EJB Modules
This chapter describes EJB module structure and how to manage the modules.
1. Overview
EJB modules represent the deployable unit for a JEUS EJB engine. It is a concept of grouping EJB components and using deployment descriptors (hereafter DD) to describe the configuration settings. Even if you are only deploying one Enterprise JavaBean, it must be packaged in an EJB module.
|
A DD (ejb-jar.xml) is required for components of EJB 2.1 or earlier. However, for components of EJB 3.0 or later, DD is optional because annotation is supported. |
2. Managing EJB Modules
The following outlines the four main activities involved when managing an EJB module in JEUS. For more detailed information, refer to each section.
-
Assembly: Assembling EJB Modules
-
Deployment: Deploying EJB Modules
-
Control (undeployment, redeployment, stop-application, start-application): Controlling EJB Modules
-
Monitoring: Monitoring EJB Modules
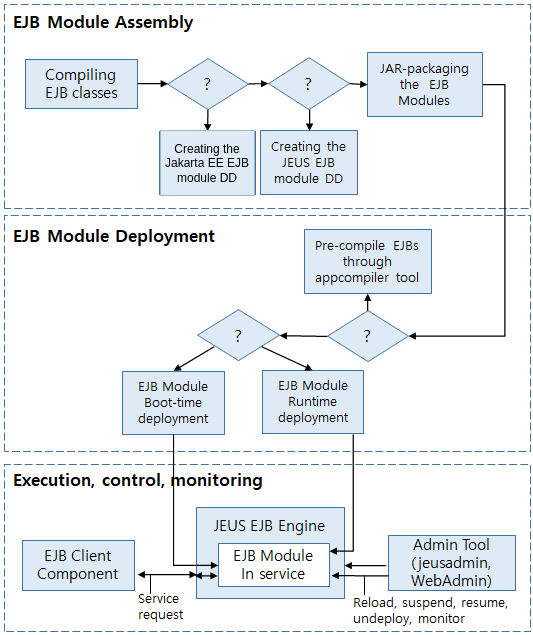
The following figure shows the flow chart for managing EJB modules.
Structure of EJB Module JAR File
The following figure explains the structure of standard EJB module JAR file.
EJB Module JAR
|--META-INF
| |--[X]ejb-jar.xml
| |--[X]jeus-ejb-dd.xml
|--<package_name>
| |--[C]Bussiness Interface
| |--[C]EJB Implementation
| |--[C]Helper class
|--[J]Helper library
* Legend
- [01]: binary or executable file
- [X] : XML document
- [J] : JAR file
- [T] : Text file
- [C] : Class file
- [V] : java source file
- [DD] : deployment descriptor
- META-INF
-
The following describes subordinate files.
File Description ejb-jar.xml
Actual standard EJB DD. It may not exist if annotation is used to describe configuration information. It is required for EJB 2.x style.
jeus-ejb-dd.xml
DD needed when EJB is deployed to JEUS (optional).
- <package_name>
-
Contains the EJB classes. They must be organized to reflect the Java package hierarchy as defined in the EJB source code. Example: if an EJB declares that it is part of the package called "mypackage", the EJB classes must reside directly beneath a directory named "mypackage" in the EJB JAR file.
The following table describes the components of EJB.
Element Description Interface
EJB 2.x, 3.0, or later style interface used for client access.
Enterprise Bean class
Bean classes that implement the actual business logic according to the interfaces.
- Helper library
-
Library defined in the MANIFEST.MF Class-Path entry.
3. Assembling EJB Modules
As we see in Flow Chart for Managing EJB Modules, steps for assembling an EJB module are as follows:
-
Compile the EJB classes
Compile the EJB source files implemented by the developer
-
Create the DDs
-
Create ejb-jar.xml DD
-
Create jeus-ejb-dd.xml DD
-
-
Package the EJB JAR file
Package the EJB classes and DDs into a JAR file
We will illustrate the procedures by using a simple example bean called counter. The counter bean is a stateful session bean that resides in the JEUS_HOME/samples/ejb/basic/statefulSession/ directory. It contains the following two Java source files:
-
Counter.java (business interface)
-
CounterEJB.java (bean implementation)
|
For more information about stateful session beans and the other bean types, refer to Session Bean and Message Driven Bean(MDB). |
3.1. Compiling EJB Classes
The first step in assembling an EJB module from existing EJB source files is to compile the source files. This is accomplished by using the JDK javac compiler. The default classpath is JEUS_HOME/lib/system/jakarta.ejb-api.jar, but if you are using annotations that correspond to the jeus-ejb-dd.xml file, set the classpath to JEUS_HOME/lib/system/jeusapi.jar. If there are other helper classes, add them all to the classpath.
The following example shows how to compile EJB Java files for the counter bean in a Unix environment.
$ javac –classpath JEUS_HOME/lib/system/jakarta.ejb-api.jar *.java
The previous command will create the class files.
3.2. Creating Deployment Descriptors
There are two DDs that must be prepared before deploying an EJB module:
-
Standard EJB DDs
DD with the name, ejb-jar.xml, placed in the META-INF directory of the EJB module. Some or all parts of configuration information can be created using annotation when you create the EJB components. If you want to apply DD setting without using annotation, set the <metadata-complete> attribute in ejb-jar.xml as true. If annotation and DDs are used together, DD settings override the annotation settings.
-
JEUS EJB DD
DD with the name, jeus-ejb-dd.xml, placed in the META-INF directory of the EJB module. For more information, refer to Creating JEUS EJB DD (jeus-ejb-dd.xml).
Creating standard EJB DDs (ejb-jar.xml)
The DD format complies with the EJB specification. Annotation is enough in most cases, but a DD can be used when necessary.
package ejb.basic.statefulSession;
@Remote
public interface Counter
{
public void increase();
...
}
package ejb.basic.statefulSession;
@Stateful
@EJB(name="counter")
@TransactionManagement( TransactionManagementType.BEAN)
public class CounterEJB implements Counter {
private int count = 0;
public void increase()
{
count++;
}
...
}
The following example is a simple Java EE EJB DD of the counter bean.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<ejb-jar version="4.0" xmlns="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee
https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee/ejb-jar_4_0.xsd">
<enterprise-beans>
<session>
<ejb-name>counter</ejb-name>
<business-remote>ejb.basic.statefulSession.Counter</business-remote>
<ejb-class>ejb.basic.statefulSession.CounterEJB</ejb-class>
<session-type>Stateful</session-type>
<transaction-type>Bean</transaction-type>
</session>
</enterprise-beans>
<assembly-descriptor/>
</ejb-jar>
|
For EJB 3.0 or later, ejb-jar.xml is optional because all contents of ejb-jar.xml can be described using annotation. |
Creating JEUS EJB DD (jeus-ejb-dd.xml)
The main reason for creating JEUS EJB DD is to map the basic settings and external references, which are needed for deployment to an EJB engine. Instance pooling, entity bean, and DB table mappings are also configured in the DD.
|
Such settings are needed to deploy EJB modules according to JEUS, but some parts can be configured using annotation. Also, since they can be deployed using the default values without the jeus-ejb-dd.xml file, this file is only necessary when separate environment settings are needed. |
JEUS EJB DDs are additional settings added to the standard Java EE DDs. Like the standard EJB DDs, JEUS EJB DDs are also applied to an EJB module.
The following are the main elements of a JEUS EJB DD:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<jeus-ejb-dd xmlns="http://www.tmaxsoft.com/xml/ns/jeus">
<module-info>
<role-permission>
<!-- See chapter "Configuring EJB Security" -->
. . .
</role-permission>
</module-info>
<beanlist>
<jeusbean>
<!-- See chapters "Common Characteristics of EJB"
and "Session Bean" -->
. . .
</jeusbean>
<jeusbean>
<!-- See chapters "Common Characteristics of EJB"
and "Session Bean" -->
. . .
</jeusbean>
. . .
</beanlist>
<ejb-relation-map>
<!-- See chapter "Entity Bean" -->
</ejb-relation-map>
<message-destination>
<jndi-info>
<ref-name>ejb/AccountEJB</ref-name>
<export-name>ACCEJB</export-name>
</jndi-info>
</message-destination>
<library-ref>
<library-name>jsf</library-name>
<specification-version>
<value>1.2</value>
</specification-version>
<implementation-version>
<value>1.2</value>
</implementation-version>
</library-ref>
</jeus-ejb-dd>
The following are the main elements of a JEUS EJB DD:
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
<module-info> |
Specifies the information that is applied to all EJB modules. For more information about role assignment, refer to Configuring EJB Security. |
<beanlist> |
Defines EJBs included in the EJB module. The name and content of this element can have various features according to the bean type (SessionBean. Entity Bean, and MDB). For detailed explanations about <beanlist> and its child tags, see Common Characteristics of EJB and from Session Bean to Message Driven Bean(MDB). |
<ejb-relation-map> |
Configures EJB relationship mappings that define CMR mappings for CMP 2.0 beans. Since using CMP is no longer recommended, use JPA instead. |
<message-destination> |
Maps message destination defined in the <message-destination> element of ejb-jar.xml and the actual destination object registered with JNDI. |
<library-ref> |
Configures the shared library information that is used by the application. |
3.3. Packaging an EJB JAR File
The following explains how to package EJB classes and DDs into a JAR file. You can create an EJB JAR file using a JAR utility. We assume that:
-
The counter EJB class files reside in the ejb/basic/statefulSession directory.
-
The ejb-jar.xml and jeus-ejb-dd.xml do not exist because annotations are used in the classes.
The following explains how to pack an EJB JAR file.
-
Pack the EJB classes into a JAR file as follows.
$ jar cf countermod.jar ejb/basic/statefulSession
The Jakarta EE EJB module named countermod.jar is created.
-
In order to use this EJB in a client, you need an interface file. Create the counterbeanclient.jar file, which will be distributed for client use, as follows:
$ jar cf counterbeanclient.jar ejb/basic/statefulSession/Counter.class
The counterbeanclient.jar is a library distributed for remote clients to use.
4. Deploying EJB Modules
This section describes how to deploy EJB modules.
4.1. Deployment
In general, deployment is accomplished by compiling EJB classes. But you can reduce the deployment time by using the appcompiler to precompile the classes. You can also use the Auto Deploy function for easy deployment of EJB modules. For more information about deployment, refer to JEUS Applications & Deployment Guide.
EJB modules are deployed on JEUS by using the following methods as described in Flow Chart for Managing EJB Modules.
-
Using the appcompiler tool
For EJB 2.x modules, the stub and skeleton files can be created in advance by using the appcompiler tool, speeding up the deployment process.
-
Boot-time deployment
EJB modules are automatically deployed to an EJB engine whenever the engine boots.
-
Runtime deployment of an EJB module
EJB modules are deployed to an already running EJB engine using the console tool.
Using the appcompiler tool
For EJB 2.x modules, stub and skeleton files can be created in advance by using the appcompiler tool, speeding up the deployment. When you are using the appcompiler tool, specify the -fast option with the deployment command in the console tool. Without this option, the appcompiler tool is not effective. For more information about the appcompiler tool, refer to appcompiler in JEUS Reference Guide.
Boot-time Deployment of an EJB Module
Boot-time Deployment refers to deploying EJB modules to an EJB engine whenever an MS boots. Boot-time deployment is applied to the applications deployed through MASTER. For more information about application deployment settings, refer to Application Implementation and Deployment in JEUS Applications & Deployment Guide.
Multiple applications can be registered to a single domain.
Runtime Deployment of an EJB module
Runtime-deployment is an act of actually deploying an EJB module to an already running EJB engine. By using the deploy command in the console tool, an EJB module can be installed to a running EJB engine.
The following explains how the countermod EJB module is deployed. The following assumes that:
-
On JEUS, adminServer (MASTER) and server 1 (MS) are already running.
-
The countermod module exists in the form of countermod.jar file or countermod directory under the JEUS_HOME/apphome directory.
The runtime of an EJB module is deployed using the console tool.
-
Using the Console Tool
The following explains how to deploy an EJB module by using the console.
-
Run the console tool. For detailed information about the console tool, see Local Commands in JEUS Reference Guide.
$ jeusadmin -host localhost:9736
-
Enter user name and password.
User name: administrator Password: Attempting to connect to localhost:9736. The connection has been established to Domain Administration Server adminServer in the domain domain1. JEUS8 Administration Tool To view help, use the 'help' command. [MASTER]domain1.adminServer>
-
Deploy the countermod EJB module using the deploy command.
[MASTER]domain1.adminServer> deploy countermod -servers server1
-
In order to verify the deployment result, execute the following command. All the deployed applications, including the countermod module, are displayed.
[MASTER]domain1.adminServer> application-info
-
4.2. Directory Structure of a Deployed EJB Module
After an EJB module has been deployed, its class files and configuration files will be distributed throughout the JEUS installation directory as shown in the following structure.
{JEUS_HOME}
|--domain/<domain_name>/servers/<server_name>
|--.workspace/deployed
|--<application_id>
| |--<EJB_archive_file>_jar__
| | |--META-INF
| | | |--[X]Jakarta EJB DD
| | | |--[X]JEUS EJB DD
| | |--[C]Bussiness Interfaxe(Home Inferface, Component Interface)
| | |--[C]EJB Implementation
| | |--[C]Helper calss
| |--[J]<EJB_archive_file>
|--<EAR_archive_file>_ear__
|--APP-INF
|--lib
|--META-INF
|--<EJB_archive_file>_jar__
| |--META-INF
| | |--[X]Jakarta EJB DD
| | |--[X]JEUS EJB DD
| |--[C]Bussiness Interfaxe(Home Inferface, Component Interface)
| |--[C]EJB Implementation
| |--[C]Helper calss
|--[J]<EJB_archive_file>
* Legend
- [01]: binary or executable file
- [X] : XML document
- [J] : JAR file
- [T] : Text file
- [C] : Class file
- [V] : java source file
- [DD] : deployment descriptor
JEUS_HOME/domains/<domain_name>/servers/<server_name>/.workspace/deployed/ directory contains applications deployed to the MS specified by the <server name> option. It will contain deployed EJB implementation classes of the EJB module as well as helper classes.
Deployed files are placed in the following directories.
| Deployment Mode | Description |
|---|---|
EAR Deploy Mode |
When EAR file is deployed, the modules are placed under the directory created with the EAR file name. |
Standalone Deploy Mode |
When JAR file is deployed, the file is placed under the "<jar file_name>_jar___" directory, which is under the root directory that has the JAR file name. |
Exploded EAR Deploy Mode |
Unpacked EAR file is deployed. |
Exploded Standalone Deploy Mode |
Unpacked JAR file is deployed. |
For Exploded EAR deployment and Exploded Standalone deployment, the reference to the original directory is used, instead of copying the files to the webhome directory. JEUS classifies deploying the packaged archive file as a COMPONENT type and deploying the directory with the unpacked files as an EXPLODED COMPONENT type.
|
The following description only covers the standalone module. For a detailed explanation of the EAR deployment method or deployment in general, see the deployment related sections in JEUS Applications & Deployment Guide. |
5. Controlling and Monitoring EJB Modules
You can control and monitor the status of the deployed EJB modules by using the console tool. (refer to Flow Chart for Managing EJB Modules.)
5.1. Controlling EJB Modules
You can control the execution status within a deployed EJB module by using the console tool’s stop-application, start-application, redeploy-application, and undeploy commands.
Using the Console Tool
The deployed EJB module can be controlled by using the stop-application, start-application, redeploy-application, and undeploy commands. All the commands take the EJB module ID as a parameter. For more information about the console tool, refer to jeusadmin in JEUS Reference Guide.
-
redeploy-application
Reloads the specified EJB module. This means that the EJB module that is currently running will be discarded from the EJB engine’s runtime environment and then re-read or redeployed from the disk.
When the EJB module is redeployed, all the transactions performed by the EJB module will be rolled back together.
redeploy-application <application-id>
-
stop-application
Suspends the specified EJB module. This means that the EJB module that is currently running will be temporarily inaccessible. The start-application command can make the EJB module accessible.
stop-application <application-id>
-
start-application
Activates the EJB module which was suspended with the stop-application command.
start-application <application-id>
-
undeploy
Removes the selected EJB module from the EJB engine’s runtime memory so that the EJB clients are not able to access the EJB. However, the physical file is not deleted.
undeploy <application-id>
Following is a simple example illustrating how to undeploy an EJB module using the console tool:
-
Execute the console tool.
$ jeusadmin -host localhost:9736
-
Enter user name and password.
User name: administrator Password: Attempting to connect to localhost:9736. The connection has been established to Domain Administration Server adminServer in the domain domain1. JEUS8 Administration Tool To view help, use the 'help' command. [MASTER]domain1.adminServer>
-
To undeploy the countermod EJB module, enter the following:
[MASTER]domain1.adminServer> undeploy countermod
-
To verify the undeployment result, enter the following. The countermod module is not included in the list of deployed modules that is displayed.
[MASTER]domain1.adminServer> application-info
-
5.2. Monitoring EJB Modules
EJB modules can be monitored using the console tool. To monitor the status and runtime information of an EJB module, execute the application-info command in the console tool. For more information about the application-info command, refer to EJB Engine Commands in JEUS Reference Guide.
-
Monitoring module information
Displays information about the module.
[MASTER]domain1.adminServer>application-info -server server1 -id countermod -detail General information about the EJB module [countermod]. ============================================================== +-------------+----------------------------------------------+ | Module Name | Unique Module Name | +-------------+----------------------------------------------+ | countermod | countermod | +-------------+----------------------------------------------+ ============================================================== Beans ================================================================================ +-----------+-------------------------+-------------------+--------------------+ | Bean Name | Type | Local Export Name | Remote Export Name | +-----------+-------------------------+-------------------+--------------------+ | Count | StatelessSessionBean | | Count | +-----------+-------------------------+-------------------+--------------------+ ================================================================================
-
Monitoring EJB list
Displays a list of EJBs of the relevant module("application-id").
[MASTER]domain1.adminServer>application-info -server server1 -id countermod -bean Count Module name : countermod Bean name : Count ================================================================================ +---------------+-----------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+ | Name | (Count) | WaterMark(High:Low| Bound(Upper:L| Time(Max:Min:T| | | | :Cur) | ower) | otal) | +---------------+-----------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+ | create | times(0) | | | | +---------------+-----------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+ | comitted | transactio| | | | | |n(0) | | | | +---------------+-----------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+ | total-remote-t| |thread(100:100:100)| | | |hread | | | | | +---------------+-----------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+ | timed-rb | transactio| | | | | |n(0) | | | | +---------------+-----------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+ | remove | times(0) | | | | +---------------+-----------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+ | active-bean | | bean(0:0:0) | | | +---------------+-----------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+ | request | request(0)| | | | +---------------+-----------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+ | total-bean | | bean(0:0:0) | | | +---------------+-----------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+ | rolledback | transactio| | | | | |n(0) | | | | +---------------+-----------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+ | active-thread | | thread(0:0:0) | | | +---------------+-----------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+ | MethodReadyCou| | bean(0:0:0) | | | |nt | | | | | +---------------+-----------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+ ================================================================================
|
EJB modules can be monitored in detail by using the console tool. For more information about EJB module monitoring, refer to Checking Bound Objects in JEUS Server Guide, and Timer Monitoring in this guide. |