JEUS Introduction
This chapter describes the basics of JEUS and Jakarta EE specification. It also explains the concepts of a JEUS system, its components, and features of each edition.
1. Overview
Java Enterprise User Solution (JEUS) provides a platform for the development, operation, and execution of applications in a web environment. It also supports Java-based web application services and their management. JEUS provides a platform and the following components that are required to execute Jakarta EE applications.
-
EJB containers
-
Web containers (JSPs/Servlet engines)
-
Security modules
-
Naming Server
-
Transaction managers
-
JDBC Connection Pool
-
Session managers
Jakarta EE
JEUS conforms to the Eclipse Foundation’s Jakarta EE specification, and is Jakarta EE 9 certified.
Jakarta EE is briefly described in the following quotes from the official Jakarta EE website.
"Jakarta EE is a set of specifications that enables the world wide community of java developers to work on cloud native java enterprise applications. The specifications are developed by well known industry leaders that instills confidence in technology developers and consumers."
|
For more information about Jakarta EE, refer to the Jakarta EE website. (Jakarta EE Official Web Site) |
The following table lists the features that are implemented in JEUS 9.
| Spec | JEUS 9 |
|---|---|
Jakarta EE |
Jakarta EE 9 |
JakartaTM Activation |
2.0 |
JakartaTM Annotations |
2.0 |
JakartaTM Authentication |
2.0 |
JakartaTM Authorization |
2.0 |
JakartaTM Batch |
2.0 |
JakartaTM Bean Validation |
3.0 |
JakartaTM Concurrency |
2.0 |
JakartaTM Connectors |
2.0 |
JakartaTM Contexts and Dependency Injection |
3.0 |
JakartaTM Debugging Support for Other Languages |
2.0 |
JakartaTM Dependency Injections |
2.0 |
JakartaTM Enterprise Beans |
4.0 |
JakartaTM Enterprise Web Services |
2.0 |
JakartaTM Expression Language |
4.0 |
JakartaTM Faces |
3.0 |
JakartaTM Interceptors |
2.0 |
JakartaTM JSON Binding |
2.0 |
JakartaTM JSON Processing |
2.0 |
JakartaTM Mail |
2.0 |
JakartaTM Managed Beans |
2.0 |
JakartaTM Messaging |
3.0 |
JakartaTM Persistence |
3.0 |
JakartaTM RESTful Web Services |
3.0 |
JakartaTM Security |
2.0 |
JakartaTM Server Pages |
3.0 |
JakartaTM Servlet |
5.0 |
JakartaTM SOAP with Attachments |
2.0 |
JakartaTM Standard Tag Libraries |
2.0 |
JakartaTM Transactions |
2.0 |
JakartaTM WebSocket |
2.0 |
JakartaTM Web Services Metadata |
3.0 |
JakartaTM XML Binding |
3.0 |
JakartaTM XML Web Services |
3.0 |
Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations(XSLT) |
1.0 |
Java API for XML Processing(JAXP) |
Supported |
Java Authentication and Authorization Service(JAAS) |
1.0.1 |
Java Database Connectivity(JDBC) API |
4.2 |
Java Naming and Directory Interface(JNDI) API |
1.2.1 |
Java Transaction Service(JTS) |
1.0 |
Simple Object Access Protocol(SOAP) |
1.1/1.2 |
Streaming API for XML(StAX) |
Supported |
Universal Description,Discovery Intergration(UDDI) |
2.0/3.0 |
Web Services Description Language(WSDL) |
1.1/2.0 |
WebServer |
WebtoB 5.0 |
HTTP |
1.0/1.1/2.0 |
CGI |
1.1 |
PHP |
3.x/4.x/5.x |
RMI-IIOP |
Supported |
EJB to CORBA Mapping |
1.1 |
IBM MQ |
Supported |
Sonic MQ |
Supported |
WS-I Basic Profile |
1.1 |
WS-Policy |
1.5 |
WS-Policy Attachment |
1.5 |
WS-Addressing |
1.0 |
WS-Security |
1.1 |
WS-Security Policy |
1.2 |
WS-Trust |
1.4 |
WS-Secure Conversation |
1.4 |
WS-Reliable Messaging |
1.2 |
WS-AtomicTransaction |
1.2 |
WS-Coordination |
1.2 |
OTS |
Supported |
Java IDL API |
Supported |
IDE Tool |
Not supported |
GUI Tool |
Not supported |
Monitoring Tool |
Console Tool |
JDK |
8, 11, 17 |
|
2. System Concepts and Roles
The following figure shows how JEUS integrates with other Web servers or DBMSs to provide enterprise application solutions.
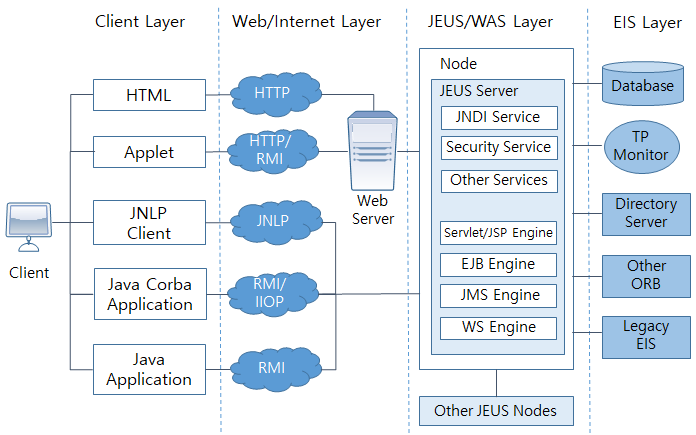
The following are the four layers shown in the previous figure.
-
Client Layer
Consists of Java applications and native applications. End users use various clients to access WAS services, and the clients use various protocols to access WAS services.
-
Web/Internet Layer
Consists of the web server and protocols used by clients and WAS. This layer deals with static contents and load balancing.
-
JEUS/WAS Layer
Consists of Java-based middleware and deals with requests from the web and client layers.
-
EIS Layer
Consists of data and existing legacy services. WAS interoperates with legacy services through various mechanisms such as JDBC, directory services, and Jakarta EE connector.
3. Architecture and Components
JEUS is made up of various components. These components operate differently depending on which communication technologies they use to communicate with clients, data storage devices, and JEUS, as shown in the following figure (JEUS Web Application Architecture).
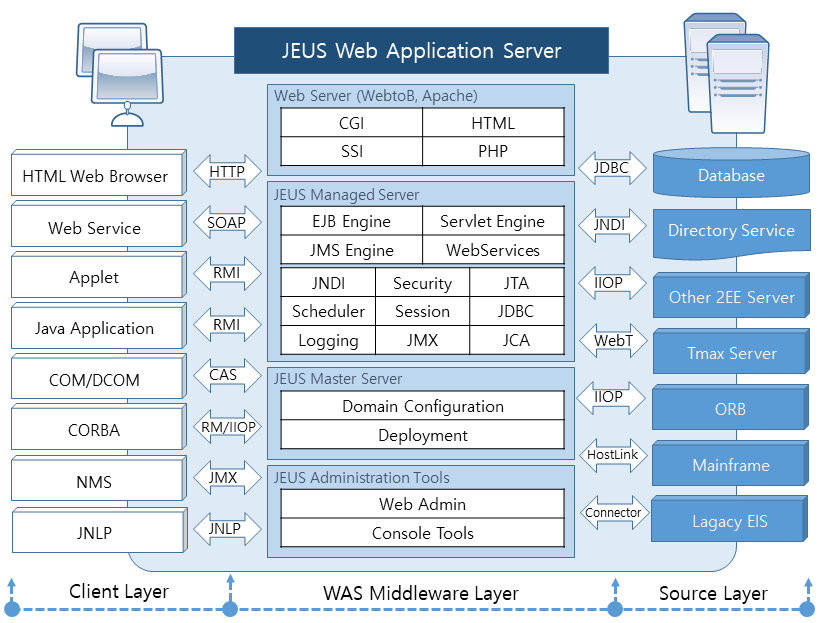
The client layer in the previous figure shows a diverse set of client applications and communication protocols. The source layer shows various types of data storage devices. The WAS middleware layer contains JEUS and the web server. The web server connects with client applications and is tightly coupled with the web application server. The web gateway (WebT) connects the web application server to the TP-Monitor (Tmax server), and the mainframe gateway (Host-Link) provides connection between a mainframe system and TP-Monitor.
Each layer (Client Layer, WAS Middleware Layer, Source Layer) is explained in more detail in the following sections.
3.1. Client Layer
The client layer consists of remote and local applications that use JEUS.
It contains the following components.
| Client Layer | Description |
|---|---|
Web browser |
The most common client application is a standard web browser that sends requests to a JEUS Servlet Engine and WebtoB Light Web server to retrieve HTML contents. The communication protocol used is HTTP. |
Web Services |
Provides web service implementations. |
Applet |
Provides a special applet container that can access JEUS’s components. |
Java Application |
Standalone Java applications are executed by using RMIs within client containers provided by JEUS. Clients are called application clients in the Jakarta EE specification. |
COM/DCOM |
EJBs can be invoked as COM objects in Microsoft Windows. |
CORBA |
CORBA applications can use JEUS via RMI/IIOP. |
NMS |
Network Management System manages and uses JEUS via JMX. |
JNLP |
Java Network Launching Protocol (JNLP) clients are supported. |
3.2. WAS Middleware Layer
The JEUS WAS layer in JEUS Web Application Architecture corresponds to JEUS 9. Its components are as follows:
-
JEUS Master Server
Each domain must have a special server called Master Server. The Master Server centrally manage the configurations that define the relationship between servers of a domain, and applications and resources in the domain. It controls and monitors servers by communicating with the management tools, such as jeusadmin.
Service Description Domain Configuration
Manages domain configurations.
Application Management
Manages domain applications.
Administration
Centrally monitors and controls all domain servers, services, applications, and resources by using jeusadmin.
-
JEUS Managed Server(MS)
An MS contains several types of engines configured within a JEUS system. There are the following four engine types.
Engine / Service Description EJB Engine
Runs EJB applications.
Servlet Engine
Web container that handles both JSP/Servlet applications and static contents like HTML.
JMS Engine
Supports JMS structures.
Web Services Engine
JEUS Web server that acts as the front end of the servlet engine.
JNDI Service
Naming system.
Security Service
Handles authentication and authority.
JTA
Provides complete transactions for various applications running on Web application servers.
Scheduler
Supports timers that trigger an event at a predefined time.
Session Manager
Reliably stores client session information when clustering is needed.
JDBC
Configurable database connection pool.
Logging
Stores and records jobs that have been executed on JEUS.
JMX
Allows NMS/JMX clients to manage JEUS.
JCA
JCA stands for JakartaTM Connector Architecture. JCA allows any legacy Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) solution to integrate with a legacy EIS if the EAI solution supports JCA.
-
Web Server (WebtoB, Apache)
The web server handles the transfer of static content, such as HTML, and dynamic content, such as CGI. It serves as the front end for the servlet engine. TmaxSoft offers two versions of its web server product, WebtoB: the full version, which fully supports all web server features, and a limited version, JEUS Web Server, which supports only a subset of WebtoB’s features.
JEUS Web server comes with JEUS but not with WebtoB. As an alternative, open-source web server Apache may be used with JEUS.
-
JEUS Administration Tools
The following management tool is available for use.
Tool Description Console tool (jeusadmin)
Command-line based console tool for controlling the JEUS server.
3.3. Source Layer
The source layer shown in JEUS Web Application Architecture shows the back-end resources and data storage used by JEUS system. The following are the components.
| Source Layer | Description |
|---|---|
Database |
Can be accessed by JEUS through JDBC. |
Directory Service |
JNDI is used to access services like LDAP. |
Other Jakarta EE Server |
JEUS interoperates with Jakarta EE Servers from other vendors. |
Tmax Server |
TmaxSoft’s TP-monitor. WebT API library is used to access JEUS or Tmax. |
ORB |
Can be referenced by using IIOP (Internet Inter-ORB Protocol). |
Mainframe |
Accessed by using Host-Link (connector) products. |
Legacy EIS |
Supports JCA and interoperates with JEUS. |
4. Interoperable Modules
Interoperability refers to the ability of two or more systems, such as computers, communication devices, networks, software, and other information technology components, to interact with one another and exchange data according to a prescribed method in order to achieve predictable results (ISO ITC-215). JEUS supports different communication protocols and technologies such as web services, JNLP, and RMI-IIOP.
The following are the modules provided for JEUS interoperability.
| Module | Description |
|---|---|
RMI-IIOP |
RMI technology that uses Internet Inter-ORB Protocol (IIOP) and enables distributed CORBA computing jobs in Java. |
JEUS |
Interoperates with other vendors' web applications and services. |
WebT |
Provides a connection between TP-Monitor and JEUS. |
Host-Link |
Adapter module that enables clients to use services that are running on an EIS. |
JCA |
Enables JEUS and JEUS clients to virtually interoperate with any legacy EIS. |
5. Edition
The following table shows the main features of each JEUS 9 edition.
| Edition | Main Features |
|---|---|
JEUS Standard Edition |
|
JEUS Enterprise Edition |
|
|