Using WebTier
This chapter describes how to deploy servlet, JSP, JSTL, and JSF applications, and how to package and deploy WAR (Web application ARchive) modules.
1. Examples
This section shows sample code for a web application and how to compile and deploy the code.
|
For more details, see JEUS Server Guide, JEUS Web Engine Guide, and JEUS Web Service Guide. |
The following sample servlet displays the message "Hello World!" in a web browser.
import java.io.*;
import jakarta.servlet.*;
import jakarta.servlet.http.*;
public class HelloWorldServlet extends HttpServlet
{
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res)
throws IOException, ServletException
{
res.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = res.getWriter();
out.println("<HTML>");
out.println("<HEAD>");
out.println("<TITLE>Hello World Sample</TITLE>");
out.println("</HEAD>");
out.println("<BODY>");
out.println("<CENTER><H1>Hello World!</H1></CENTER>");
out.println("</BODY>");
out.println("</HTML>");
out.close();
}
}The sample file is in the following directory.
JEUS_HOME/samples/getting_started/helloservlet/src/java
The following sample JSP program named 'snoop.jsp' shows information about the request it receives.
<html>
<body bgcolor="white">
<h2> Request Information </h2>
<font size="4">
JSP Request Method: <%= request.getMethod() %>
<br>
Request URI: <%= request.getRequestURI() %>
<br>
Request Protocol: <%= request.getProtocol() %>
<br>
Servlet path: <%= request.getServletPath() %>
<br>
Path info: <%= request.getPathInfo() %>
<br>
Path translated: <%= request.getPathTranslated() %>
<br>
Query string: <%= request.getQueryString() %>
<br>
Content length: <%= request.getContentLength() %>
<br>
Content type: <%= request.getContentType() %>
<br>
Server name: <%= request.getServerName() %>
<br>
Server port: <%= request.getServerPort() %>
<br>
Remote user: <%= request.getRemoteUser() %>
<br>
Remote address: <%= request.getRemoteAddr() %>
<br>
Remote host: <%= request.getRemoteHost() %>
<br>
Authorization scheme: <%= request.getAuthType() %>
<hr>
The browser you are using is <%= request.getHeader("User-Agent") %>
<hr>
</font>
</body>
</html>The sample file is in the following directory.
JEUS_HOME/samples/getting_started/helloservlet/web
The following sample JSP program has the same functionality as snoop.jsp except that it uses JSTP and JSF.
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html" prefix="h" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core" prefix="f" %>
<html>
<body>
<h2> Request Information </h2>
<font size="4">
<c:set var="req" value="${pageContext.request}"/>
JSP Request Method: <c:out value="${req.method}"/>
<br/>
Request Protocol: <c:out value="${req.protocol}"/>
<br/>
Servlet path: <c:out value="${req.servletPath}"/>
<br/>
Path info: <c:out value="${req.pathInfo}"/>
<br/>
Path translated: <c:out value="${req.pathTranslated}"/>
<br/>
Query string: <c:out value="${req.queryString}"/>
<br/>
Content length: <c:out value="${req.contentLength}"/>
<br/>
Content type: <c:out value="${req.contentType}"/>
<br/>
Server name: <c:out value="${req.serverName}"/>
<br/>
Server port: <c:out value="${req.serverPort}"/>
<br/>
Remote user: <c:out value="${req.remoteUser}"/>
<br/>
Remote address: <c:out value="${req.remoteAddr}"/>
<br/>
Remote host: <c:out value="${req.remoteHost}"/>
<br/>
Authorization scheme: <c:out value="${req.authType}"/>
<hr/>
<f:view>
The browser you are using is <h:outputText value=
"#{header['User-Agent']}"/>
</f:view>
<hr/>
</font>
</body>
</html>JSP programs are automatically compiled by the servlet engine and don’t need to be compiled manually.
2. Compilation
The sample code can be built by using jant as in the following.
%JEUS_HOME%/samples/getting_started/helloservlet>jant build
After the sample code has been built successfully, a WAR file named 'hello-servlet.war' will be created in the dist folder.
3. Deployment
A packaged WAR application can be deployed by using the console tool.
In JEUS, there are two steps for deploying applications, installation and deployment.
|
For more information about deployment, see JEUS Application & Deployment Guide. |
The following describes how to deploy WAR applications.
Using the console tool
You can deploy a WAR application using the console tool (jeusadmin).
-
Log in to JEUS as jeusadmin.
jeusadmin –u jeus –p <password>
-
Install the application on MASTER.
[MASTER]domain1.adminServer>install-application -id helloworld C:\TmaxSoft\JEUS\samples\getting_started\helloservlet\dist\hello-servlet.war Successfully installed application[helloworld].
-
Deploy the application to an MS (Server3).
[MASTER]domain1.adminServer>deploy helloworld -servers server3 deploy the application for the application [helloworld] succeeded.
-
Verify that the application has been deployed successfully.
4. Execution Result
This section describes how to execute the deployed servlets and JSPs.
Executing a Deployed JSP
Deployed JSPs can be executed by:
-
Opening snoop.jsp
Open a browser window and enter the following URL into the address bar to open the 'snoop.jsp' page. Opening a JSP page for the first time takes a little longer because it is automatically compiled by the servlet engine.
http://localhost:8088/helloworld/faces/snoop.jsp
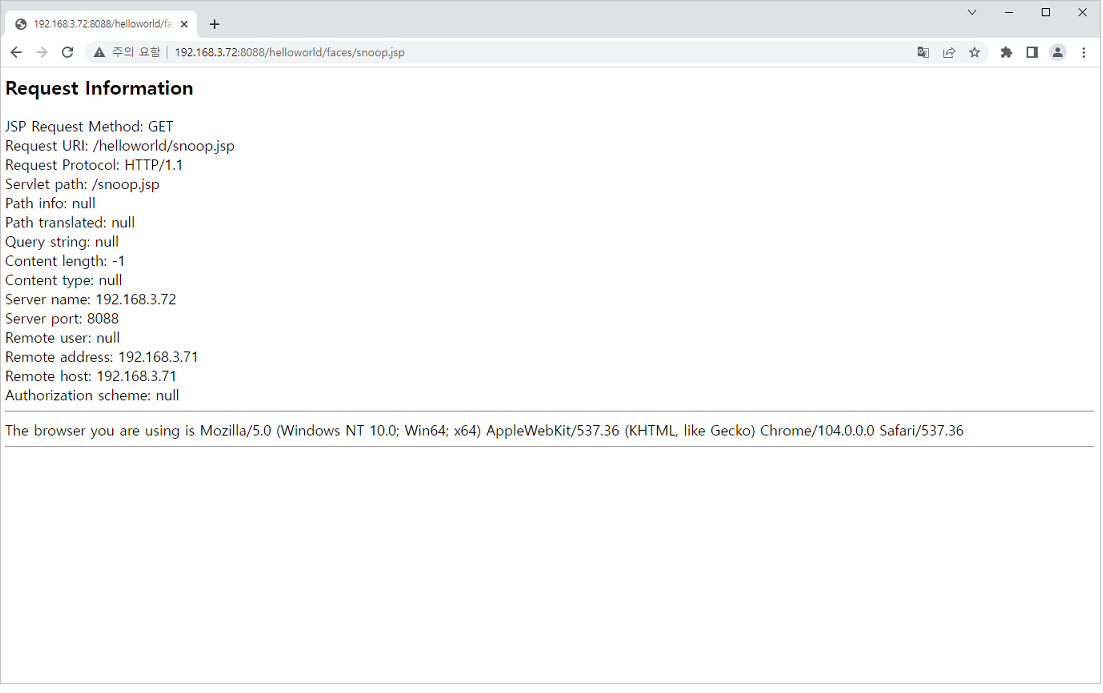 Executing a JSP
Executing a JSP -
Opening snoop_jstl.jsp
Open a browser window and enter the following URL into the address bar to open the snoop_jstl.jsp. The result of a page is the same with the result of opening snoop.jsp.
http://localhost:8088/helloworld/snoop_jstl.jsp
Executing a Deployed Servlet
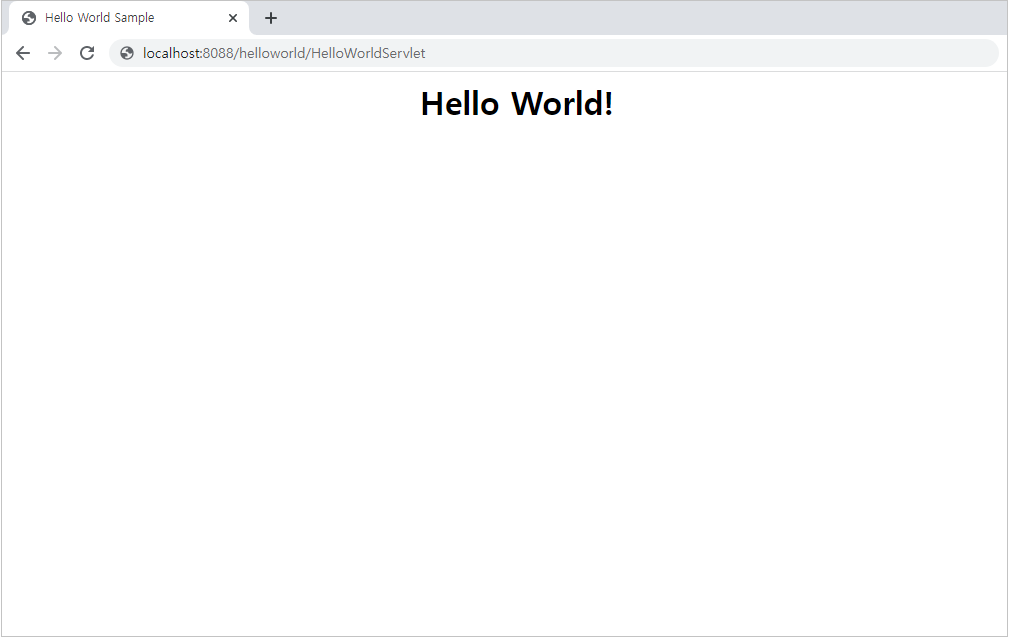
To access the 'helloworld' servlet, open a browser window and enter the following URL into the address bar.
http://localhost:8088/helloworld/HelloWorldServlet
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
http |
HTTP protocol is used to access JEUS. |
localhost |
Server that provides the service is on the local machine. |
8088 |
Port number of the HTTP listener created on the MS. |
helloworld |
Web application context path. This path is set in the <context-path> element of 'jeus-web-dd.xml'. By default, it has the same name as the WAR file. |
HelloWorldServlet |
URL pattern defined in the servlet. |
The following message will appear if the servlet engine has started normally and the Hello World servlet has been deployed successfully.