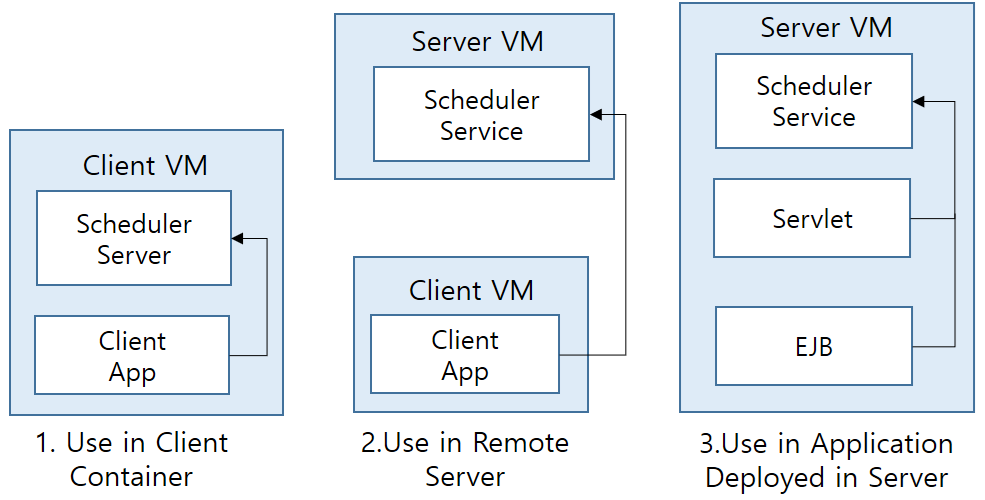
The following describes each Scheduler Service type.
-
Server Scheduler Service
It is used for a recurring task. A recurring task on the server may be registered in the Job-list and executed when the server starts.
It is usually used for tasks that periodically execute Jakarta EE components such as a servlet, JSP, and EJB. A task can be registered in the JNDI repository for remote client use.
-
Client Scheduler Service
The JEUS Scheduler Service runs in a standalone mode in the application client. It is normally used to periodically execute a task in an application client. It is also used for tasks that no longer need to be executed after the client is terminated.