Introduction to EJB
This chapter describes the components and characteristics of EJB, and how to install EJB and to configure its environment.
1. Overview
JEUS supports JSR 345 Jakarta™ Enterprise Beans 4.0 (hereafter EJB 4.0), which describes architecture for creating fully portable business components. The architecture simplifies the development efforts when implementing complex, mission-critical, and performance sensitive business logic.
|
Starting with Jakarta EE 9, EJB 4.0 is introduced. However, it is not a completely new version that diverges from the existing EJB specifications. Instead, it mandates continued support for the features of EJB 2.x and EJB 3.x. As a result, in practice, users will primarily continue to work with EJB 2.x and 3.x. This guide, therefore, focuses on explaining the functionality of EJB 2.x and EJB 3.x, without delving into additional details about EJB 4.0. |
According to the EJB 4.0 specification, the following is the concept of EJB.
“The Enterprise JavaBeans architecture is component architecture for the development and deployment of component-based distributed business applications. Applications written using the Enterprise JavaBeans architecture are scalable, transactional, and multi-user secure. These applications may be written once, and then deployed on any server platform that supports the Enterprise JavaBeans specification.”
JEUS represents one such "server platform" mentioned in the excerpt. This guide describes how EJB is implemented in JEUS, and additional functions that are essential in an enterprise environment.
|
For more detailed specification implementation information, refer to JEUS Introduction Guide. |
For increased performance and reliability, the JEUS implementation offers two non-standard features through clustering:
-
Load-balancing for better performance
-
Failover for increased reliability
Both of these functions require the clustering of two or more Managed Servers (hereafter MS).
|
For more information about EJB clustering, see EJB Clustering. For details on MS clustering, see JEUS Clustering in JEUS Domain Guide. |
2. Components
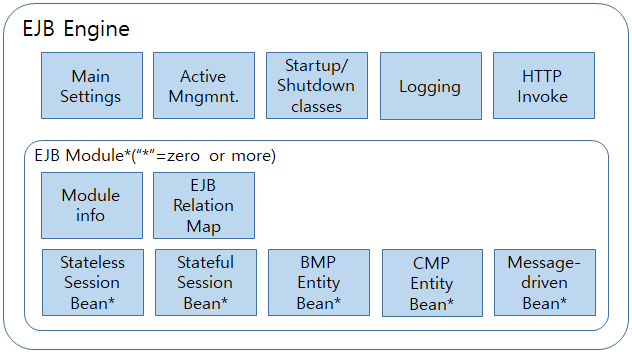
The following figure shows main components of an EJB implementation entity.
-
The EJB engine
Refers to the EJB container described in EJB 4.0. It provides a runtime environment for deployed EJB modules. The EJB engine will be described in detail in EJB Engine.
-
The EJB module
Used to group and manage a set of Enterprise JavaBeans as a single unit. EJB module is the unit used to assemble, deploy, and control EJB in JEUS. Therefore, all EJBs must be part of an EJB module. The EJB module will be described in detail in EJB Module.
-
The EJB components
Represents the actual business components of an EJB module. For information about common characteristics of EJB components, refer to Common Characteristics of EJB.
The following are the five types of EJB components. For more detailed information, refer to the following chapters:
-
Stateless Session Bean : Session Bean
-
Stateful Session Bean : Session Bean
-
BMP Entity Bean : Entity Bean
-
CMP 1.1 & CMP 2.x Entity Bean : Entity Bean
-
MDB : Message Driven Bean(MDB)
Entity Bean has been replaced by JPA since EJB 3.0. For information about JPA, refer to JEUS JPA Guide.
-
3. EJB Environment and Configuration
This section describes configuration elements related to JEUS EJB, such as the directory structure, EJB configuration files, and various tools. It also describes system properties related to EJB and their characteristics.
3.1. Directory Structure
This section describes directories and files related to JEUS EJB.
{JEUS_HOME}
|--bin
| |--appcompiler
| |--jeusadmin
|--domains
| |--<domain_name>
| | |--config
| | | |--domain.xml
| | |--servers
| | |--<server_name>
| | |--logs
| | |--error.log
| |--.application
| |--<EAR_archive_file>
| | |--APP-INF
| | |--Lib
| | |--META-INF
| | |--<EAR_archive_file>_jar__
| | |--META-INF
| | |--EJB class file
| |--<EJB_archive_file>
| |--<EJB_archive_file>_jar__
| |--META-INF
| |--ejb-jar.xml
| |--jeus-ejb-jar.xml
|--lib
| |--schemas
| |--jakartaee
| |--jeus
|--sample
|--ejb
|--.java EJB sample
- bin
-
The directory where scripts for launching tools, that are used to help the administrator manage EJBs, are stored. These tools are: jeusadmin and appcompiler.
- domains\<domain name>\config
-
The most important configuration files of JEUS system. This directory contains the domain.xml file.
- domains\<domain name>\servers\<server name>\logs
-
The directory where the log files of EJB engine are stored. If a separate file handler is specified, a separate file will be created, otherwise, the setting in the server log configuration file will be followed.
- domains\<domain name>\.application\
-
The archive files of applications used by domains are copied and decompressed to this directory. It contains EJB implementation classes and helper classes.
File Description <EAR archive file>
EAR application configuration file is copied to the directory named EAR application-id.
<EJB archive file>
EJB module configuration file is copied to the directory named EJB module-id.
- lib\schemas
-
The schema files relating to EJB are located in each directory as shown below.
Sub directory Description jakartaee
Contains all Jakarta EE XML schema files related to EJB.
jeus
Contains all JEUS XML schema files related to EJB.
- samples\ejb
-
Contains several sub-directories and sample code, demonstrating the implementation of various types of EJBs.
|
The bracket expressions used in the above directory list (such as "<server name>/”) means that the string in between the brackets must be replaced with an actual system or configuration dependent value. For instance, if the current machine is called server1, the corresponding JEUS MS must also be called server1. Thus the "<server name>/" expression is replaced with the actual directory name of "server1/" on the actual system. |
3.2. XML Configuration File
The following XML configuration files pertain to the management and configuration of JEUS EJB.
The contents of the previous files must always start with a standard JEUS-defined XML header. The XML schema files are located in the JEUS_HOME/lib/schemas/jeus/supportLocale/ko directory. And the root element should specify the namespace of JEUS XML schema as the current namespace.
-
domain.xml (jeus-domain.xsd)
EJB engine configuration. For more information, see JEUS Server Guide and EJB Engine in this guide.
-
Location
JEUS_HOME/domains/<domain name>/config
-
XML header of domain.xml
XML Header: <domain.xml><?xml version="1.0"?> <domain version="8.0" xmlns="http://www.tmaxsoft.com/xml/ns/jeus">
-
-
ejb-jar.xml (ejb-jar_4_0.xsd)
Main EJB engine configuration file. For more information, refer to the EJB 4.0 specification.
-
Location
META-INF\ Structure in the standard JAR file
-
XML header of ejb-jar.xml
The XML header of ejb-jar.xml is included in the EJB standard.
XML Header: <ejb-jar.xml ><?xml version="1.0"?> <ejb-jar version="4.0" xmlns="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee/ejb-jar_4_0.xsd">
-
-
jeus-ejb-dd.xml (jeus-ejb-dd.xsd)
Configures JEUS Deployment Descriptors (hereafter DD) for JEUS EJB module. For more information, refer to EJB Module.
-
Location
META-INF\ Structure in the standard JAR file
-
XML Header of jeus-ejb-dd.xml
XML Header: <jeus-ejb-dd .xml><?xml version="1.0"?> <jeus-ejb-dd xmlns="http://www.tmaxsoft.com/xml/ns/jeus" version="8.0">
-
|
The order of all tags used in the manual follows the order of the XML schema configuration file. Refer to the Reference Book for more information about tag ordering. But since it is not easy to maintain the order in actual use, JEUS provides automatic function for ordering tags. This eliminates the need to consider the order when writing XML configuration file. When an XML example from any of these files is used in this manual, the standard header will usually be omitted. You must make sure that these headers are included in the actual XML configuration files. |
3.3. Related Tools
The following tools may be used to manage EJB engines, modules, and components:
-
Console Tool (jeusadmin)
The tool used to control and to monitor EJB engines. For more information, refer to EJB Engine Commands in JEUS Reference Guide.
|
For detailed description of the appcompiler for EJB 2.x, refer to appcompiler in JEUS Reference Guide. |
4. EJB Basic Settings
This section describes the installation steps for using EJB in JEUS. In the following example, we shall assume that the EJB engine is configured on the server named server1.
-
Make sure that JEUS has been properly installed on the system.
-
Execute the command screen and enter the following command in the $JEUS_HOME/bin directory to start MASTER.
$ startMasterServer -domain domain1 -u administrator -p passsword1 -verbose . . . [2016.08.06 21:33:15][2] [adminServer-1] [SERVER-0248] The JEUS server is STARTING. . . . [2016.08.06 21:33:16][3] [adminServer-1] [Security-0082] The JEUS security manager started. . . . [2016.08.06 21:33:16][3] [adminServer-1] [SERVER-0173] The JNDI naming server started. . . . [2016.08.06 21:33:28][2] [launcher-10] [Launcher-0034] The server[adminServer] initialization completed successfully[pid : 2380]. [2016.08.06 21:33:28][0] [launcher-1] [Launcher-0040] Successfully started the server. The server state is now RUNNING.[3] represents the log level, CONFIG. It is only displayed when the specified log level is higher than CONFIG.
-
The EJB engine can be set in domain.xml. If no setting is made, the default value is used.
Modifying the MS setting using the tool provided by JEUS is possible only when MASTER is running.
-
Open another command prompt and enter the following. (Host information is that of MASTER.)
$ jeusadmin -host localhost:9736 User name: -
Enter your administrator user name and password (as configured during JEUS installation).
User name: administrator Password:
-
At the command line, enter the following. The server will start.
$ startManagedServer -domain domain1 -server server1 -u administrator -p passsword1 -verbose ... [2016.08.07 14:10:10][2] [server1-1] [SERVER-0248] The JEUS server is STARTING. ... [2016.08.07 14:10:17][2] [server1-1] [SERVER-0248] The JEUS server is RUNNING. -
Enter 'help' to get a list of commands that can be used to monitor and control the EJB engine.
[MASTER]domain1.adminServer>help -g EJB [ EJB] ______________________________________________________________________ cancel-ejb-timer Cancels active EJB timers. ejb-timer-info Lists the active EJB timers. If no options are specified, a list of all EJB modules that containtimers will be displayed. modify-active-management Modify the active management configuration. modify-check-resolution Set the check resolution of the EJB engine on the server. show-active-management Shows the active management of the EJB engine on the server. show-check-resolution Shows the check resolution of the EJB engine on the server. To show detailed information for a command, use 'help [COMMAND_NAME]'. ex) help connect -
Enter stop-server (stop server) → local-shutdown (stop MASTER) → exit (stop tool) in at the command line.
[MASTER]domain1.adminServer>stop-server server1 Server [server1] was successfully stopped. [MASTER]domain1.adminServer>local-shutdown The server [adminServer] has been shut down successfully. offline>exit
-
The entire JEUS system has been terminated now.
|
For more information on installation and setup, refer to JEUS Getting Started Guide and JEUS Server Guide. |